Resources
Glossary
SAE Flat Washer
The SAE Washers prevent imbedding or distortion to the material being clamped. The washers provide a smooth, level protective bearing surface to fasten nuts and bolts. Without washers, the bolts, nuts, and screws can lose their clamping load if they imbed into the clamping material. SAE Washers are used in assemblies that are bolting together soft metals, wood and steel and are designed to be used with Grade 2 and 5 strength levels fasteners.

SAE Hardened Flat Washer (RC 38-45)
An SAE Hardened Flat Washer (RC 38-45) is a flat washer made to SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards, specifically designed to provide extra strength and durability. The washer is hardened to a Rockwell hardness range of 38-45 on the C scale (RC 38-45), making it suitable for use in high-stress or heavy-load applications.

SAE International
SAE International is a global, professional engineering organization that develops technical standards, publishes research, and provides education for industries involved in mobility, including automotive, aerospace, commercial vehicles, off-highway equipment, and industrial manufacturing. Although rooted in the automotive world (originally the Society of Automotive Engineers), SAE has evolved into a broad standards body that supports any sector dealing with vehicles, engines, motion, mechanical systems, and materials.
For the fastener industry, SAE International is particularly important because it creates and maintains the SAE J-standards—the specifications used for SAE bolt grades such as Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8, along with numerous standards covering material composition, mechanical properties, testing methods, and marking requirements. Manufacturers, distributors, and engineers rely on SAE’s standards to ensure fasteners are consistent, safe, and interchangeable, regardless of who produced them.
Outside of fasteners, SAE International manages thousands of specifications and publishes technical papers, organizes conferences, provides training and certifications, and serves as a major source of engineering knowledge for mobility-related industries. Its work influences vehicle design, aerospace components, lubricants, materials, testing protocols, and emerging technologies like electric vehicles and autonomous systems.

SAE J429 Grade 1
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners made from low-carbon steel. SAE J429 Grade 1 fasteners provide the lowest strength level within the SAE J429 standard and are typically used in light-duty, non-critical applications where only minimal strength is needed. Common uses include furniture assembly, light-duty brackets, automotive trim, electrical enclosures, and other non-load-bearing or temporary connections not subject to high stress or vibration.
SAE J429 Grade 2
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners that are made from low to medium carbon steel. SAE Grade 2 fasteners offer a basic level of strength and are typically used in non-critical, general-purpose applications where high strength is not required.
SAE J429 Grade 4
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners made from medium carbon steel that are typically quenched and tempered. SAE J429 Grade 4 fasteners provide a moderate strength level under the SAE J429 standard and are commonly used in applications requiring greater strength than Grade 2 but not as high as Grade 5. These fasteners are suitable for general-purpose mechanical and structural applications where improved load capacity is needed. Common uses include automotive components, machinery parts, and light structural assemblies.
SAE J429 Grade 5
A strength classification for medium carbon steel fasteners that have undergone heat treatment to enhance their strength and durability. SAE Grade 5 fasteners provide greater strength than Grade 2 and are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and structural applications where higher load-bearing capacity is required.
SAE J429 Grade 5.1
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are typically quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 5.1 fasteners provide a higher strength level than Grade 5 and are intended for applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance and durability. Common uses include automotive, heavy machinery, and structural applications where improved toughness and tensile strength are necessary.
SAE J429 Grade 5.2
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are typically quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 5.2 fasteners offer a higher strength level than Grade 5.1 and are used in demanding applications requiring superior mechanical performance and durability. Common uses include heavy-duty automotive, industrial machinery, and structural applications where maximum toughness and tensile strength are critical.
SAE J429 Grade 8
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that have been heat treated to provide high tensile strength and excellent durability. SAE Grade 8 fasteners are stronger than Grade 5 and are commonly used in heavy-duty automotive, industrial, and structural applications requiring maximum load capacity and toughness.
SAE J429 Grade 8.1
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 8.1 fasteners provide higher tensile strength and improved toughness compared to Grade 8, making them suitable for high-stress, heavy-duty applications. Typical uses include automotive suspension components, heavy machinery, and structural assemblies requiring superior strength.
SAE J429 Grade 8.2
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners, quenched and tempered to exceed the mechanical properties of Grade 8.1 under the SAE J429 standard. Grade 8.2 fasteners are designed for extremely demanding applications where maximum strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue are required. Common applications include critical heavy machinery parts, high-performance automotive, and structural components subjected to intense stress.
SAE J995 Grade 2 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from low-carbon steel. Grade 2 nuts are intended for use in light-duty, non-critical applications and are typically paired with SAE J429 Grade 1 or Grade 2 bolts. They offer low mechanical strength and usually lack grade markings.
SAE J995 Grade 5 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered. Grade 5 nuts are intended for medium-strength applications and are typically used with SAE J429 Grade 5 bolts. They offer greater mechanical strength than Grade 2 nuts and are identified by two circumferential grade markings located 120 degrees apart, typically with one mark on the top face and the other wrapping partially around the side of the nut.
SAE J995 Grade 8 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from medium carbon alloy steel, quenched and tempered. Grade 8 nuts are used in high-strength applications and are typically paired with SAE J429 Grade 8 bolts. They provide the highest strength among SAE J995 grades and are identified by two circumferential grade markings located 60 degrees apart, both positioned clearly on the top face of the nut.
SAE NT Hardened Flat Washer (RC 38-45)
An SAE NT Hardened Flat Washer (RC 38-45) is a hardened flat washer made to SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards, specifically designed to withstand high loads and stress in demanding applications. The washer is hardened to a Rockwell hardness of 38-45 on the C scale (RC 38-45), indicating its high strength and resistance to wear. The "NT" in the name stands for "Narrow Thickness", meaning it has a thinner profile compared to standard hardened washers.
SAE NT2 Hardened Thick Flat Washer (RC 38-45)
An SAE NT2 Hardened Thick Flat Washer (RC 38-45) is a type of hardened flat washer designed to meet SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards with added thickness. The "NT2" indicates a thicker profile compared to standard washers, while the RC 38-45 refers to the washer's Rockwell C hardness rating, meaning it is heat-treated for enhanced strength and durability.
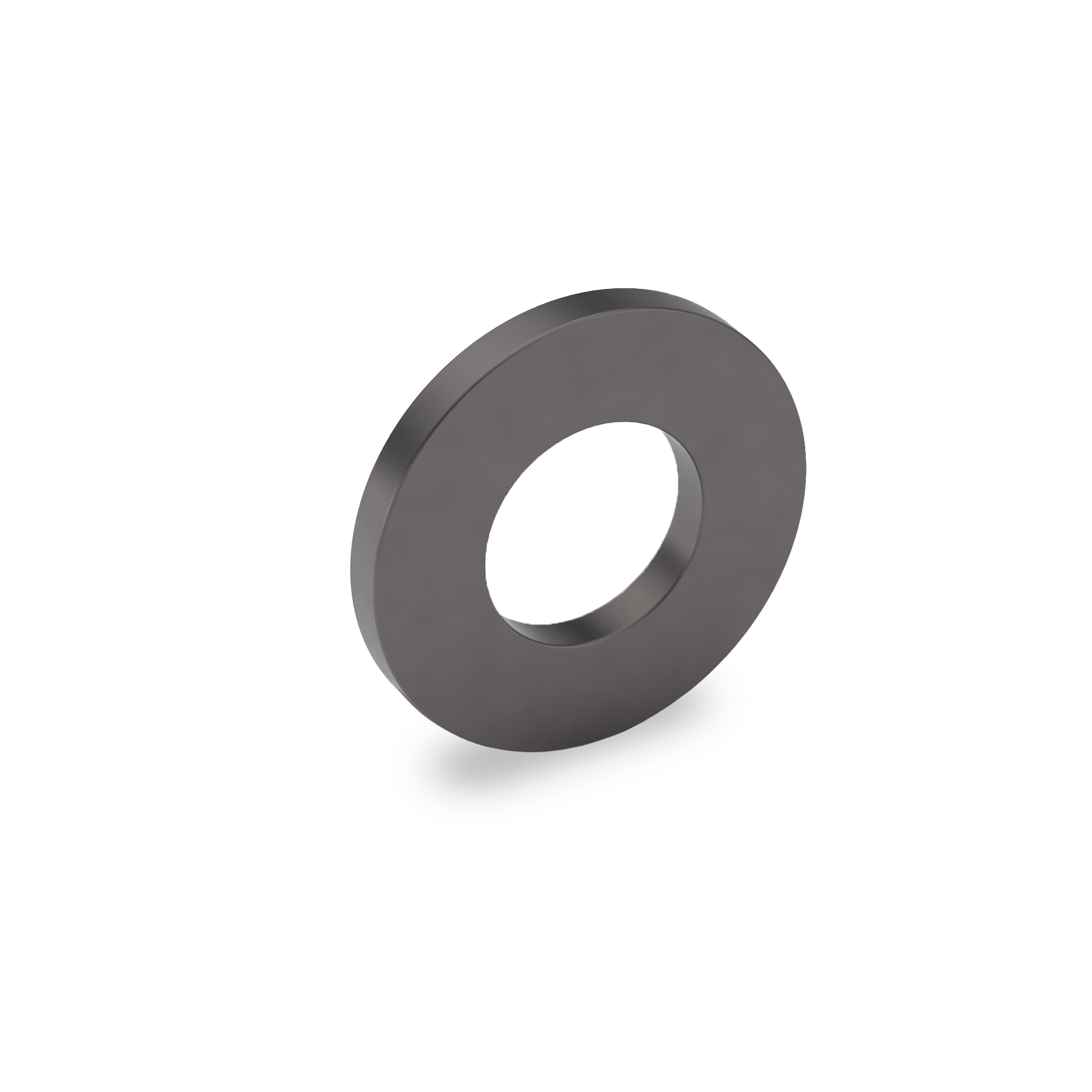
SAE NTX Hardened Extra Thick Flat Washer (RC 38-45)
An SAE NTX Hardened Extra Thick Flat Washer (RC 38-45) is a specialized type of flat washer designed to meet SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards, with an extra thick profile for added durability and support. The washer is hardened to a Rockwell hardness of 38-45 (RC 38-45), providing high strength, wear resistance, and the ability to withstand heavy loads and stress.

Salt Spray Testing
This laboratory procedure is designed to quickly assess how well fasteners, materials, or their protective finishes withstand corrosion. Within a sealed chamber, these fasteners are exposed to a controlled, corrosive environment. A fine mist or a fog of salt water (typically a 5% sodium chloride solution) is continuously sprayed onto the items at a consistent temperature. This process mimics and accelerates the effects of harsh environmental conditions, allowing manufacturers to determine how resistant a fastener or its protective finish is to rusting and other forms of deterioration over time. The results from these tests are key for quality control, choosing the right materials, and comparing how different protective coatings perform.
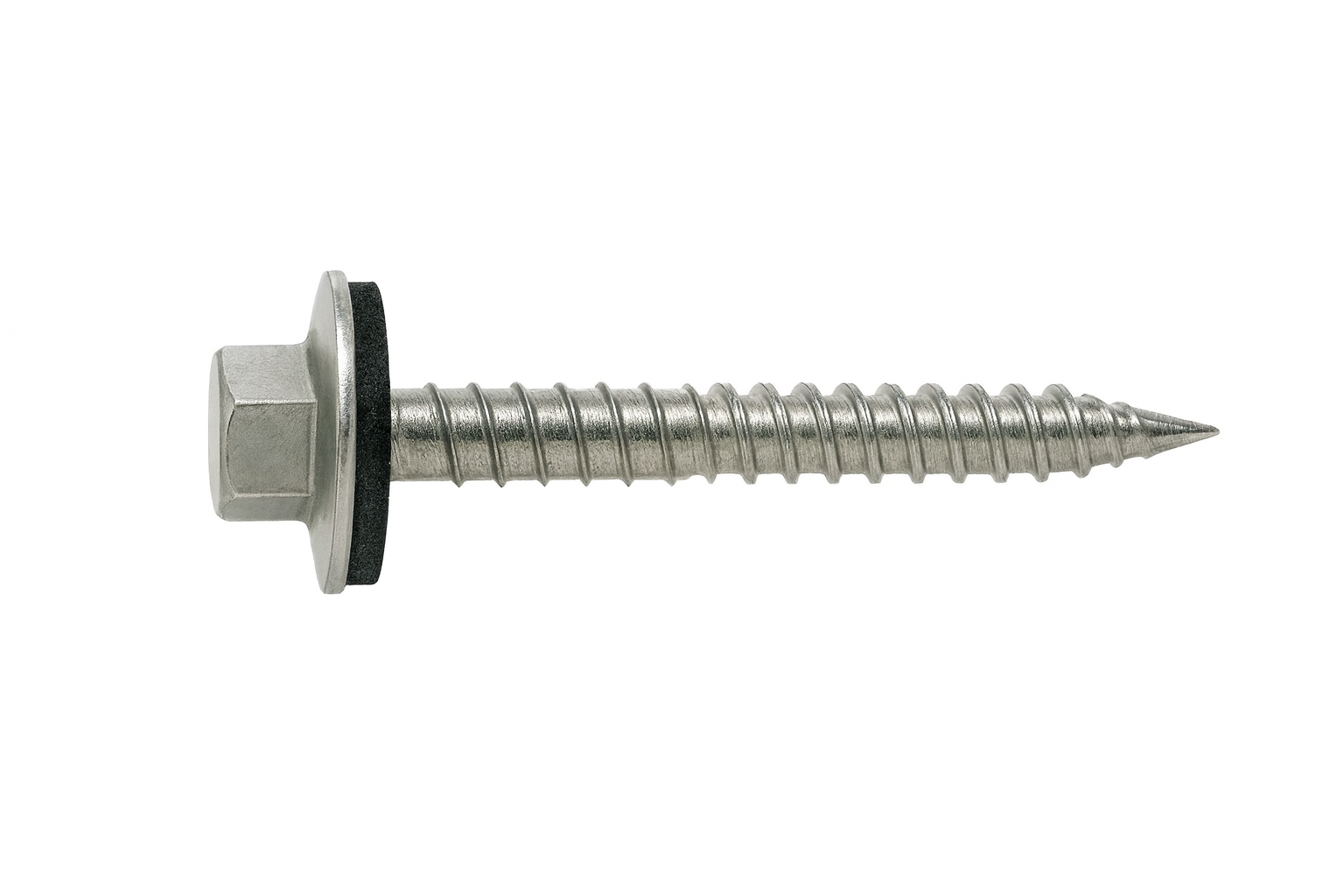
Sandwich-Panel Screw
A sandwich-panel screw is a fastener specifically designed to secure lightweight composite panels, which are built from two strong face sheets bonded to a soft or hollow core such as honeycomb, foam, or balsa. Standard screws can easily crush or strip these materials, so sandwich-panel screws use wide threads, collars, or captive washers to spread out the load and prevent damage.
They are commonly found in aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction industries, where lightweight yet strong materials are critical. Some versions feature self-drilling tips for clean penetration of the face sheet, while others include built-in spacers or bushings to avoid over-tightening. This makes them essential for safely fastening panels in aircraft interiors, vehicle bodies, marine decks, and insulated building systems.

Screw
A screw is a heavy-duty fastener designed to join materials together by creating its own threads within a material or fitting into a pre-threaded hole. Industrial screws are used in applications such as construction, manufacturing, machinery, and automotive industries, where strong and reliable fastening is required.
Screw Eye Bolt
A screw eye bolt is a fastener with a looped head and a threaded shaft, commonly used to anchor cables, ropes, or chains into wood. It's often used in light-duty applications like hanging items or guiding wires.
Screw-In Anchor
A screw-in anchor is a fastener that creates a secure point in drywall or similar materials for holding screws. It has sharp threads that cut into the material as it’s driven in, providing a strong grip for hanging items like shelves, pictures, or light fixtures.
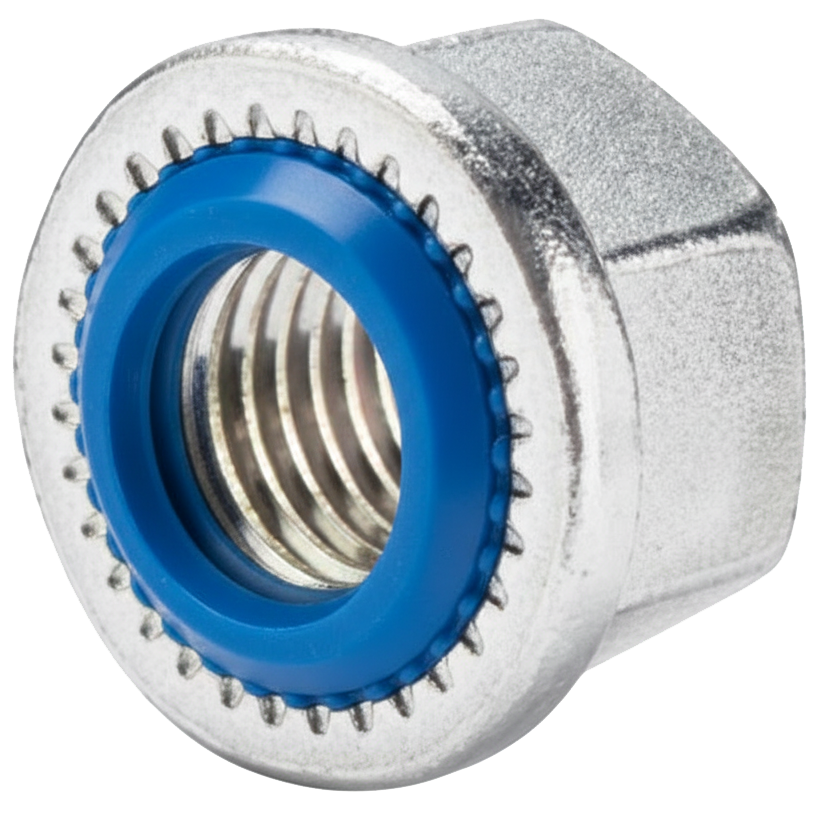
Sealing Nut
A sealing nut is a specialized type of fastener designed to create both a mechanical lock and a fluid-tight seal when installed on a bolt, stud, or threaded component. Unlike a standard nut, which only provides clamping force, a sealing nut also prevents the leakage of liquids, gases, oils, or contaminants through threaded joints.
The key feature of a sealing nut is its built-in seal, typically made from an elastomeric or polymer material such as neoprene, silicone, nitrile rubber (NBR), or fluorocarbon (Viton®). This sealing element is often bonded or mechanically retained in a groove on the nut’s bearing surface or encapsulated in a metal washer. When the nut is tightened, the seal compresses against the mating surface, filling any microscopic gaps in the threads or flange area to create a hermetic seal.
Design and Function
Sealing nuts are usually made from stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, or brass, and the sealing material is chosen based on the operating environment (temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure).
- The metal portion provides structural strength and thread engagement.
- The seal provides environmental and fluid sealing protection.
Some designs incorporate metal-to-metal contact for proper torque retention while maintaining the integrity of the seal. Others may feature captive O-rings or integrated sealing washers for more aggressive sealing applications.
Applications
Sealing nuts are used wherever vibration resistance and fluid-tight connections are critical. Common applications include:
- Aerospace and defense – to seal hydraulic, fuel, and pneumatic systems.
- Automotive and heavy equipment – in engines, transmissions, and brake systems.
- Electronics and enclosures – to prevent moisture or dust ingress.
- Industrial machinery and piping – to contain pressure or prevent leakage of process fluids.
Advantages
- Provides leak-free sealing without additional gaskets or sealants.
- Reduces assembly time and maintenance.
- Offers vibration resistance and thread locking in dynamic applications.
- Works under high pressure and temperature conditions when properly selected.

Sealing Patch
A pre-applied material on a fastener’s threads that creates a seal to prevent fluid or gas leakage when installed. Unlike locking patches, which focus on preventing loosening, sealing patches are designed to fill gaps between mating threads, providing both a chemical and mechanical seal. They are often used in applications where pressure containment or environmental protection is critical.
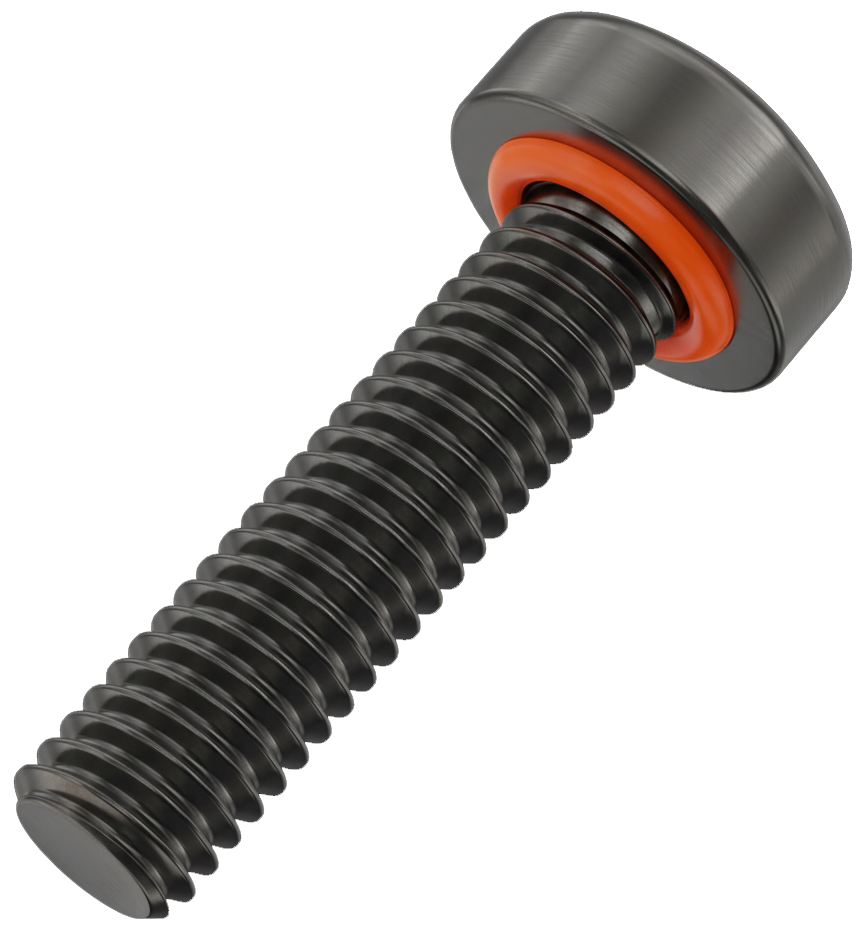
Sealing Screw
A sealing screw is a type of fastener specifically designed to prevent the passage of liquids, gases, or contaminants through the threaded joint or the hole it secures. It combines the mechanical fastening capability of a standard screw with an integrated sealing feature, such as an O-ring, captive washer, or sealing patch, to create a tight, leak-resistant barrier.
These screws are commonly used in electronic enclosures, hydraulic systems, fuel systems, outdoor equipment, and aerospace or marine applications, where protection against fluid ingress or environmental contamination is critical. The sealing element—often made of rubber, silicone, nylon, or fluoropolymer materials like Viton®—compresses when the screw is tightened, filling gaps between the threads and the mating surface.
Sealing screws can be manufactured from materials such as stainless steel, brass, or coated carbon steel, and they are often rated for specific pressure, temperature, or chemical exposure conditions.

Seams
Longitudinal surface discontinuities or defects found on fasteners. These imperfections typically originate from flaws in the raw material (such as the wire or bar stock) or are introduced during early manufacturing stages like rolling or drawing. Seams generally appear as straight or slightly irregular lines running along the length of the fastener, commonly located on the shank, under the head, or extending into the threads. They are a significant concern because they can act as stress concentrators, reducing the fastener's fatigue life and serving as initiation points for cracks and eventual failure.
Secondary Operation
A process used to modify or enhance a fastener after its initial manufacturing. Common secondary operations include drilling, tapping, slotting, shaving, or adding grooves. These steps are necessary when standard cold forming can’t achieve the required detail or precision.
Security Spline Lug Nut
A security spline lug nut is a specialized wheel fastener designed to help prevent wheel theft while also offering a compact profile for tight clearance applications.
Instead of the common hex-shaped head, these lug nuts feature narrow grooves (splines) machined around their exterior. A matching “spline drive” socket is required to install or remove them. Because standard sockets won’t grip the splines, it makes them more secure against theft than conventional lug nuts. The splined design also allows for a smaller outside diameter, which is especially useful on wheels with small lug recesses where a standard hex nut would not fit.
You’ll find security spline lug nuts most often in the automotive aftermarket—on custom alloy wheels, tuner cars, or performance vehicles—where both theft deterrence and aesthetics matter. They provide the dual benefit of locking-style security and a sleek, low-profile appearance.
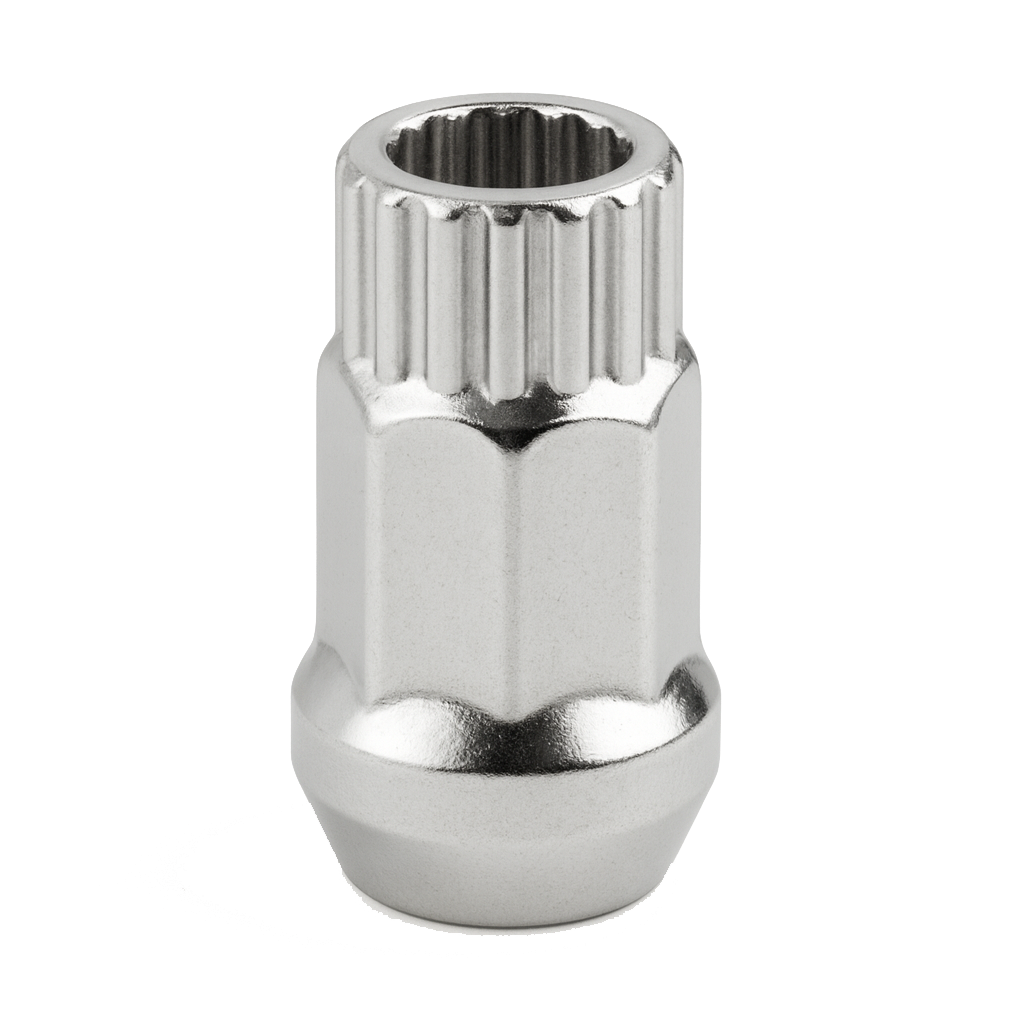

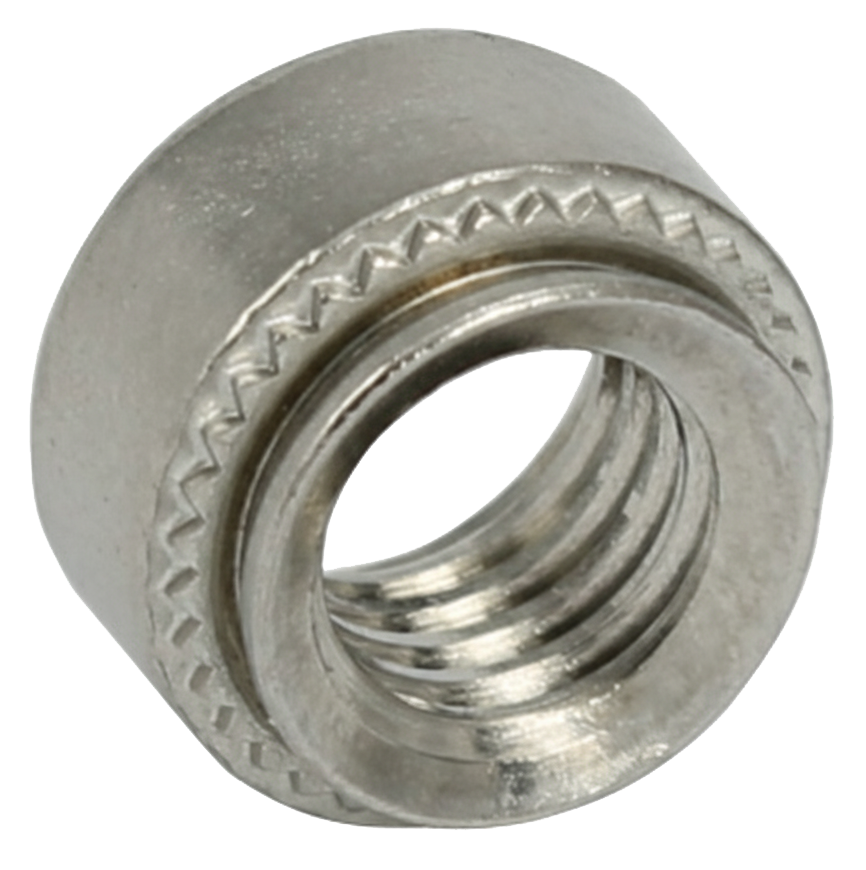
Self-Clinching Nut
A self-clinching nut is a permanently installed fastener designed to anchor into sheet metal or thin materials by mechanically locking in place when pressed into a properly sized hole. It provides a strong, reusable internal thread in materials that are too thin or too soft to be tapped or threaded conventionally, such stainless steel, aluminum, or brass.
The self-clinching nut was originally developed by PennEngineering® (under the brand name PEM® nuts) and has become a standard solution for joining thin-gauge sheet metal in industries like electronics, automotive, aerospace, and enclosures.
The principle behind it is simple: when the nut is pressed into a punched or drilled hole using a press (not hammered), its knurled or serrated clinching ring displaces the surrounding material into an undercut groove on the nut’s shank. This creates a cold-flow interlock—the sheet metal plastically deforms around the nut, mechanically locking it in place. The head of the nut sits flush with or slightly above the surface, while the threads remain captive and can withstand repeated assembly and disassembly without stripping.
A key feature is that installation occurs without heat or adhesives, and once installed, the nut cannot rotate or fall out under normal torque or vibration. The surrounding sheet provides axial retention, while the displaced material around the undercut provides torque resistance.
There are several types of self-clinching nuts, each optimized for different materials and applications:
- Standard self-clinching nuts (type S) for steel or aluminum sheets.
- Stainless steel versions (type CLS) for corrosion-resistant applications.
- Floating self-clinching nuts, which allow minor misalignment between mating parts.
- Flush-head and mini versions, designed for low-profile assemblies or thin sheets.
Installation is quick and reliable—typically done with a hydraulic or mechanical press that applies steady pressure (not impact), embedding the nut cleanly and permanently. The resulting joint can achieve thread strengths comparable to a tapped hole in much thicker material.

Self-Drilling Screw
Self-Drilling Screws are versatile fasteners used to attach different materials together, such as metal to metal, metal to wood, and plastic. These screws have a pointed drill bit that allows them to create their own thread without the need for a pre-drilled pilot hole. This feature makes these screws more versatile compared to traditional screws, as they have the ability to tap, similar to self-tapping screws. As a result, Self-Drilling Screws are suitable for use with a wide range of materials across various industries.
SEMS Screw
A SEMS screw (or SEMS fastener) is a screw that comes pre-assembled with a captive washer or set of washers during manufacturing. The washer is permanently held in place, typically by rolling the screw threads after the washer is added, which traps it on the shank without preventing rotation. This creates a one-piece fastener that cannot lose its washer, making assembly faster, simpler, and more consistent.
The construction of SEMS screws allows for a variety of configurations. The most common design includes one or two washers—such as flat, lock, or conical washers—positioned beneath the head. These screws can feature different head styles, such as pan heads, hex heads, or Phillips, slotted, or Torx drives. They are also manufactured with various thread types, from machine screw threads to self-tapping versions, depending on the intended application.
The advantages of SEMS screws are clear. They save time by eliminating the need to handle washers separately and prevent washers from being lost during assembly or maintenance. By supplying the washer already in place, they guarantee the correct type is always used, reducing assembly errors. When equipped with lock washers or conical washers, SEMS screws also provide resistance to loosening caused by vibration. Overall, they offer a cost-effective solution in high-volume production environments by cutting down on labor and handling.
Because of these qualities, SEMS screws are used widely across industries. In the automotive industry, they are essential for both interior and engine applications where assembly speed and vibration resistance are critical. In electronics, they secure components in tight spaces where reliability and speed are necessary. In appliances and machinery, they ensure repeatable, dependable fastening for parts that require regular maintenance. They are also used in construction and general manufacturing for efficient, secure joints.
There are also variations of SEMS screws to suit different needs. A common configuration combines a flat washer with a lock washer to provide both load distribution and vibration resistance. Some versions use a tooth lock washer for extra grip in high-vibration conditions. Others feature multiple washers stacked together to deliver a combination of benefits. This versatility makes SEMS screws a highly adaptable and reliable choice in modern fastening applications.
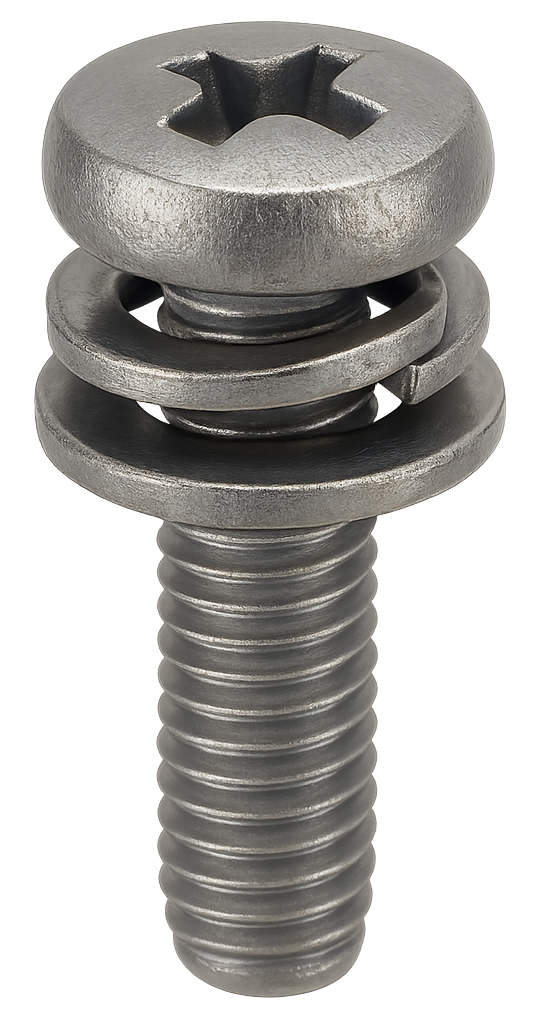

Serrated Flange Bolt
A serrated flange bolt is a hex-head bolt with a built-in washer-like flange under the head. The flange has serrations (ridges) that grip the surface to prevent the bolt from loosening due to vibration. It's commonly used in automotive and machinery applications where secure fastening is critical.
Sex Bolt
A sex bolt is a two-piece mechanical fastener consisting of a male machine screw and a female internally threaded barrel (post) that fasten together through a clearance hole. The barrel passes through the joined materials and the screw threads into the barrel from the opposite side, creating a finished, low-profile appearance on both faces of the assembly. Sex bolts are commonly used when access is available from both sides and where a traditional nut would be bulky, unattractive, or prone to pull-through in softer materials.

Key identifying features
- Two-piece construction: screw + internally threaded barrel/post
- Flush/finished look: heads can be low-profile on both sides
- No protruding threads: barrel contains the threads internally
- Good pull-through resistance: large bearing surface compared to a small nut/washer stack (varies by head style)
Common applications
- Leather goods (belts, straps, bags, tack)
- Bookbinding and menus
- Signage and displays
- Furniture and cabinetry panels
- Light-duty mechanical assemblies where both sides are visible
Common head styles
- Flat head (countersunk) – sits flush in a countersink
- Truss / binding / low-profile head – larger bearing surface, decorative look
- Button head / pan head – clean appearance, moderate bearing area
Materials and finishes
- Steel (often zinc plated for corrosion protection)
- Stainless steel (commonly 18-8 / A2 for corrosion resistance)
- Brass / aluminum (decorative or corrosion-resistant, lighter duty)
- Finishes vary by material and application (zinc, black oxide, polished stainless, anodized aluminum, etc.)
Sizing notes
- Typically specified by thread size (e.g., #8-32, 1/4-20, M6) and post length/grip range (the barrel length must match the combined material thickness).
- The barrel OD must fit the clearance hole, and the head style may require a countersink (flat head) or a larger bearing surface (truss/binding).
Installation tips
- Choose barrel length to match the stack thickness; too short won’t fully engage threads, too long can bottom out before clamping.
- Use medium threadlocker if vibration is expected.
- Avoid over-torque in softer materials (leather, plastics) to prevent crushing.
AKA: Barrel nut, Chicago screw, binding post, binding screw, two-piece post and screw.
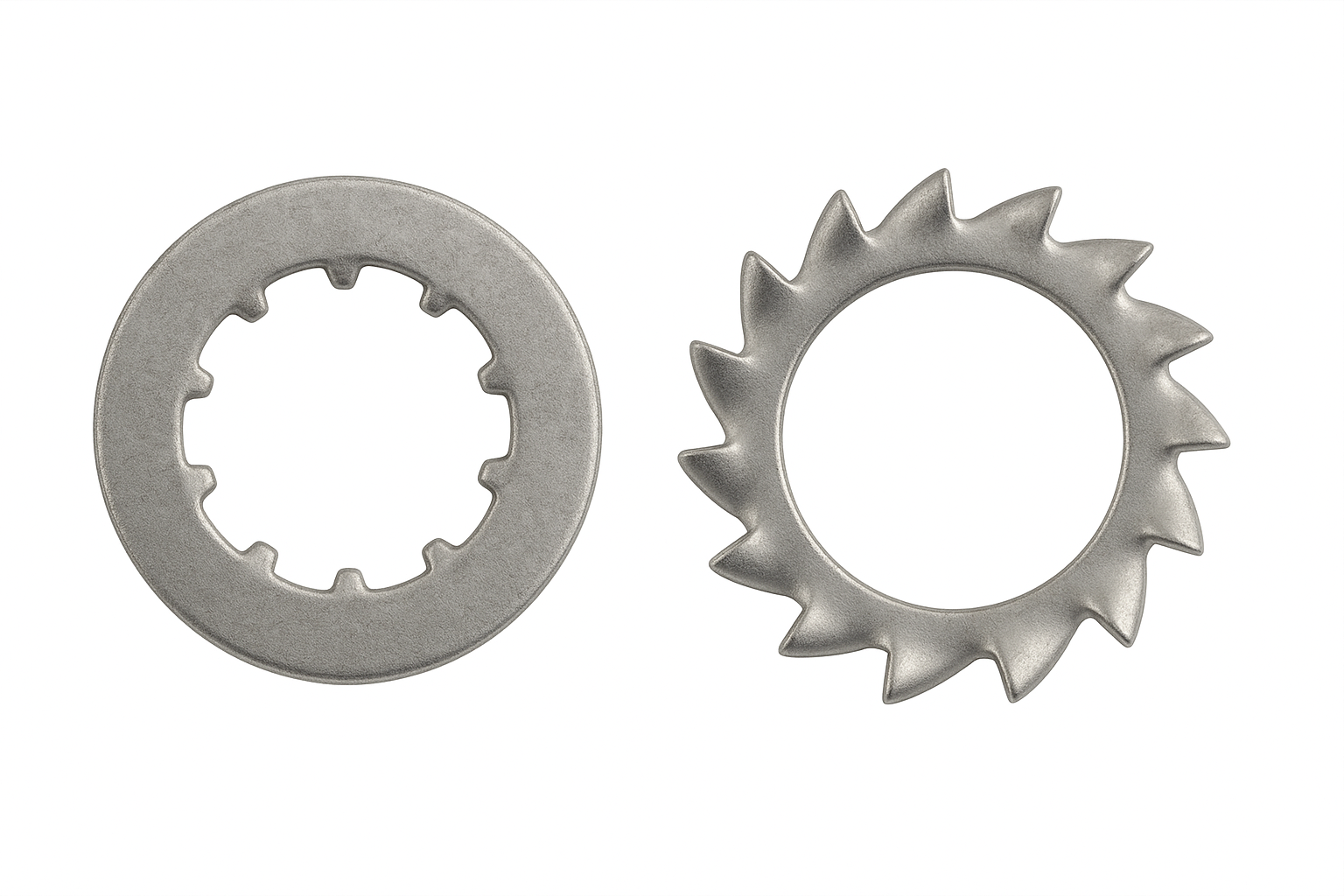
Shakeproof Washer
A shakeproof washer is a type of lock washer designed to stop fasteners from loosening under vibration or movement. Unlike flat washers that only distribute load, shakeproof washers have serrated teeth—either on the inside edge (internal-tooth) or around the outside edge (external-tooth)—that bite into the fastener and the surface material. This added friction helps resist rotation and keeps the joint secure.
They are commonly used in automotive, electrical, and machinery applications where vibration is a concern. While effective, they can mark softer surfaces and aren’t always the best choice for high-strength structural joints, where more advanced locking solutions may be required.
Shaker Screen Bolt (also called Carriage Bolt)
A carriage bolt, also known as a shaker screen bolt, is a fastener featuring a rounded, dome-shaped head and a square neck directly beneath it, designed to fit into a corresponding square hole or embed into wood or metal to prevent rotation during tightening. These bolts are typically used with a nut and washer to secure materials together. The smooth, rounded head provides a clean, tamper-resistant finish while the square neck locks the bolt in place as torque is applied. Commonly used in wood-to-metal connections, shaker screens, agricultural equipment, and structural assemblies, these bolts are valued for their strength, vibration resistance, and ability to maintain a secure, flush appearance.

Shank Diameter
The diameter of the unthreaded, cylindrical portion of a bolt or screw. This precise measurement is typically slightly smaller than the major diameter of the threaded portion. This smaller size provides necessary clearance, enabling the fastener to pass through pre-drilled holes smoothly and aiding in proper alignment before the threads engage, ensuring a proper fit within the assembly.
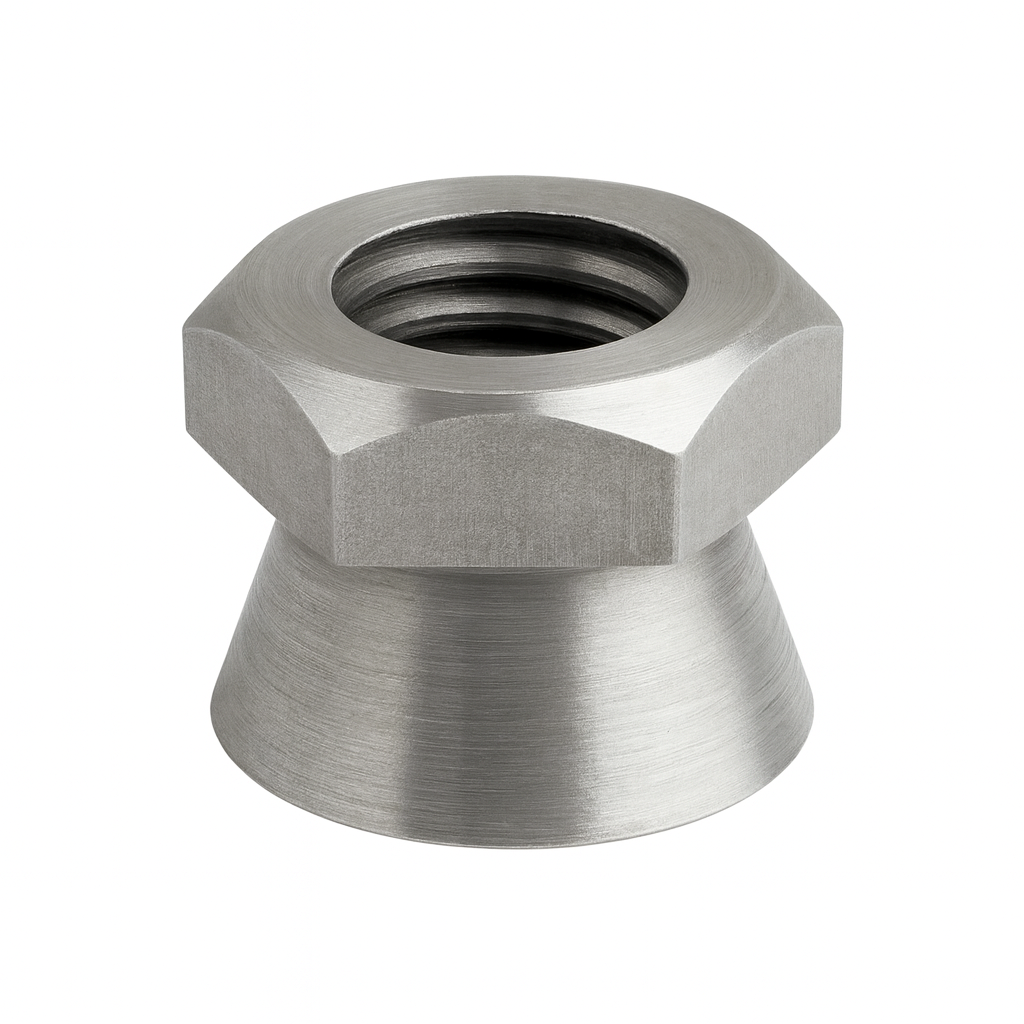
Shear Nut
A shear nut is a type of security fastener designed to prevent tampering or unauthorized removal. It consists of a hexagonal upper section used for tightening and a smooth, conical lower section. During installation, the hex portion breaks off (shears) once a specified torque is reached, leaving behind only the tamper-resistant cone.
Because the remaining section has no grip points for standard tools, shear nuts are extremely difficult to remove without specialized equipment. They are commonly used in security-sensitive applications such as fencing, street signs, utility installations, and other public infrastructure where theft or vandalism is a concern.

Shear Screw
A shear screw is a tamper-resistant fastener specifically designed so that its drive head intentionally breaks off, or “shears,” when tightened to a predetermined torque. Once this happens, the drive portion separates from the body of the screw, leaving behind a smooth, often conical or headless surface. Because there is no usable drive left, the fastener cannot be engaged with standard tools, making it extremely difficult to remove.
The main purpose of a shear screw is to create a permanent and secure fastening in situations where tampering or unauthorized removal must be prevented. By eliminating the head after installation, the screw ensures that it cannot be loosened without specialized methods such as drilling or destructive extraction, which adds a strong layer of security.
Shear screws are widely used in applications that demand high security and reliability. They are commonly found in access panels, electrical enclosures, and public fixtures, where tampering could compromise safety or operations. They are also used as theft-prevention fasteners in items such as meter housings, street furniture, and alarm systems. Additionally, they serve an important role in safety-critical assemblies where loosening could lead to hazards or failures.
While they share similarities with break-off screws, the defining characteristic of a shear screw is that the head shears away at a calibrated torque, leaving behind a permanent, tamper-proof fixing that is non-removable under normal conditions. This ensures that once installed, the fastener provides long-term security and reliability.
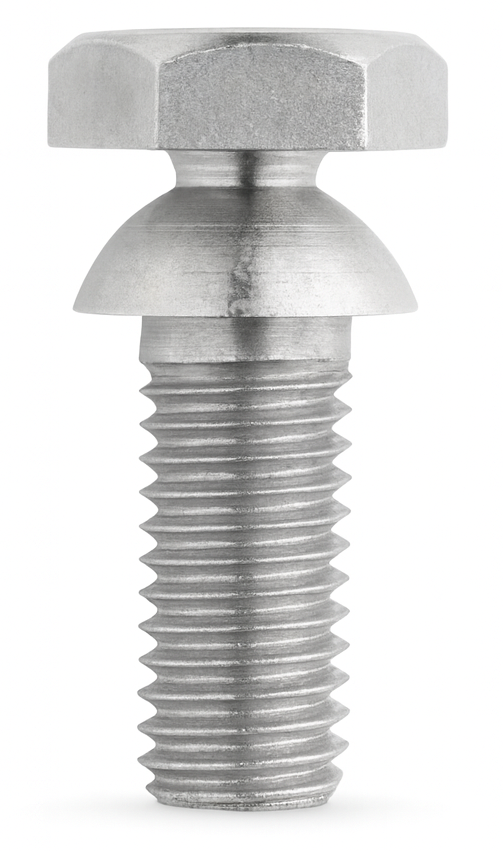

Shear Strength
Shear strength is the maximum amount of force a material or fastener can withstand when two opposing forces try to slide one part of it across another, essentially trying to “cut” or “shear” it. Instead of pulling the fastener apart (tension) or crushing it (compression), shear acts sideways, across the fastener’s cross-section.

In fasteners, shear strength is a critical measure of how a bolt, pin, rivet, or screw will perform when loads push across it rather than pull on it. A bolt holding two plates together in double-shear, a clevis pin in machinery, a wheel stud supporting a rotating hub, or a rivet in sheet metal all experience shear loads. Typically, shear strength for steel fasteners is roughly 60% of their tensile strength, though the exact value depends on material, grade, heat treatment, and manufacturing method.
Understanding shear strength is essential in industrial design, construction, and fastener selection because a fastener may meet tensile requirements but still fail if exposed to high lateral forces. In applications with vibration, shock loading, joints that shift, rotating equipment, or structural members that bear sideways loads, choosing a fastener with the correct shear capability is just as important as selecting the right tensile strength or hardness.
Sheet Metal Lancing
Sheet metal lancing is a metal fabrication process in which a cut or slit is made in a sheet of metal without completely removing the material. Instead of punching out or removing a section of the sheet, the metal is sheared and displaced, creating a tab, vent, or louvers that remain attached to the parent material. This controlled deformation allows manufacturers to form features such as bends, flanges, or openings in a single operation while maintaining the sheet’s structural integrity.
During lancing, a punch and die setup is used—similar to traditional stamping—but the key difference is that the material is not entirely separated. The punch penetrates only partway through the metal, causing it to bend or raise a section rather than create a hole. Because no scrap is generated, lancing is an efficient and cost-effective process, ideal for high-volume production.
Lanced features are often used for airflow or drainage openings, fastening points, or locating tabs. For instance, louvers made through lancing can help ventilate enclosures, while retaining tabs can hold components in place before final assembly. The process is commonly performed on ductile metals like mild steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, which can withstand localized deformation without cracking.
Lancing offers several advantages:
- It reduces waste, as no material is discarded.
- It requires fewer operations, combining cutting and forming in one step.
- It maintains dimensional accuracy and part strength since the base sheet remains intact.
However, because the displaced material can cause localized stresses and surface irregularities, lancing is generally limited to thin-gauge sheet metal and applications where precise cosmetic finishes are not the primary concern.
Sheet Metal Screw
Sheet metal screws are versatile fasteners designed for securing metal, plastic, and other thin materials. They feature sharp, self-tapping threads that cut into material, creating a secure hold without the need for pre-drilled holes in some applications. Earnest Machine offers Type A, Type AB, and Type B sheet metal screws in various head styles to suit different fastening needs.
Shock Absorber Nut
A shock absorber nut is a specialized fastener used to secure a vehicle’s shock absorber to its mounting points, typically at the chassis and suspension. It is designed to withstand the high levels of vibration, impact, and dynamic forces that occur as the suspension absorbs shocks from the road. These nuts are often paired with bolts or threaded studs that pass through the shock absorber’s bushings or mounting eyes.
From a design standpoint, shock absorber nuts are usually made from high-strength steel or alloy steel to handle repeated stress cycles. They are often plated with zinc, phosphate, or other coatings to resist corrosion from moisture, road salts, and debris. Many are also designed with locking features—such as nylon inserts (nyloc nuts), distorted threads, or prevailing torque mechanisms—to prevent loosening under constant vibration and movement.
The purpose and function of a shock absorber nut is to maintain a secure, rigid connection between the shock absorber and the suspension or chassis. If the nut loosens, the shock absorber cannot effectively dampen vibrations and impacts, which compromises vehicle stability, safety, and ride comfort. The locking design ensures that preload is maintained over time, even in harsh driving conditions.
In terms of applications, these nuts are used in virtually all types of vehicles—cars, trucks, motorcycles, and heavy equipment. They are critical in suspension systems where reliability under repeated stress is essential.
The advantages of shock absorber nuts are their ability to maintain a secure connection despite constant vibration, their contribution to ride safety and handling, and their corrosion resistance in outdoor environments.
The limitations are that they can be more difficult to remove due to their locking features, may require replacement after disassembly (especially nylon-insert or prevailing torque types), and are application-specific, meaning they need to be matched carefully to the vehicle’s design and shock absorber size.
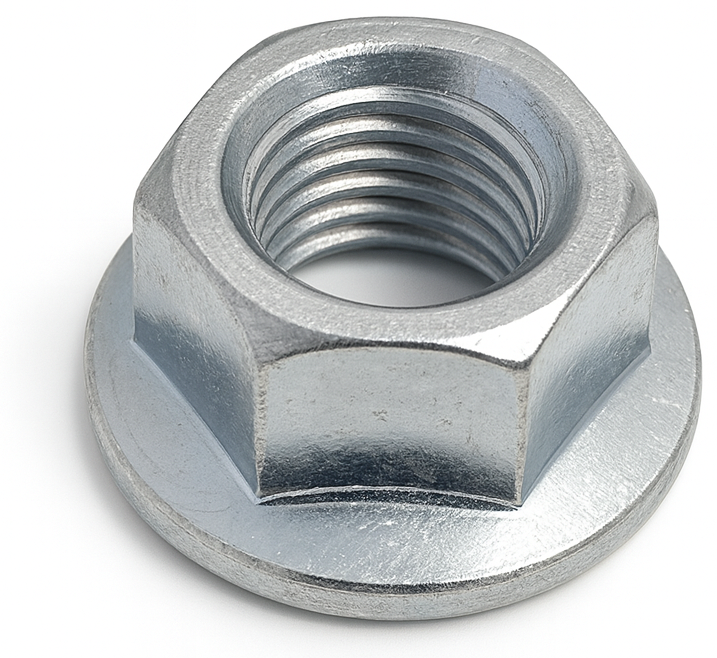

Short Neck Carriage Bolt
Short Neck Carriage Bolts feature a shorter, shallower square neck under the rounded head, making them suitable for use with thinner materials like sheet metal. This design prevents damage to the installation surface or connecting material. Due to their versatility, Short Neck Carriage Bolts are commonly used in the assembly of construction equipment, heavy machinery, and furniture where both aesthetics and functionality are important.

Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process that strengthens metal parts by bombarding their surface with small, spherical media such as steel, glass, or ceramic balls. This process introduces a layer of beneficial compressive stress on the metal's surface, which significantly improves its resistance to fatigue and cracking.

The process works by using a controlled stream of media to repeatedly strike the metal part. Each impact creates a small dimple, and the plastic deformation of the outer layer creates a compressive stress as it is constrained by the underlying material. This compressive layer is crucial because cracks typically form in areas of tensile stress. By counteracting these stresses, shot peening increases the part's resistance to stress corrosion cracking and fretting, thereby extending its fatigue life.
Shot peening is a vital process in industries where component durability and reliability are essential, including aerospace, automotive, and heavy manufacturing. It's commonly used on parts like turbine blades, crankshafts, and gears to ensure they can withstand high-stress environments and meet rigorous quality and safety standards.
Shoulder Bolt
A shoulder bolt—also known as a shoulder screw or stripper bolt—is a fastener with three distinct sections: a head, a precisely machined unthreaded shoulder, and a smaller-diameter threaded portion. The shoulder portion is larger in diameter than the threads and is manufactured to tight tolerances, allowing it to function as a precision pivot, spacer, guide, or bearing surface, rather than purely as a clamping fastener.
The defining feature of a shoulder bolt is the smooth cylindrical shoulder, which provides a low-friction surface for components to slide, rotate, or accurately position relative to each other. Because the shoulder carries shear loads and controls alignment, the threads typically engage only at the end of the bolt, allowing the joint to be tightened without restricting movement on the shoulder itself.
Shoulder bolts are used extensively in machinery, tooling, automotive assemblies, robotics, and manufacturing equipment—anywhere components must rotate, slide, hinge, or align. They are common in punch-and-die setups, pulleys, cams, linkages, linear guides, and moving mechanical assemblies. They are often made from alloy steel or stainless steel and may have hex socket heads for precise torque control.
AKA: Shoulder Screw, Stripper Bolt
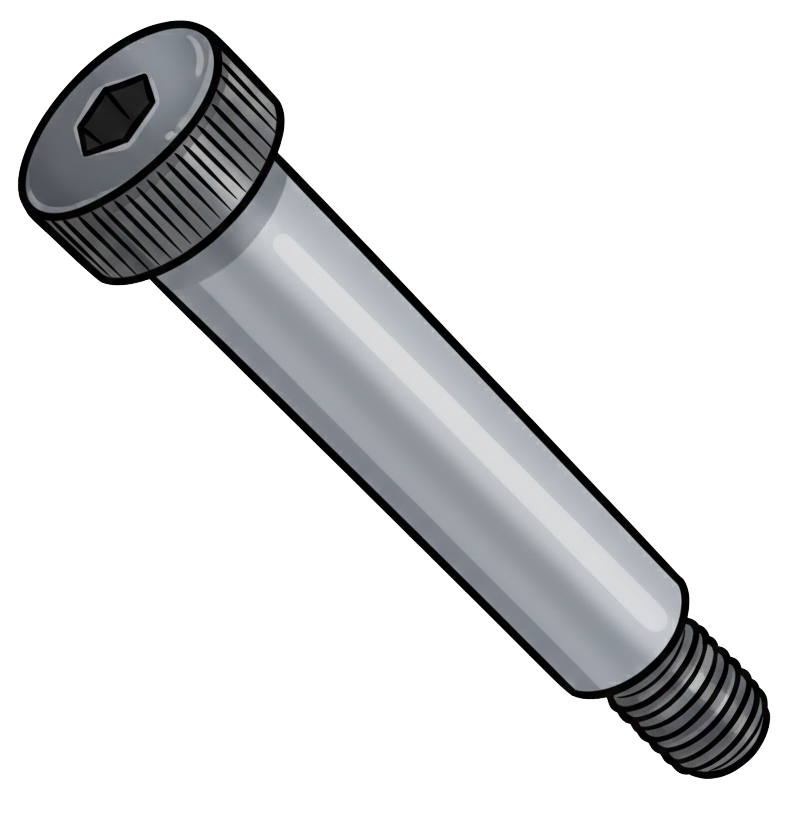

Shoulder Nut
A shoulder nut is a specialized nut that has an integral cylindrical shoulder extending from one side of the nut body, creating both a threaded fastening surface and a built-in locating, spacing, or bearing surface. Unlike a standard hex nut—which only provides clamping force along a flat face—a shoulder nut provides precise axial positioning and can act as a stop, spacer, guide, or alignment feature within an assembly.
The shoulder is typically larger in diameter than the threaded section, giving it a controlled bearing surface that interfaces with holes, brackets, bushings, or rotating components. This design allows the shoulder to carry shear loads, maintain alignment, or provide a standoff distance while the threads simply clamp onto a stud, bolt, or shaft. Because the shoulder portion is smooth and unthreaded, it can also serve as a pivot or sliding interface, similar to how a shoulder bolt functions, but from the nut side of the connection.
Shoulder nuts are commonly found in machinery, pulleys, cams, linkages, tooling assemblies, and motion systems where accurate positioning or rotational clearance is required. They may be used with shoulder bolts, shafts, or threaded rods and are often machined from hardened steel or stainless steel for strength and wear resistance.
Silicon (Si)
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a metalloid, meaning it has properties of both metals and nonmetals, and is the second most abundant element in Earth’s crust (after oxygen), making up about 28% by weight. Silicon plays a critical role in both nature and technology, serving as the foundation of modern electronics and materials science.
In its pure crystalline form, silicon is a hard, dark-gray, shiny solid with a metallic luster and a brittle structure similar to glass. It does not occur naturally in its pure state, but is found extensively in compounds such as silica (SiO₂) and silicates, which form the main components of sand, quartz, clay, and many rocks.
Silicon’s semiconducting properties are what make it so important in modern life. When precisely purified and doped with trace elements such as phosphorus or boron, silicon becomes the key material used in computer chips, transistors, diodes, solar cells, and microprocessors—earning it the nickname “the backbone of the digital age.” The region in California known as Silicon Valley is named after its central role in semiconductor and computer innovation.
Beyond electronics, silicon is also vital in metallurgy, construction, and chemistry. It is used in the production of alloys such as ferrosilicon, which strengthen steel and aluminum, and in the manufacture of glass, ceramics, and concrete. In polymer form, silicones (polysiloxanes) are flexible, rubber-like materials used in seals, adhesives, lubricants, medical implants, and cookware due to their stability and resistance to temperature and moisture.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide (SiC) is a compound of silicon and carbon that is recognized for its exceptional hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. While it occurs naturally in extremely rare mineral forms such as moissanite, it is primarily produced synthetically and has become one of the most important advanced ceramics in modern industry. Its unique combination of properties allows it to be used both as a high-performance structural material and as a semiconductor in power electronics.
![]()
Silicon carbide’s strength comes from its crystalline structure, in which silicon and carbon atoms alternate in strong covalent bonds. This gives it a hardness of about 9–9.5 on the Mohs scale, placing it just below diamond and cubic boron nitride. Unlike many ceramics, it also has high thermal conductivity, which allows it to transfer heat efficiently. SiC can withstand temperatures above 1,600 °C (2,912 °F) without losing strength and is highly resistant to oxidation, corrosion, and chemical attack. In addition, certain forms of SiC function as semiconductors, offering a wide bandgap, high voltage resistance, and efficiency that make them highly valuable in advanced electronics.
The material is typically manufactured through the Acheson process, in which a mixture of silica sand (SiO₂) and carbon, often from petroleum coke, is heated in an electric resistance furnace at temperatures between 2,000–2,500 °C (3,632–4,532 °F). The reaction produces silicon carbide crystals, which can then be ground into abrasive powders, sintered into ceramic components, or grown into wafers for use in electronics.
Applications of silicon carbide are diverse. Its hardness makes it ideal for abrasives such as grinding wheels, sandpapers, and polishing compounds, as well as cutting tools that must endure high wear. In ceramics and refractories, it is used for furnace linings, kiln shelves, and crucibles that must tolerate high heat. In the electronics sector, silicon carbide is increasingly important as a semiconductor material for high-performance power devices used in electric vehicles, solar inverters, and high-frequency systems. The automotive industry uses SiC in performance brake discs, clutches, and heat exchangers, while its lightweight hardness makes it suitable for armor in protective vests and vehicles.
The advantages of silicon carbide include its extreme hardness and wear resistance, ability to withstand very high operating temperatures, chemical stability, corrosion resistance, and efficiency in conducting both heat and electricity in specialized applications. However, it does have limitations. It is brittle compared to metals and can fracture under sudden impact or shock loads. Production costs, particularly for semiconductor-grade SiC, are relatively high. Additionally, its hardness requires specialized equipment and processes for shaping, machining, and finishing. Despite these challenges, silicon carbide remains an essential material for industries demanding high performance in extreme environments.
Silver (Ag)
Silver is a naturally occurring metallic element with the symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It is classified as a precious metal and is known for its brilliant white luster, high reflectivity, and exceptional physical performance. Silver is the best electrical conductor of all elements, the best thermal conductor of all metals, and one of the most malleable and ductile materials in existence. In nature, it appears both as native metal and within mineral ores such as argentite, chlorargyrite, galena, and chalcopyrite. Most commercial silver is produced as a byproduct of refining copper, lead, zinc, and gold. Although silver has a long history in currency, jewelry, and decorative objects, the majority of modern silver usage is driven by industrial manufacturing, especially in electronics, photovoltaics, catalysts, brazing alloys, batteries, medical technology, and other applications that require high reliability and efficient energy transfer.
Silver has a unique set of physical and chemical properties that make it exceptionally valuable in manufacturing. It possesses the highest electrical conductivity, highest thermal conductivity, and one of the highest levels of reflectivity among metals. It is corrosion-resistant but will tarnish in sulfur-rich environments, and although silver is soft and not suitable for structural or load-bearing components, it can be formed, drawn, or plated into extremely fine and precise geometries. Silver also exhibits natural antimicrobial behavior, making it useful in medical devices, filtration systems, and sterilization applications. Because of these attributes, silver has become an essential industrial material that supports modern electronics, precision optics, energy systems, and chemical processing.
While silver itself is not used as a structural fastener due to its softness and cost, it is important in the fastener ecosystem through coatings, plating, and specialized alloys. Silver-plated screws, studs, nuts, washers, and electrical terminals are widely used in high-performance electrical equipment such as switchgear, contactors, circuit breakers, and high-amperage connectors where conductivity and low resistance are critical. In aerospace, cryogenic systems, and high-temperature environments, silver plating provides excellent galling resistance, stable torque-tension behavior, and reliable performance under thermal cycling. Silver also functions as a dry-film lubricant at elevated temperatures—often up to around 650°C—allowing threaded components in turbines, exhaust assemblies, and aircraft engines to achieve accurate preload without seizing.
Silver’s industrial presence extends even further through brazing rods, solder alloys, and filler metals used to join components in HVAC systems, electrical assemblies, and precision mechanical applications. Silver-bearing brazing materials produce strong, conductive, and heat-resistant joints. The metal also appears in optical coatings, mirrors, catalytic converters, photovoltaic cells, RFID antennas, circuit boards, sensors, automotive electronics, antimicrobial coatings, and precision instruments. Today, more than half of all mined silver is consumed directly by industry rather than decorative or monetary uses.

Slag
Industrial slag is a byproduct of metal smelting, refining, and other metallurgical processes, consisting mainly of molten mixtures of metal oxides, silicates, and fluxes that form when impurities are separated from molten metals such as iron, steel, copper, or nickel. Once cooled and solidified, slag becomes a rock-like material that can be processed for use in various industrial, construction, and environmental applications.

In simple terms, slag is the waste layer that floats on top of molten metal during refining, acting as both a purifier and a protective blanket for the molten metal beneath. It’s intentionally formed by adding fluxes (like limestone, dolomite, or silica) that react with unwanted oxides and impurities in the ore or metal, creating a molten mixture that can be easily separated.
Formation and Chemistry
The chemistry of slag depends on the metal being produced and the flux materials used, but it generally includes:
- Metal oxides: such as FeO, MnO, CaO, MgO, and Al₂O₃
- Silicates: formed from reactions between silica (SiO₂) and metal oxides
- Minor constituents: including sulfides, phosphates, or residual metals
For example, in iron and steelmaking, slag forms through a series of reactions:
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
CaO + SiO2 → CaSiO3
The calcium silicate (CaSiO₃) produced is a major component of blast furnace slag—a molten compound that floats on the molten iron and traps impurities like sulfur and phosphorus.
Types of Industrial Slag
1.Blast Furnace Slag: Produced during pig iron manufacture. It’s rich in calcium silicates and often granulated for use in cement and concrete.
2. Steelmaking Slag: Formed in basic oxygen furnaces (BOF) or electric arc furnaces (EAF); contains oxides of iron, calcium, and magnesium. Used in road construction and as a fluxing agent in secondary processes.
3. Non-Ferrous Slags: Produced from copper, nickel, lead, and zinc smelting. These often contain silicates and residual metals, requiring proper disposal or recycling.
Functions During Metal Production
- Refining: Slag removes impurities from the molten metal, including sulfur, phosphorus, and silica.
- Protection: It shields molten metal from oxidation by the air.
- Thermal Insulation: It helps maintain heat in the furnace and stabilize temperature distribution.
- Desulfurization: It absorbs sulfur from the molten bath through chemical reactions with calcium oxide and magnesium oxide.
Post-Processing and Uses
Rather than being discarded, modern industries treat slag as a valuable secondary resource. Once cooled and processed, it can be used for:
- Cement production: Granulated blast furnace slag (GBFS) is a key ingredient in Portland cement and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs).
- Construction materials: Crushed slag is used in road base, rail ballast, and asphalt aggregate.
- Soil stabilization and reclamation: Slag’s alkaline nature can neutralize acidic soils or mine tailings.
- Metallurgical recycling: Some slags are reprocessed to recover valuable metals.
Slotted Flat Countersunk Head Cap Screw
A Slotted Flat Countersunk Head Cap Screw is a type of fastener designed to sit flush with or below the surface of the material it is securing, thanks to its flat, countersunk head. It features a slotted drive, meaning it has a single straight cut across the head, which is compatible with a flathead or slotted screwdriver. These screws are commonly used in applications where a smooth surface is required after installation, such as in furniture, machinery, and construction.
Slotted Hex Jam Nut
Jam Slotted Nuts are half as thick as Slotted Nuts. They are designed for low-clearance rotating applications. The slots’ width and depths are manufactured to provide clearance for full engagement of cotter pins or wires — ensuring maximum resistance to loosening.
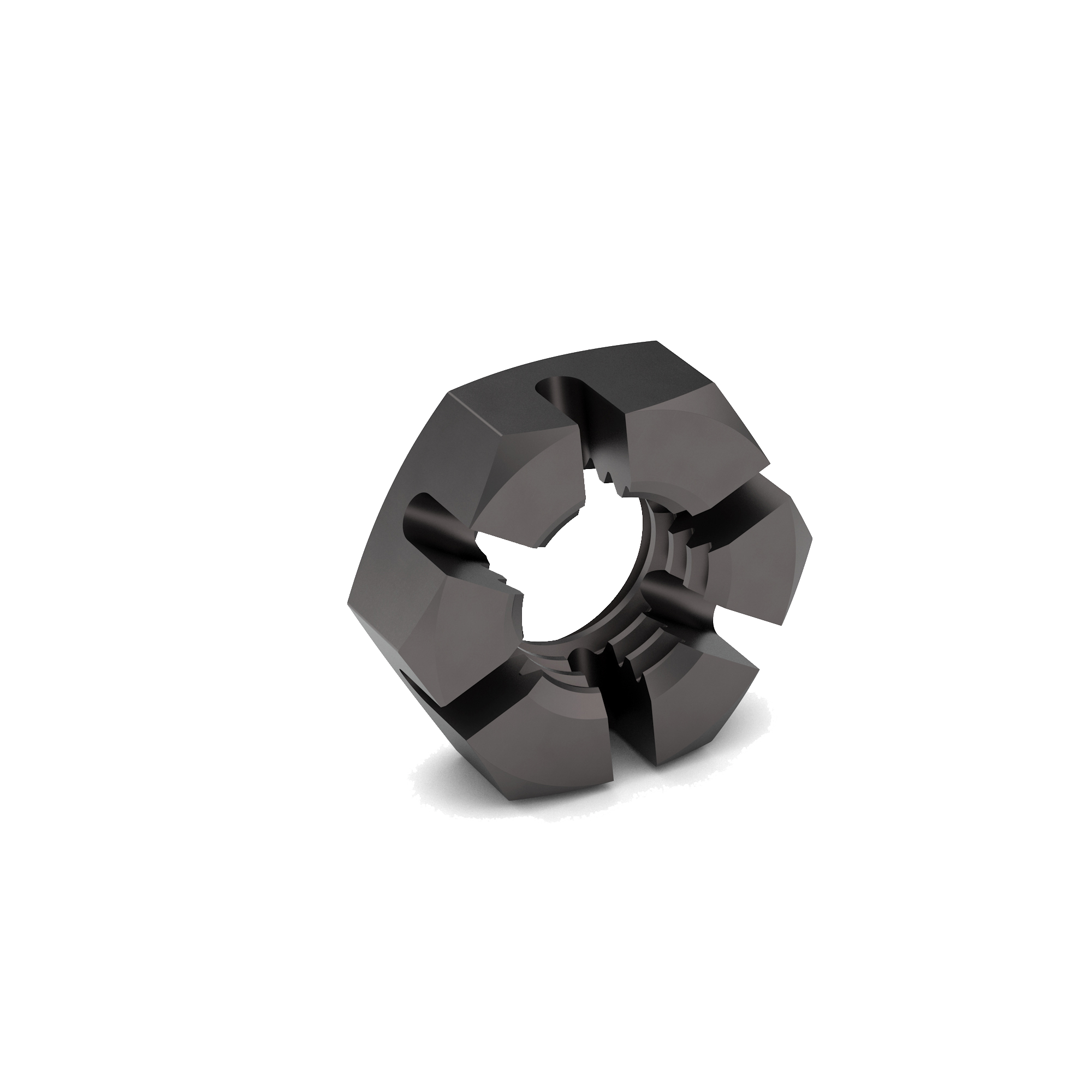
Slotted Hex Nut
Hex Slotted Nuts. Castellated Nuts. Slotted Nuts. Whatever you may call them, the nuts perform well under rotating applications. They can be found used in hold bearings and bushing sleeves in place. The castle turret-like features on the top of these nuts permit a cotter pin to lock the nuts in place and prevent loosening.

Slotted Reduced Shank Screw
A slotted reduced-shank screw is a screw with a straight slotted drive and an unthreaded section under the head that’s turned down smaller than the thread’s major diameter—typically near the root diameter. That reduced, smooth shank lets the top material clear the threads so only the far (bottom) material is threaded.
This design pulls joints tight without thread-jacking, lowers driving torque, and reduces splitting in wood, plastics, or thin sheet. The smooth portion can also aid alignment and place the shear plane on solid shank rather than on threads. You’ll see them in cabinetry, plastics assemblies, light machinery, and stacked sheet-metal joints. They’re also called reduced-diameter shank, relieved shank, or waisted screws (distinct from shoulder screws).
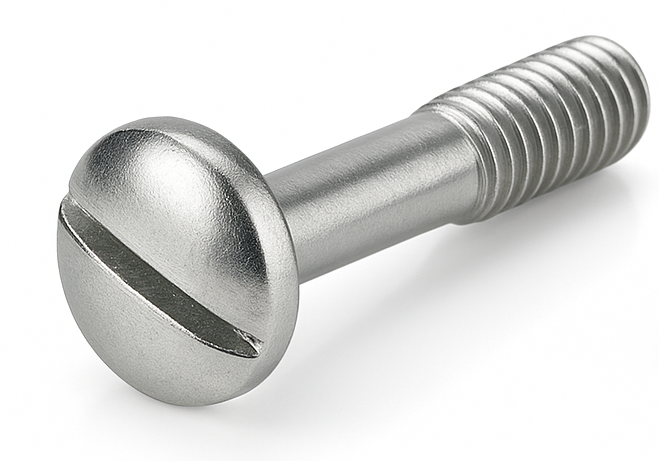

Snap Safety Pin – Two-Wire
A Snap Safety Pin – Two-Wire (also called a double-wire snap pin or snapper pin) is a quick-release retainer with a solid pin and a spring latch made from two parallel wires. The pin passes through aligned parts and has an annular groove near its end. When you flip the double-wire latch over the tip, it snaps into that groove and prevents the pin from backing out under vibration. The two-wire design provides higher spring force, a sturdier latch, and a bigger grip area than single-wire versions.
To use it, insert the pin through the holes, rotate the latch over the chamfered end, and let it snap into the groove. To remove, pull the loop outward to clear the groove and swing it off, then withdraw the pin. This makes it ideal for applications that need fast, tool-free attachment and removal.
Common uses include trailer hitches and drawbars, jack stands, agricultural and landscaping equipment, and material-handling fixtures—anywhere parts are frequently attached and removed. Pins are typically low-carbon or alloy steel with zinc plating, or 300-series stainless; latches are spring steel (zinc-plated) or stainless. Heads may be button/washer style or small forged heads, and pins come straight or bent, commonly in ¼″ to ⅝″ diameters with various usable lengths.
These pins are meant for convenient retention, not for overhead lifting. Choose a pin diameter that closely fits the hole and always confirm the latch is fully engaged in the groove after installation.
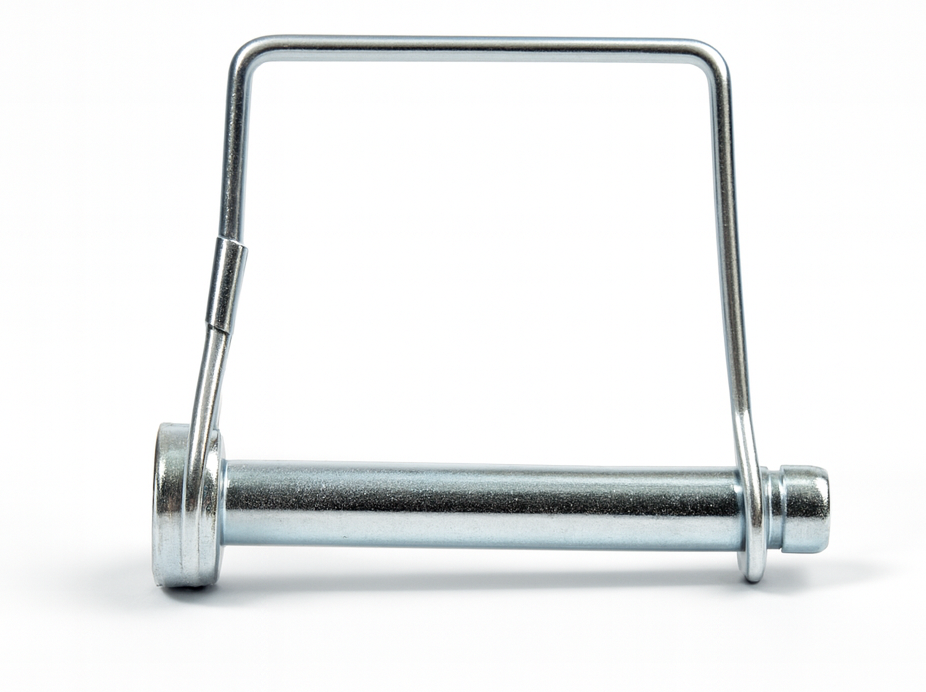

Socket Head Cap Screw
A Socket Head Cap Screw, also known as a Socket Head Bolt, is a high-strength fastener with a cylindrical head that contains a hexagonal (Allen) socket drive in its center. It is designed to be installed using an Allen wrench or hex bit, which makes it ideal for applications where torque must be applied in tight or recessed spaces that cannot accommodate a traditional wrench or socket.
These screws are typically manufactured from alloy steel, stainless steel, or other high-strength materials, giving them greater tensile strength than standard hex bolts of the same size. They are offered in a range of finishes such as black oxide, zinc plating, stainless steel, and specialty coatings, all of which provide added resistance to corrosion or chemicals depending on the application. In terms of threading, smaller diameters are often fully threaded, while larger sizes may be partially threaded in accordance with industry standards and performance requirements.
Socket Head Cap Screws are widely used in machinery assembly, automotive applications, aerospace, robotics, and other engineered products where strength, precision, and compact installation are necessary. They are particularly useful in countersunk or flush applications because their small head profile allows them to sit neatly in place without requiring excess clearance.
The advantages of using Socket Head Cap Screws are considerable. Their high tensile strength makes them more durable and reliable under heavy loads. Their recessed drive style allows installation in compact or recessed areas while also providing better torque transmission and reducing the risk of cam-out compared to slotted or Phillips head fasteners. They also create a clean, streamlined appearance, which is valued in many engineered products.
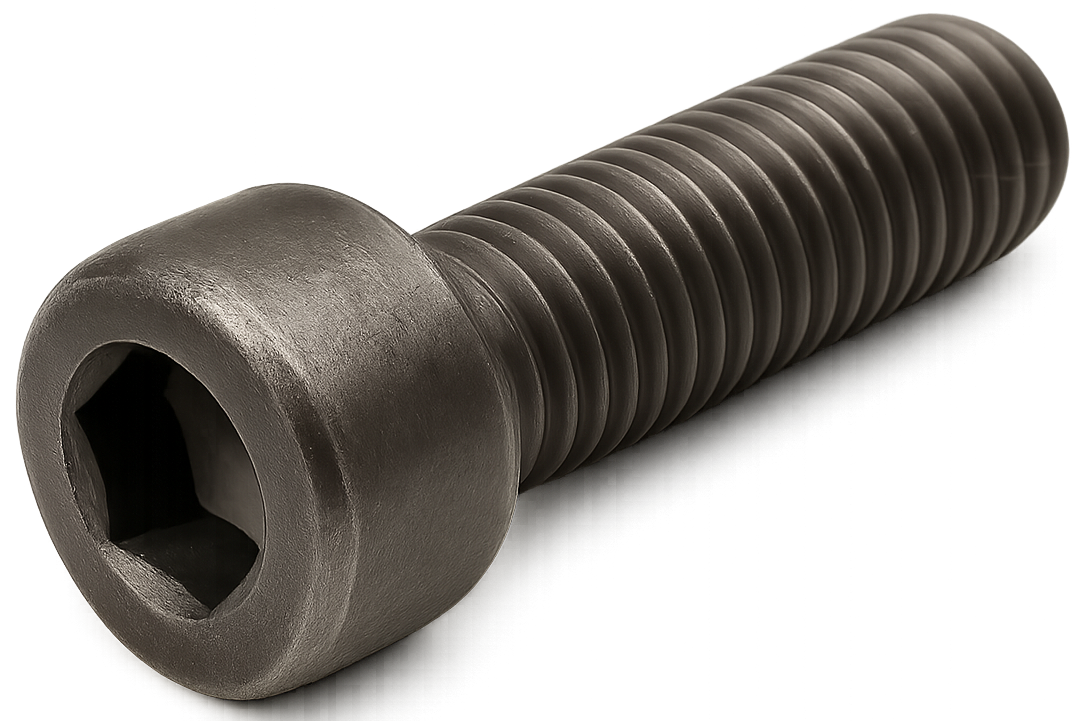

Solid Rivets
A solid rivet is a type of mechanical fastener used to permanently join two or more pieces of material together.
Spade-Head Thumb Screw
A spade-head thumb screw is a hand-tightened machine screw whose head is a single flat “paddle” (the spade) projecting from a short round boss. The spade gives your fingers a broad, low-profile surface to pinch and turn, so you can tighten and release the screw without tools. Compared with a knurled-head thumb screw it offers more leverage; compared with a wing-head it occupies less space and is less likely to snag, which is useful where fasteners sit close together, near panels, or in recessed pockets.
Spade-head thumb screws use standard machine threads (inch UNC/UNF or metric) and install into tapped holes or mate with a nut. Length is measured from under the head to the thread end, and some versions include an unthreaded shoulder or a captive washer to provide a smooth bearing surface on panels. Common materials are zinc-plated steel for general use, stainless steel (A2/A4) for corrosion resistance, and brass or nylon where non-marring or non-sparking characteristics are helpful. Many catalogs follow ASME B18.6.8 for inch-series thumb/wing screws; the spade head is one of the common thumb-screw head forms offered to those proportions.
Like all thumb screws, spade-head versions are intended for tool-free, moderate clamping—think guards, covers, jigs, fixtures, and access panels—rather than high-preload or vibration-critical joints. For better retention, users often add a flat washer, lock washer, nylon-insert nut, or a thread-locking patch, and they choose materials/finishes that suit the environment. In short, a spade-head thumb screw trades the maximum torque of a two-wing head for a compact, sleek tab that’s easy to grip and ideal where clearance is tight.
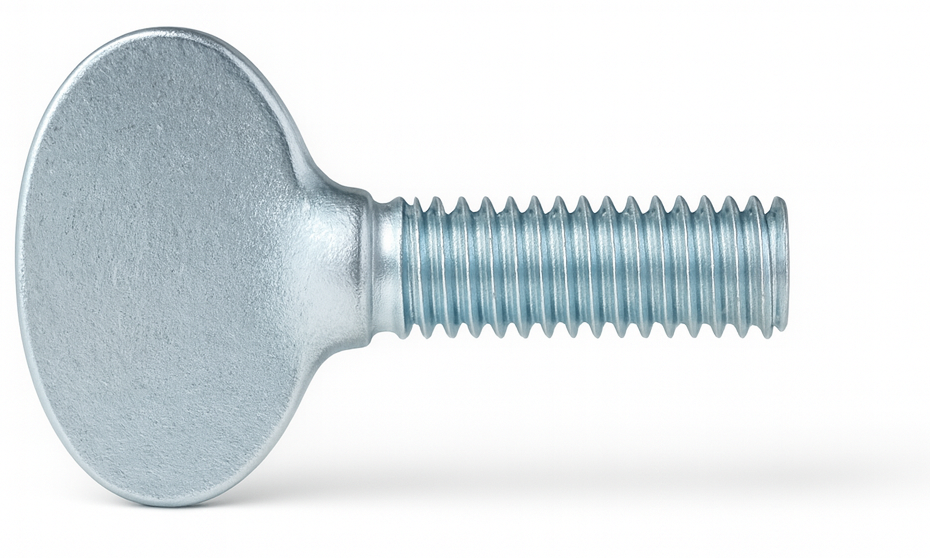
Spanner Screw
A Spanner screw, also known as a Snake-Eye screw, is a tamper-resistant fastener distinguished by its head design, which features two small round holes instead of a traditional slot or cross recess. It requires a special spanner driver with two matching pins for installation and removal, making it difficult to manipulate with standard tools.
These screws are commonly used in public fixtures, electronics, and environments prone to vandalism—such as restrooms, elevators, and playground equipment—where extra security is needed. While they deter casual tampering, they are not entirely foolproof since the drivers are commercially available, so they’re best described as tamper-resistant rather than tamper-proof.
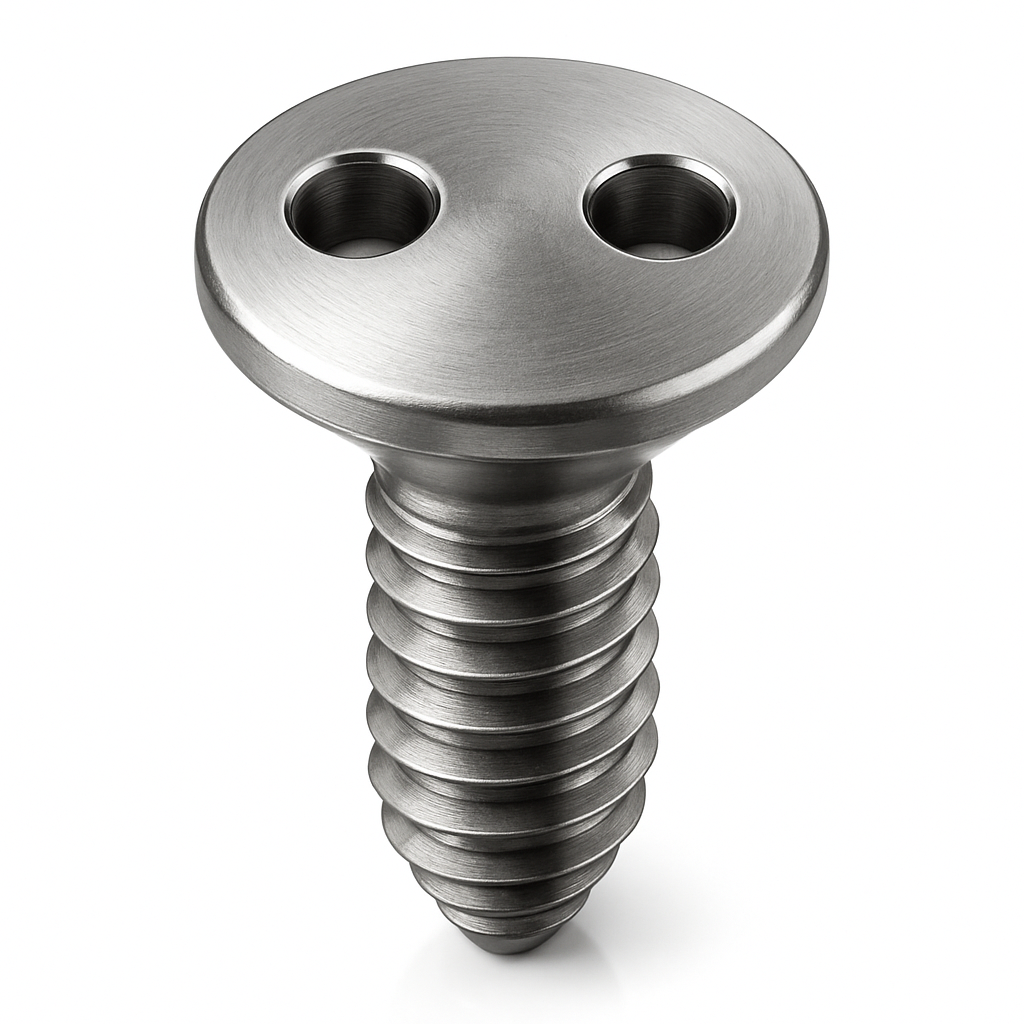

Spindle Clamp Nut
A spindle clamp nut is a specialized fastener used to secure cutting tools, grinding wheels, or other rotating components to a spindle in machine tools, grinders, CNC equipment, and similar machinery. It ensures that the tool remains firmly fixed during high-speed operation while still allowing for relatively quick installation and removal when tools need to be changed.
In terms of design and construction, a spindle clamp nut is typically circular with a threaded inner bore that matches the spindle threads. The exterior of the nut is shaped with spanner wrench slots, flats, or other gripping profiles so that it can be tightened or loosened with the proper tool. Many designs also feature a clamping mechanism—such as a split collar, spring-loaded section, or locking feature—that provides additional grip and prevents the nut from backing off under vibration. They are most often made from hardened steel or alloy steel to endure the repeated tightening and stresses of high-speed rotation.
The purpose and function of a spindle clamp nut are centered on securing tooling in place with strength and precision. By clamping the tool holder, wheel, or cutter against the spindle face, the nut ensures that the tool runs true, minimizes vibration, and prevents dangerous loosening. In high-precision applications, clamp nuts are manufactured with tight tolerances and are sometimes balanced to reduce runout, which improves accuracy and surface finish in machining or grinding operations.
Spindle clamp nuts have common applications across various industries. They are used in milling machines and CNC machining centers to secure tool holders and cutters, in grinding machines to fasten grinding wheels, in woodworking and routers to hold bits in place, and in other industrial equipment where rotating tools must be firmly secured. Their reliability makes them critical for both metalworking and woodworking environments.
The advantages of spindle clamp nuts include their ability to provide strong, secure tool retention even at high rotational speeds. They resist loosening under vibration, can be reused many times, and in some designs, enable fast tool changes that improve shop efficiency. Their construction makes them essential for safety, as a loose cutting tool or wheel could cause catastrophic damage or injury.
However, there are also limitations. They must be matched carefully to the spindle thread size and design to ensure proper fit. Many require specific spanner wrenches or other tools for tightening and removal, which adds to the handling process. If installed incorrectly, a spindle clamp nut can cause imbalance or vibration that reduces precision and tool life. Precision clamp nuts, especially those designed for high-speed CNC applications, are also more expensive than standard fastening alternatives.
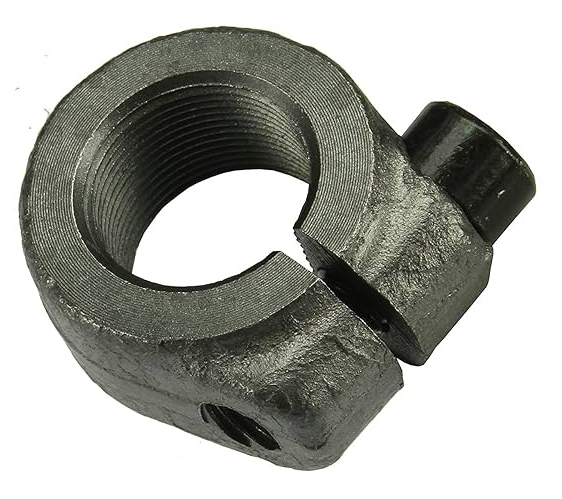

Split Drive Anchor
Flat Head Split Drive Anchors offer easy installation and are used in various building materials, such as concrete, brick, mortar, and cement blocks. This fastener is installed into a pre-drilled hole and driven into place using a hammer. A wedging action is created by the crimped f ins on the working end of the fastener, which engages with the walls of the pre-drilled hole, resulting in a secure bond and f lush mounting. With six popular lengths available, Earnest makes it easy to f ind the size needed for your next project.
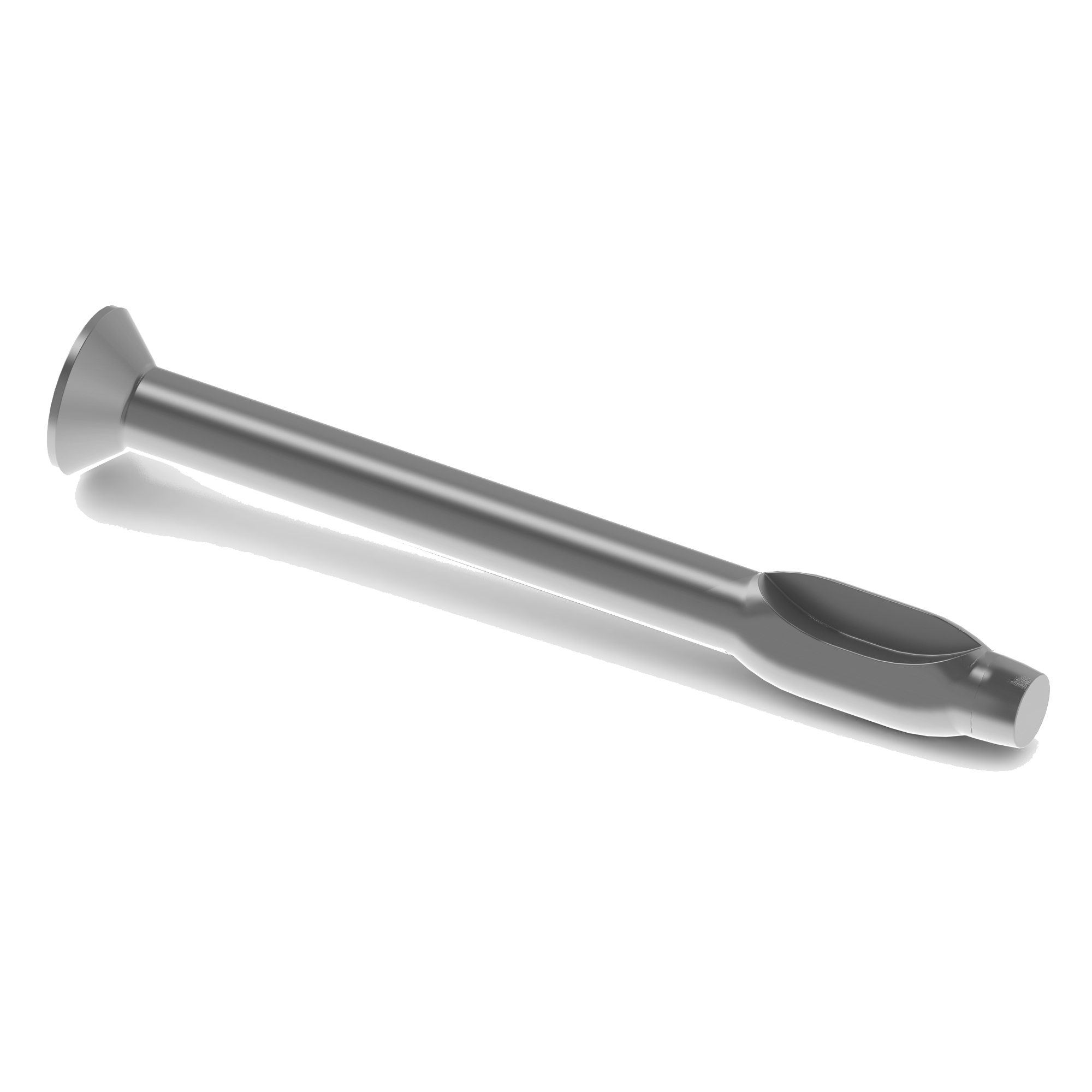
Split Lock Washer
A split lock washer, also known as a spring lock washer, is a type of washer designed to prevent nuts and bolts from loosening due to vibration or torque. It features a helical (split-ring) shape, meaning the washer is cut at one point and slightly twisted so that it exerts a spring-like tension when compressed under a fastener.
When a bolt or nut is tightened against a split lock washer, the sharp edges of the split section dig into the mating surfaces — one edge bites into the underside of the fastener, and the other grips the surface of the material being fastened. This creates friction and tension that help resist rotation, keeping the fastener secure even under vibration or thermal expansion.
Split lock washers are commonly made from hardened steel, stainless steel, or spring steel, and are used in machinery, automotive, and construction applications where vibration is present.

Split Rivet
A split rivet is a type of mechanical fastener designed for joining thin materials such as sheet metal, leather, plastic, or wood. Unlike solid rivets, a split rivet has a slotted or split shank that separates into two legs when inserted and spread apart during installation, anchoring the materials together.
When driven into a pre-drilled hole, the split shank flexes and spreads outward as pressure is applied—either with a hammer, a rivet press, or by pulling the legs apart. This expansion creates a mechanical lock on the blind side of the assembly, holding the materials tightly together without the need for access to both sides in some cases.
Split rivets are commonly made from soft metals such as aluminum, brass, or copper, and are often used in light-duty applications like attaching tags, nameplates, hinges, or trim pieces. They’re not designed for high-strength or structural loads but are valued for their ease of installation, low cost, and secure hold in thin or soft materials.
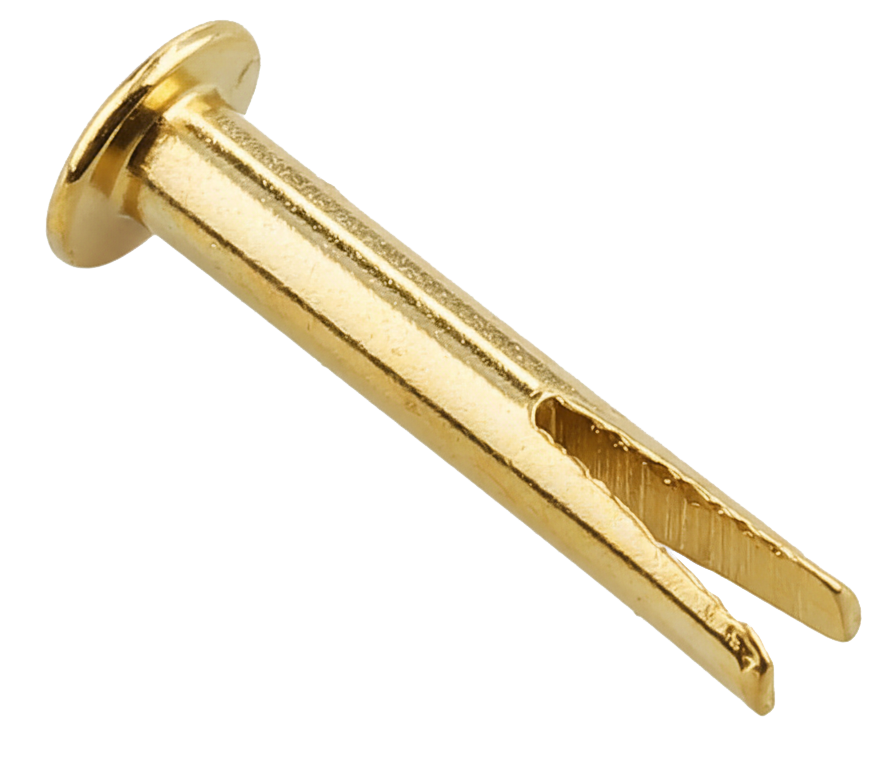

Spring Bar
A spring bar is a small, spring-loaded metal rod commonly used in watches, jewelry, and some light mechanical assemblies to connect parts that need to be both secure and removable.
In wristwatches, spring bars are the tiny cylindrical bars that attach the watch strap or bracelet to the watch case. Each end of the bar has a spring-loaded pin that retracts when you push it inward with a tool. Once the pressure is released, the pins expand back outward, locking into the lug holes of the watch case. This design allows straps to be swapped quickly while keeping them firmly in place during regular use.
Spring bars are typically made of stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance. They come in a variety of lengths and thicknesses to match different watches and straps, and some are double-flanged or quick-release for easier handling.
Beyond watches, the same principle can be found in other applications where a secure but removable pivot or connector is needed—using the internal spring to keep the bar in place under tension.
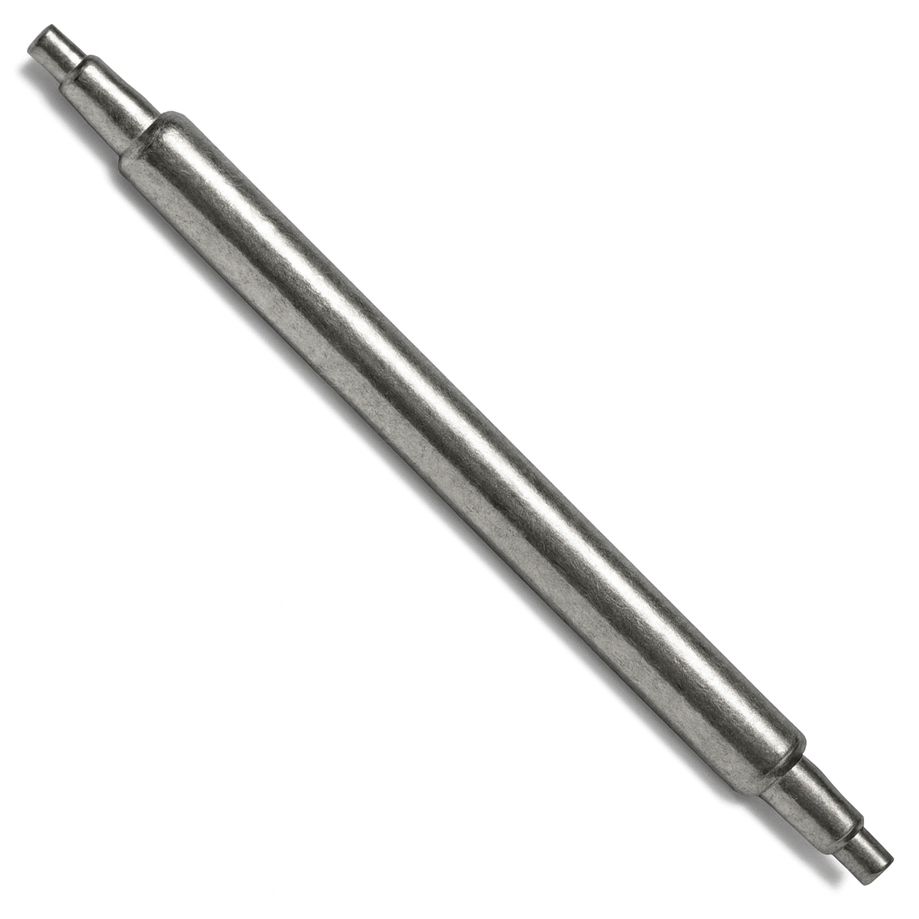

Square Head Bolt
Square Head Bolts have been a staple in the locomotive industry for generations. In addition to aesthetic appeal, the square head provides a wider surface area to distribute clamping loads. Earnest provides bolts in Grades 5 and 8 for durability and strength. Get modern strength with a classic look.
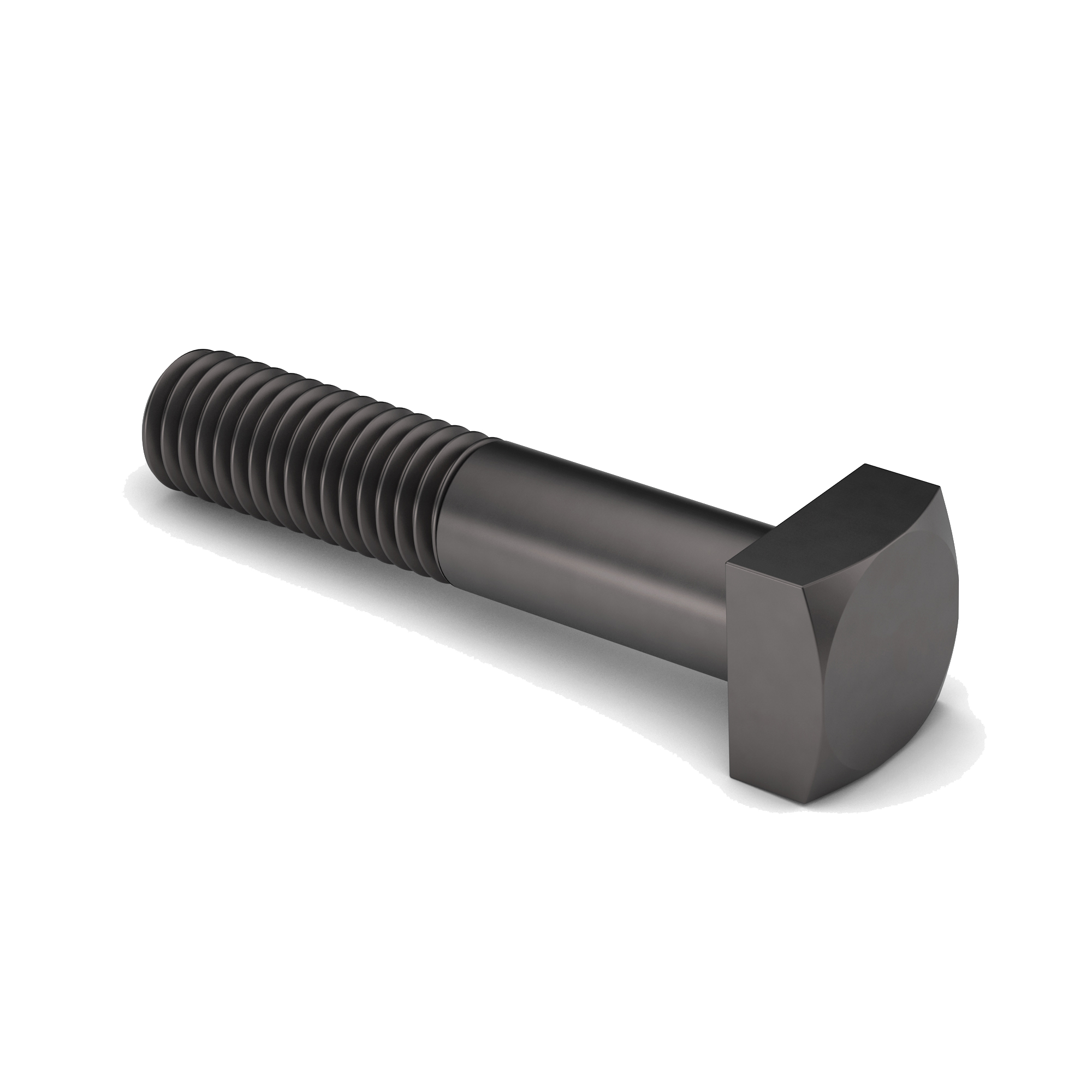

Square Washer
A square washer, also known as a square plate washer or construction square plate washer, is a flat washer with a square or rectangular shape. Unlike the more common round washers, square washers offer distinct advantages in specific applications, particularly in heavy-duty and structural contexts.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a corrosion-resistant alloy of iron that contains a minimum of 10.5% chromium (Cr) by mass, along with varying amounts of carbon, nickel, molybdenum, and other elements. The presence of chromium is what gives stainless steel its defining property — the ability to form a thin, invisible layer of chromium oxide on its surface when exposed to oxygen. This layer, known as the passive film, protects the metal beneath from rust and oxidation, and it self-heals if scratched or damaged.
Stainless steel is both strong and durable, with excellent resistance to corrosion, heat, and chemical attack, which makes it one of the most versatile materials in modern engineering, manufacturing, and architecture. Its composition can be modified to enhance certain properties — for example, adding nickel improves ductility and toughness, while molybdenum increases resistance to acids and chlorides (such as in seawater or salt-rich environments).
There are several major categories of stainless steel, each with distinct characteristics:
- Austenitic stainless steels (e.g., 304, 316): The most common type, containing high levels of chromium and nickel. They are non-magnetic, highly formable, and extremely corrosion-resistant. Grade 304 is widely used in kitchen equipment and architecture, while 316 includes molybdenum for added marine and chemical resistance.
- Ferritic stainless steels: Contain chromium but little or no nickel. They are magnetic, less ductile, and typically used in automotive exhaust systems and appliances.
- Martensitic stainless steels: Have higher carbon content, allowing them to be hardened by heat treatment. They are used for cutting tools, blades, and fasteners.
- Duplex stainless steels: Combine austenitic and ferritic structures for greater strength and stress corrosion resistance, often used in chemical plants and pipelines.
- Precipitation-hardening stainless steels: Can be heat-treated to very high strengths, used in aerospace and high-performance applications.
Stainless steel’s appeal lies not only in its performance but also in its aesthetic and hygienic qualities. Its smooth, reflective surface resists staining and bacterial buildup, making it ideal for food processing, medical instruments, architecture, and consumer products.

Stamping
A manufacturing process that shapes or cuts metal by pressing it with a die. In fastener production, stamping is used to create features like heads, slots, or markings quickly and precisely from sheet metal or wire.
Strength Level
The measure of how much force a fastener can withstand before it begins to deform or break. In fasteners, strength level indicates how well the material performs under load and stress. It is usually defined by standardized properties such as tensile strength and yield strength.
Stripped Threads
Threads on a fastener or inside a hole that have been damaged, worn down, or torn away, preventing proper engagement. Stripped threads cause loose or insecure fastening, reducing the strength and reliability of the connection.
Structural Bolt
A structural bolt is a specialized type of bolt designed for use in structural applications, primarily in steel-to-steel connections in buildings, bridges, and other structures where safety and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Stud
A stud is a type of fastener that consists of a long, threaded rod used to securely join two or more components in construction, manufacturing, and heavy machinery applications. Unlike bolts, industrial studs typically do not have a head and are secured using nuts on both ends or by threading into a tapped hole.
Sulfur
Sulfur is a nonmetallic chemical element (symbol S, atomic number 16) known for its bright yellow color, distinctive smell when burned, and essential role in both industrial processes and biological systems. It is abundant on Earth, occurring naturally in minerals like pyrite, gypsum, and galena, as well as in volcanic regions where elemental sulfur can form large deposits. In its pure form, sulfur is brittle, crystalline, and odorless—its characteristic “rotten egg” smell actually comes from hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), a sulfur-containing gas.
Industrially, sulfur is extremely important. It is used to produce sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), one of the most widely manufactured chemicals in the world and a key ingredient in fertilizers, battery acids, petroleum refining, mineral processing, wastewater treatment, and chemical synthesis. Sulfur is also used in vulcanizing rubber, improving durability and elasticity in tires and industrial elastomers. It appears in pharmaceuticals, fungicides, matches, gunpowder, dyes, and detergents, and plays a role in metal ore processing and mining.
In metallurgy and fasteners, sulfur is intentionally added in small amounts to steels—especially free-machining steels—because it forms manganese sulfide (MnS) inclusions that help break chips and improve machinability. However, sulfur can also reduce weldability and toughness if not properly controlled, particularly in structural steels or components subjected to high stresses.
Biologically, sulfur is essential for life. It appears in amino acids like cysteine and methionine, in vitamins, in proteins, and in metabolic processes. It is part of the natural sulfur cycle, circulating through the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms.

Superalloy
A superalloy is a high-performance metallic alloy engineered to maintain exceptional strength, toughness, and stability at high temperatures—often above 1000°C (1832°F)—while resisting creep, corrosion, and oxidation. These materials are specifically designed for environments where conventional metals like steel or aluminum would quickly weaken, deform, or oxidize.

Superalloys are typically based on three primary metals: nickel, cobalt, or iron (or combinations of them). Of these, nickel-based superalloys are the most widely used because of their outstanding performance under both mechanical and thermal stress. The alloys achieve their remarkable properties through a combination of precise chemical composition and complex microstructural strengthening mechanisms.
Their key alloying elements include:
- Chromium (Cr) – enhances oxidation and corrosion resistance.
- Cobalt (Co) – stabilizes the microstructure and improves strength at high temperatures.
- Molybdenum (Mo), tungsten (W), and tantalum (Ta) – increase creep resistance.
- Aluminum (Al) and titanium (Ti) – form strengthening precipitates known as γ′ (gamma-prime) phases in nickel-based alloys, which give superalloys their superior heat strength.
- Niobium (Nb) – further improves strength and stability in alloys such as Inconel 718.
Superalloys are produced through advanced metallurgical techniques like vacuum induction melting (VIM), vacuum arc remelting (VAR), and powder metallurgy, which ensure purity and precise control over grain structure. Some are precipitation-hardened, meaning they gain strength from fine, stable particles distributed throughout the metal that block dislocation movement at high temperatures.
These alloys are critical in industries where materials must withstand extreme thermal, chemical, and mechanical conditions. They are used in jet and rocket engines, gas turbines, nuclear reactors, chemical processing plants, and marine and oil drilling equipment. For example, turbine blades in jet engines—arguably one of the most demanding engineering components—are often made of single-crystal nickel-based superalloys to eliminate grain boundaries and prevent creep.
Superconductivity
Superconductivity is a phenomenon in which a material, when cooled below a certain critical temperature, suddenly loses all electrical resistance and allows electric current to flow indefinitely without any energy loss. At the same time, the material also expels magnetic fields from its interior—a property known as the Meissner effect. Together, these two characteristics define a superconducting state, a unique quantum mechanical condition of matter.
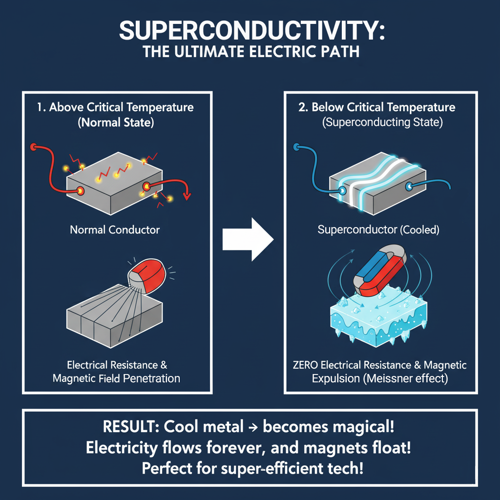
In a normal conductor like copper or aluminum, electrical resistance arises because moving electrons collide with atoms and imperfections, converting some electrical energy into heat. However, in a superconductor, once the material is cooled below its critical temperature (Tc), these collisions effectively disappear. The electrons pair up into what are called Cooper pairs, named after physicist Leon Cooper. These paired electrons move through the atomic lattice in a coordinated quantum state, which allows them to flow without scattering—hence, without resistance.
The Meissner effect is equally remarkable: when a material becomes superconducting, it actively expels magnetic fields from its interior, causing a magnet to levitate above it. This happens because the superconductor generates surface currents that exactly cancel the applied magnetic field within the material. This behavior distinguishes superconductors from mere perfect conductors, since the Meissner effect demonstrates a true phase change in the material’s electromagnetic properties.
Superconductivity occurs in a range of materials, including pure metals like mercury (the first discovered superconductor, in 1911 by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes), metal alloys, and ceramic high-temperature superconductors. Traditional (low-temperature) superconductors, such as lead or niobium-titanium, require cooling with liquid helium to temperatures near absolute zero (around 4 K). High-temperature superconductors—such as yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO)—can operate at higher critical temperatures, around 77 K, allowing cooling with liquid nitrogen, which is more economical and practical.
Superconductors have profound technological applications. They are essential in MRI machines, maglev trains, particle accelerators, fusion reactors, and superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs) used for ultra-sensitive magnetic field detection. They are also being researched for lossless power transmission, high-efficiency motors, and quantum computing.
Superelasticity
Superelasticity (also called pseudoelasticity) is a material behavior where a metal can undergo very large, reversible strains and then return to its original shape upon unloading, without permanent deformation. Unlike ordinary elasticity (where reversible strain is small and proportional to stress), superelasticity comes from a stress-induced phase transformation rather than simple stretching of atomic bonds.
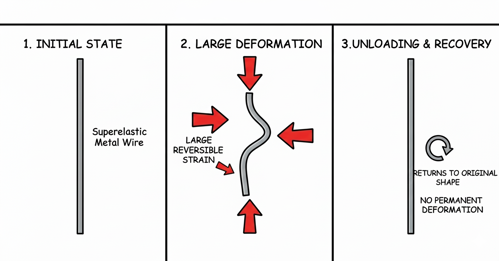
It is most strongly associated with shape memory alloys, especially nickel-titanium (NiTi / Nitinol). Under load at a temperature where the alloy is in the austenite phase, the material transforms to martensite as stress increases, allowing substantial strain at nearly constant stress (a characteristic plateau). When the load is removed, the martensite transforms back to austenite and the strain is recovered, producing a distinct hysteresis loop on the stress–strain curve.
In industrial hardware contexts, superelastic NiTi is used when you want parts that can flex repeatedly without taking a set, maintain contact force over movement, or tolerate deformation during installation—examples include certain clips, springs, retaining components, and specialty fastener-like devices. Its practical limits depend on alloy composition, temperature, and design; outside the superelastic temperature window or if overstressed, the material can still permanently deform or fatigue like other metals.
Superfinishing
Superfinishing is a precision surface finishing process used to improve the smoothness, accuracy, and performance of metal parts beyond what conventional grinding or polishing can achieve. It involves the use of fine abrasive stones or tapes that lightly rub against the workpiece under controlled pressure while the part is oscillated or rotated. This removes only a very thin layer of material—measured in microns—but it eliminates surface irregularities, reduces roughness, and creates a highly refined finish.

The key benefit of superfinishing is that it produces surfaces with extremely low roughness and high dimensional accuracy. Unlike standard polishing, which can leave directional scratches or waviness, superfinishing produces a uniform crosshatch pattern that helps retain lubrication on the surface. This makes it especially useful in components subject to friction, wear, or rolling contact.
Common applications include engine components such as crankshafts, camshafts, gears, and bearings, as well as aerospace and precision tool parts. Superfinished surfaces reduce friction and heat buildup, extend component life, improve load-bearing capacity, and enhance fatigue resistance.
In the context of fasteners and mechanical assemblies, superfinishing may be applied to high-performance bolts, shafts, or washers where smooth, uniform surfaces are critical for reducing wear, improving fatigue strength, or preventing premature failure under high loads.
Surface Discontinuities
Irregularities or imperfections found on the surface of a fastener that may affect its performance or appearance. These can include cracks, seams, laps, folds, pits, or scratches and are typically caused by issues during forming, machining, or handling. Surface discontinuities are evaluated against industry standards to determine if they are acceptable or if they compromise the integrity of the part.

