Resources
Glossary
Partial Thread
A partial thread fastener is one where the threads only cover a portion of the shank, leaving a smooth, unthreaded section (called the grip length) between the head and the threaded portion. This is the opposite of a full thread fastener, where the threads run the entire length.

Passivation
Passivation is a chemical process used to improve the corrosion resistance of metals, especially stainless steel and other alloys. Even though stainless steel already contains chromium, which naturally forms a thin oxide layer that protects it from rusting, the surface can still be contaminated with free iron or other impurities during machining, forming, or handling. These contaminants can make the metal more vulnerable to localized corrosion if not removed.
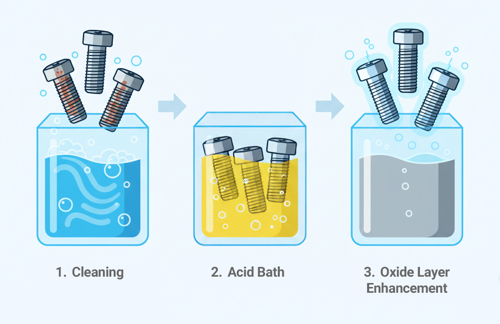
The passivation process typically involves immersing the metal in an acid solution, most commonly nitric acid or citric acid. The acid removes free iron and other foreign materials from the surface without significantly attacking the underlying metal. Once the surface is cleaned, oxygen from the air reacts with the chromium in the steel to form a stable, uniform, and self-repairing chromium oxide layer. This thin passive film serves as a barrier that greatly reduces the rate of corrosion.
In the context of fasteners, passivation is essential because bolts, nuts, and screws are often exposed to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments where corrosion resistance is critical. By undergoing passivation, stainless steel fasteners gain improved durability and maintain their structural integrity and appearance over longer service lives.
Passivation has advantages, including enhancing corrosion resistance, extending component life, and improving cleanliness without altering part dimensions or strength. However, it also has limitations: it cannot restore heavily corroded parts, requires strict control of process conditions, and is only effective on alloys that contain sufficient chromium to form the protective oxide layer.
Article: Understanding Passivation in Stainless Steel Fasteners
Pearlite
Pearlite is a lamellar (layered) microstructure found in steels and cast irons, consisting of alternating thin plates of ferrite (soft, ductile iron) and cementite (hard iron carbide, Fe₃C). It forms when austenite (γ-iron) of eutectoid composition (0.76% carbon) cools and transforms at about 727°C (1341°F) during the eutectoid reaction:
Austenite(γ) → Ferrite(α) + Cementite(Fe3C)
Pearlite gets its name because the alternating light and dark layers resemble mother-of-pearl under a microscope. Its mechanical properties fall between those of its two components—stronger and harder than ferrite, but more ductile than cementite.
Key characteristics of pearlite:
- Formed through the eutectoid decomposition of austenite in steel.
- Appears as fine, alternating layers of ferrite and cementite.
- The spacing of the layers (lamellar spacing) determines hardness—fine pearlite is harder and stronger than coarse pearlite.
- Found in carbon steels, ductile irons, and some cast irons, often making up a large portion of their microstructure.
Mechanical significance:
Pearlite provides an excellent balance of strength, hardness, and toughness, so steels containing a high percentage of pearlite (like rail steels, prestressed wires, and springs) are used in applications demanding high wear resistance and moderate ductility. In contrast, steels with less pearlite and more ferrite are softer and more formable.
Pentalobe Screw
A pentalobe screw is a tamper-resistant fastener with a five-lobe, flower-shaped drive. It was popularized by Apple and is used where manufacturers want to discourage casual disassembly. The head’s five rounded lobes require a matching pentalobe driver—standard Phillips/Torx bits won’t fit—so it offers light security while maintaining good torque transfer.
Where you’ll see it: phones and laptops (notably iPhone and MacBook bottom cases, batteries, and trackpads), compact electronics, and some accessories.
Common sizes: P2 ≈ 0.8 mm (iPhone), P5 ≈ 1.2 mm (MacBook bottom case), P6 ≈ 1.5 mm (some older MacBooks/assemblies). Note: naming can vary by vendor, but these three sizes cover most electronics.

Permanent Fasteners
Components designed to create a connection between two or more parts that are intended to be fixed and generally not removed without damaging either the fastener itself or the joined materials. Unlike temporary fasteners (e.g., most nuts and bolts), permanent fasteners are typically designed for single-use applications. Examples include rivets, nails, and specialized tamper-proof screws designed to resist removal.
Phase Distribution Equilibria
Phase distribution equilibria refers to the stable balance, under given conditions of temperature, pressure, and composition, between the different phases (solid, liquid, gas, or distinct solid structures) present in a material or system. It describes how the material’s components are partitioned among these phases when the system has reached thermodynamic equilibrium—meaning no further net change occurs in how the phases are distributed.
In metallurgy and materials science, this concept is critical for understanding alloys. For example, in a steel alloy at a certain temperature, some portion of the iron may exist as ferrite while another portion exists as austenite. The phase distribution equilibria describes what fraction of the total material is in each phase, and how the chemical elements are shared between them. The equilibrium state is governed by thermodynamic principles, often represented using phase diagrams, which map out which phases are stable at different combinations of temperature, pressure, and composition.
This equilibrium is important because it determines a material’s microstructure, and therefore its mechanical and physical properties. By controlling heat treatment, cooling rates, and alloy composition, engineers manipulate phase distribution equilibria to achieve desired outcomes—such as hardness, ductility, corrosion resistance, or toughness.
In chemistry more broadly, phase distribution equilibria also applies to systems like liquid–liquid extraction, gas–liquid absorption, or multiphase reactions, where it governs how solutes or compounds partition themselves between two immiscible phases.
Phillips Pan Hd Machine Screw
A Phillips Pan Head Machine Screw is a type of screw designed for precision assembly in metal, plastic, or wood. It features a Phillips drive, a pan-shaped head, and a uniform thread along its shaft. These screws are typically used in machinery, electronics, and hardware applications, where reliable fastening is required.
Phosphate and Oil (Phos & Oil)
Phosphate and oil is a two-step finish applied to steel fasteners to improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction during installation. The process begins with a phosphate conversion coating, usually zinc or manganese phosphate, which creates a textured, matte surface. A light oil is then applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aid in handling.
Appearance - Phos & Oil fasteners typically have a dark gray to black matte finish with a slightly oily feel.
Photochemical Machining
Photochemical machining (PCM), also known as photo etching or chemical milling, is a precision manufacturing process that removes metal using light-sensitive photoresists and chemical etchants. It combines principles of photolithography—used in semiconductor and printed circuit board manufacturing—with controlled chemical corrosion to create detailed, burr-free metal parts. The process is especially useful for producing thin, intricate, or delicate components that would be difficult or costly to machine mechanically.
The process begins by cleaning and preparing a metal sheet such as stainless steel, copper, nickel, brass, or titanium. A photoresist, a light-sensitive polymer, is then applied to both sides of the metal. A photomask containing the component’s design is aligned over the sheet and exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, hardening the resist in the pattern of the part. The unexposed or softened areas of resist are chemically removed, exposing the metal to be etched. The exposed areas are then chemically dissolved in an etchant bath—most commonly ferric chloride (FeCl₃) or cupric chloride (CuCl₂)—while the hardened resist protects the remaining metal. For example, with ferric chloride, the reaction can be represented as FeCl₃ + Fe → 2FeCl₂, showing how the etchant consumes the exposed metal. Once etching is complete, the resist is stripped away, leaving behind the finished part.
Because the process uses no mechanical cutting, no stress, burrs, or deformation occur, allowing for extremely fine tolerances—often within ±0.01 mm. It’s also fast to prototype, since tooling involves only digital mask production rather than expensive hard dies. PCM can be applied to hard-to-machine metals and thin sheets that would warp under conventional machining, making it ideal for parts requiring delicate geometry or tight tolerances.
Industrially, photochemical machining is used across a wide range of fields. In electronics, it produces lead frames, EMI shields, and connectors; in aerospace, it’s used for filters, fuel cell plates, and turbine shims; in medical manufacturing, it’s used for stents and fine surgical components; and in automotive and optical industries, it’s used for injector plates, screens, meshes, and watch components.
AKA: Photo Etching
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a versatile family of thin film deposition processes used to produce high-purity, high-performance coatings on a wide variety of substrates, including metals, ceramics, and polymers. It is fundamentally a physical process where material transitions from a condensed, solid phase into a vapor phase, and then is transported and allowed to condense back into a thin, solid film on a cooler substrate surface, all while operating within a high-vacuum environment. This method is distinct from chemical vapor deposition (CVD) because it relies on physical means, such as heat or bombardment, to generate the vapor rather than chemical reactions.

The overall PVD process typically involves four steps: first, Ablation/Vaporization, where the solid source material (the "target") is vaporized, often through techniques like Sputter Deposition (where ions from a plasma knock atoms off the target) or Thermal Evaporation (where the target is heated until it vaporizes). Second, the vaporized material is Transported across the vacuum chamber to the substrate. Third, in an optional but common step, the vapor may undergo a Reaction with an ambient gas (like nitrogen) to form a compound coating such as titanium nitride (TiN). Finally, the vaporized atoms Condense onto the substrate, forming the desired thin film.
PVD coatings offer significant advantages, including superior hardness, wear resistance, high corrosion resistance, and excellent adhesion to the substrate. Most coatings are highly durable and are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional plating methods. This makes PVD a popular choice for high-performance applications across various industries, such as coating cutting tools to extend their life, enhancing aerospace and automotive components, and creating specialized films for semiconductor devices, optics, and decorative finishes.
Pig Iron
Pig iron is the crude, high-carbon form of iron that is produced as the first product of smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. It serves as the primary raw material for making both cast iron and steel. The term “pig iron” comes from the traditional shape of the ingots cast in sand molds: molten iron was poured into a central channel (the “runner”) with smaller branching molds that resembled piglets nursing from a sow—hence the name.

Pig iron typically contains 3.5–4.5% carbon, along with 1–3% silicon, 0.5–1% manganese, and small amounts of sulfur and phosphorus. This high carbon content makes pig iron hard and brittle, meaning it cannot be used directly for most structural or mechanical applications. However, it’s an essential intermediate material—a starting point for refining into more useful forms of iron and steel.
The process of producing pig iron begins with the blast furnace, where a mixture of iron ore (usually hematite or magnetite), coke (carbon source), and limestone (flux) is heated to temperatures of around 1,500–2,000°C (2,700–3,600°F). Inside the furnace, several key reactions take place:
1.The coke burns in the presence of air, producing carbon monoxide (CO):
C+O2→CO2
and then
CO2+C→2CO
2. The carbon monoxide reduces the iron ore (Fe₂O₃ or Fe₃O₄) to metallic iron:
Fe2O3+3CO→2Fe+3CO2
3. The limestone (CaCO₃) acts as a flux, combining with impurities like silica to form slag, which floats on top of the molten iron.
The result is a molten pool of pig iron at the bottom of the furnace, which is periodically drained and cast into ingots or transported in molten form for further processing.
There are several grades of pig iron, depending on composition and intended use:
- Basic pig iron, for conversion into steel in basic oxygen furnaces.
- Foundry pig iron, used directly for making cast iron products.
- High-phosphorus pig iron, used in certain specialized chemical processes.
Pig iron on its own is too brittle for shaping or forming, but when remelted and refined to reduce carbon and impurities, it becomes steel; when remelted with additional carbon and silicon, it becomes cast iron.
Pigtail Eye Bolt
A pigtail eye bolt is a specialized type of fastener with a unique design. It's essentially a bolt with a threaded end and a distinctive "pigtail" or spiral-shaped loop at the other end. This pigtail end allows for the attachment and suspension of various items or cables, even when access to their ends is limited.
Pin Wrench
A pin wrench is a specialized hand tool used for tightening and loosening round nuts, collars, or fittings that have drilled holes, slots, or notches instead of hexagonal surfaces. Unlike conventional wrenches, which grip flat faces, a pin wrench uses one or more hardened pins to engage with the holes or slots, allowing the user to apply torque without slipping or damaging the component. This makes the tool essential for applications where round fasteners are common.
In terms of design and construction, a pin wrench consists of a strong handle made from steel or alloy material, with hardened steel pins extending from one end. These pins are sized to fit into the holes of the fastener or collar. The wrench may be a fixed type, with set pin spacing for a specific size of nut, or an adjustable type, which allows the pins to slide to different positions to cover a wider range of sizes. The hardened pins resist wear and provide reliable engagement under repeated use.

The purpose and function of a pin wrench are to apply torque to specialized fasteners that cannot be turned with ordinary tools. By engaging directly in the holes or slots, the wrench prevents slippage and ensures even torque distribution, protecting both the tool and the part being adjusted. This makes pin wrenches particularly effective in precision assemblies where damage to the fastener would compromise performance.
Common applications of pin wrenches include machine tools, where they are used to secure or remove spindle nuts, collet nuts, and locknuts on grinders and milling machines. In plumbing and piping systems, they are used on round fittings, gland nuts, or retaining rings. In automotive and aerospace industries, they are applied to specialty fittings such as shock absorber nuts, wheel bearing retaining nuts, and slotted fasteners. They are also widely used in bicycles and motorcycles, especially for bottom brackets, headsets, and suspension components.
The advantages of a pin wrench include secure engagement with specialized fasteners, protection of delicate surfaces from damage, and versatility in the adjustable models that can handle multiple sizes with a single tool. Their precision makes them indispensable for maintaining equipment with round or slotted fittings.
However, there are also limitations. Pin wrenches are limited to use on fasteners with drilled holes, slots, or grooves and cannot be applied to standard hex bolts or nuts. The pins themselves can shear if excessive torque is applied, and using the wrong size or spacing can lead to poor engagement. Proper matching of pin size and fastener design is critical for safe use.
Pinion Shaft Bolt
A pinion shaft bolt is a critical fastener used inside a differential assembly to secure the pinion shaft (also called the cross shaft or spider gear shaft) in place within the differential carrier. The pinion shaft itself supports the spider gears, which allow the vehicle’s left and right wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.

The pinion shaft bolt locks this shaft firmly in position so that it cannot slide out of alignment or rotate independently. Without it, the spider gears would lose support, leading to catastrophic gear failure or even complete differential destruction.
Function and Design
The bolt passes through a small retaining hole in the carrier and threads into a cross shaft bore in the differential. Once tightened, it secures the pinion shaft axially, keeping it from drifting out under torque and vibration.
It is typically:
- Small in diameter but very high in strength, usually Grade 8 or higher, since it experiences significant shear forces.
- Made from hardened alloy steel with a phosphate or black oxide coating to resist corrosion.
- Equipped with fine threads for maximum holding power and sometimes threadlocker to prevent loosening from vibration.
Common Applications
Pinion shaft bolts are found in most automotive rear- and front-wheel-drive differentials, including those from GM, Ford, Chrysler, and Dana/Spicer axles. Despite their small size, they are known to be a weak point in some differentials—if overtightened or reused, they can shear off or back out, causing the pinion shaft to walk out and strike the ring gear or housing. For that reason, these bolts are always replaced during a differential rebuild or gear service.
Pitch Diameter
The pitch diameter of a thread is the imaginary diameter of a cylinder that passes through the threads at the point where the width of the thread ridge (the crest to the flank) and the width of the thread groove (the flank to the root) are exactly equal. In other words, it’s the “midpoint” between the major diameter (the outer crest) and the minor diameter (the inner root) of the thread profile.
Unlike the major and minor diameters, which are physical measurements you can see and touch, the pitch diameter is a theoretical dimension. It is critical because it represents the effective size of the thread, where the flanks of the internal and external threads actually make contact and carry the load. When a bolt is screwed into a nut, it’s primarily the flanks along the pitch diameter that engage with each other, ensuring proper fit and strength.

The pitch diameter controls whether two threaded parts will assemble correctly. If the pitch diameter of the bolt is too large or the nut’s pitch diameter is too small, the parts may not fit together. Conversely, if the diameters are too loose, the connection may lack strength or stability. Thread tolerance systems, such as ISO and Unified standards, are built largely around controlling the pitch diameter to ensure interchangeability and performance.
In summary, while the major diameter sets the nominal size and the minor diameter sets the root strength, it is the pitch diameter that defines the functional fit between mating threads and determines how well they share load and resist stripping.
Pitting Corrosion
Pitting corrosion is a localized and highly destructive form of electrochemical corrosion that produces small, deep holes or “pits” on a metal surface. Unlike uniform corrosion—which affects a surface evenly—pitting attacks specific microscopic areas, often penetrating deeply while leaving much of the surrounding surface relatively intact. This makes it especially dangerous and difficult to detect, since severe structural damage can occur beneath an otherwise smooth surface.

Pitting corrosion typically begins when a protective oxide film (the passive layer) that normally shields metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, or nickel alloys is locally damaged or weakened. This can happen due to chloride ions (from saltwater or perspiration), mechanical scratches, chemical impurities, or stagnant fluid conditions. Once the film is breached, a tiny anodic site forms where metal dissolution begins:
Anodic reaction:
Fe → Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻
The nearby intact surface acts as a cathode, where a reduction reaction consumes the released electrons:
Cathodic reaction:
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
Inside the pit, metal ions hydrolyze in the presence of water, creating acidic conditions (low pH) that further accelerate dissolution. Meanwhile, chloride ions migrate into the pit, maintaining electrical neutrality and promoting even more localized attack. The chemistry inside the pit becomes self-sustaining, causing it to deepen rapidly while the rest of the surface remains passive.
This autocatalytic process can lead to narrow, deep cavities that compromise the structural integrity of thin components like tubes, tanks, or fasteners. Because pits can penetrate metal walls without significant overall mass loss, pitting corrosion is among the most insidious and dangerous forms of corrosion, often leading to sudden leakage or failure with little visible warning.
Common causes include:
- Chloride-containing environments, such as seawater or road salts.
- Poor oxygenation, which prevents passive film repair.
- Deposits or crevices that trap corrosive agents.
- Improper alloy selection or surface contamination during fabrication.
Prevention and control of pitting corrosion rely on:
- Using more resistant alloys (e.g., 316 stainless steel instead of 304, due to its molybdenum content).
- Maintaining clean, oxygenated surfaces so the passive film can regenerate.
- Applying protective coatings or cathodic protection.
- Avoiding chloride-rich environments when possible or using corrosion inhibitors.
Place Bolt Type AA
Place Bolts — otherwise known as Locking Head Bolts, GM Lock Bolts, or Type AA Lock Bolts — are specially designed to provide a locking action between the bolt and the material being clamped. The locking comes from the crevice under the head and the slots in the top causing the head to flex as it’s tightened. These bolts are well known for their use in transition and diesel engines and many other capacities.

Plain Finish
A plain finish fastener has no additional plating or coating and is supplied in its raw, untreated metal state. Often referred to as bare metal or self-colored, this finish offers no added corrosion protection and is typically used in environments where rust is not a concern.
Appearance - Plain finish fasteners generally have a dull gray, silver, or dark metallic appearance, depending on the base material and any heat treatment. A light coating of oil may be applied to protect the surface during shipping and storage as well.
Plastic Deformation
Plastic deformation is the permanent change in shape or size of a material that occurs when it is subjected to a stress beyond its elastic limit or yield strength. In this state, the material no longer returns to its original form after the load is removed, unlike during elastic deformation where the shape fully recovers. Plastic deformation happens when the applied stress causes atoms within the material’s crystal structure to move or slip past each other, resulting in a lasting rearrangement of the internal structure.
In metals, plastic deformation often begins gradually once the yield strength is exceeded and continues until fracture. During this process, the metal stretches, compresses, or bends without breaking, which is why it’s a key property in manufacturing processes such as forging, rolling, bending, and drawing. The ability of a material to undergo plastic deformation before breaking is called ductility.
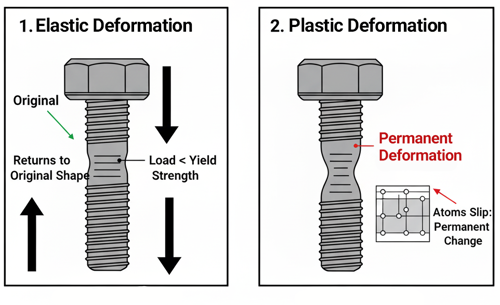
For example, when a bolt is tightened past its yield strength, it begins to stretch permanently — its diameter may slightly reduce, and the threads might elongate. If the load continues to increase, the bolt eventually “necks” and fractures. This behavior demonstrates the material’s transition from elastic to plastic deformation, showing how stress can permanently alter its geometry.
In summary, plastic deformation represents the irreversible flow of a material under stress, where it maintains its new shape even after the load is removed. It’s a crucial concept in understanding how metals and other materials behave under real-world mechanical forces and why design limits are based on avoiding excessive plastic strain that can lead to failure.
Plow Bolt
A plow bolt is a heavy-duty fastener with a flat or countersunk head that sits flush with the surface, commonly used on plows, bulldozers, and graders. It has a square neck under the head to prevent rotation during tightening and is paired with a nut. Designed for high-wear environments, it provides a smooth surface to prevent snagging or damage.
Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel
Precipitation hardening stainless steel, often abbreviated as PH stainless steel, is a class of stainless steel that achieves its exceptional high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance through a specialized heat treatment process known as precipitation hardening (or age hardening). This process involves the controlled formation of very fine particles (precipitates) within the metal’s microstructure, which strengthen the material without significantly reducing its toughness or corrosion resistance.
Chemically, PH stainless steels contain chromium and nickel as their main alloying elements, similar to austenitic grades, but they also include copper, aluminum, titanium, or niobium to enable the precipitation-hardening effect. The chromium provides corrosion resistance, while the nickel stabilizes the austenitic or martensitic structure, and the additional elements form the fine precipitates that dramatically increase strength during heat treatment.
The hardening process occurs in three main stages: solution treatment, quenching, and aging. During solution treatment, the alloying elements are dissolved at high temperature. Quenching rapidly cools the material to lock these elements in a supersaturated solid solution. Finally, during aging, the metal is reheated to a moderate temperature, allowing controlled precipitation of intermetallic compounds that impede dislocation motion — the mechanism that gives the steel its high strength.
Depending on their metallurgical structure, PH stainless steels can be martensitic, semi-austenitic, or austenitic. The most common grade is 17-4 PH (UNS S17400), which contains roughly 17% chromium and 4% nickel, along with copper and niobium for hardening. It offers excellent strength, moderate corrosion resistance (similar to 304), and can be hardened to yield strengths exceeding 1,000 MPa (145 ksi). Other notable grades include 15-5 PH, 17-7 PH, and 13-8 Mo, each designed for specific combinations of toughness, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
Precipitation hardening stainless steels are used extensively in aerospace, nuclear, and petrochemical industries, as well as for valves, shafts, turbine components, fasteners, and high-performance mechanical parts that must maintain strength at both elevated and sub-zero temperatures.
In summary, precipitation hardening stainless steels combine the corrosion resistance of austenitic grades with the strength of martensitic steels, made possible through precise heat treatment. Their ability to achieve very high mechanical performance while maintaining corrosion resistance makes them ideal for critical applications where strength, durability, and reliability are equally important.
Precision Casting
Precision casting, often called investment casting or the lost-wax process, is a manufacturing method used to create fasteners and other components with very fine detail, smooth surfaces, and tight dimensional tolerances.
In precision casting, a wax pattern of the fastener is first made, then coated with ceramic material to create a mold. Once hardened, the wax is melted out (hence “lost wax”), leaving a hollow cavity. Molten metal is poured in, filling the exact shape of the pattern. After cooling, the ceramic mold is broken away, revealing the fastener in near-final form.

Complex shapes: Precision casting can create fasteners with intricate geometries that forging or machining can’t easily achieve.
Tight tolerances: Dimensional accuracy is much higher than with sand casting, reducing the need for secondary machining.
Material versatility: Works with stainless steels, superalloys, titanium, and other high-performance metals.
Applications: Used for specialized fasteners in aerospace, defense, medical, and high-performance industries where both strength and precision are critical.
Press-In Inserts
A press-in insert is a type of threaded insert designed to be pressed into a hole in plastic, soft metal, or wood to create a strong, reusable internal thread. It typically has knurled or ribbed outer surfaces to grip the base material and resist pull-out. Press-in inserts are commonly used in electronics, consumer products, and molded plastic assemblies where reliable screw threads are needed without tapping the material itself.
Prevailing Torque
Prevailing torque is the measurable turning resistance created by a locking feature in a threaded fastener assembly—the torque required to keep a nut advancing on a bolt (or a screw advancing in a tapped hole) when the bearing surfaces are not yet in contact and no meaningful clamp load is being developed. It exists because the threads are intentionally made to interfere or increase friction, so the assembly “wants” to resist rotation even before the joint is tightened.
Prevailing torque is produced by locking designs such as nylon-insert locknuts, all-metal locknuts with a distorted/elliptical top or other deformed thread section, thread-forming or thread-deforming features, and pre-applied locking patches (nylon/chemical) on bolts or screws. Because it is fundamentally a friction/interference effect, prevailing torque is separate from the torque required to generate preload in the joint. During tightening, the torque you apply is essentially the sum of (1) the torque needed to overcome this locking resistance and (2) the torque needed to overcome underhead/bearing friction and thread friction while stretching the fastener to create clamp load.
Prevailing torque is commonly verified with a run-on/run-off test: the nut is driven onto a bolt (or the screw into a test nut) and torque is recorded while the assembly is free-running with no bearing contact, ensuring the measurement reflects only the locking feature rather than the friction under the nut face or screw head. Standards typically require prevailing torque to fall within a specified range so the fastener provides reliable resistance to loosening, but not so high that it causes galling, thread damage, or impractical installation. Prevailing torque can change with reuse, temperature, lubrication/coatings, plating thickness, and thread condition; nylon inserts and patches may soften at elevated temperatures, while all-metal prevailing-torque nuts may maintain locking performance better in heat but can be more sensitive to galling on stainless or poorly lubricated assemblies.
Prevailing Torque Nut
A prevailing torque nut is a locknut with a built-in feature that creates friction on the threads, producing a constant “drag” (the prevailing torque) as it turns. That friction resists loosening from vibration or shock, even when clamp load is low, making the joint more reliable than with a standard nut alone.
There are two main styles: nylon-insert (Nylock), which uses a polymer ring to grip the bolt and is best for general use but limited to about 120 °C/250 °F and a few reuses; and all-metal (distorted-thread/top-lock), which relies on deformed metal threads to pinch the bolt, tolerating higher temperatures and harsher service with limited reusability (the locking torque drops with cycles). Installation torque specs typically account for the added drag, and performance can vary with plating, lubrication, temperature, and reuse. These nuts are common in automotive, machinery, and structural applications where vibration resistance is critical.

Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
The Production Part Approval Process (PPAP) is a standardized supplier approval framework used to demonstrate that a supplier understands the customer’s engineering design record and specifications and that the supplier’s actual production process can consistently make conforming parts at the quoted production rate.
PPAP is most associated with automotive supply chains and the AIAG PPAP manual, and it’s closely tied to APQP (Advanced Product Quality Planning). The core output of a PPAP submission is the Part Submission Warrant (PSW), which summarizes the submission and is the formal “request for approval,” supported by the required evidence package.
A PPAP package is built from a set of required elements (often described as 18 elements, though which ones are required depends on the customer and submission level). These commonly include items such as the design record, authorized engineering changes, process flow diagram, PFMEA, control plan, measurement system analysis (MSA), dimensional results, material/performance test results, initial process studies (SPC), qualified lab documentation, sample parts/master sample, and customer-specific requirements, all tied together by the PSW.
PPAP requirements are also defined by submission levels (Level 1–5), ranging from PSW only (Level 1) to PSW plus samples and complete supporting data (Levels 3/5), with Level 4 being customer-defined. In fastener programs, PPAP evidence often emphasizes clear lot/heat traceability, dimensional layout, and required material/mechanical test documentation, because those items directly support repeatability and compliance.
Proof Load
Proof load is the maximum load that a fastener (such as a bolt, screw, or nut) can withstand without experiencing any permanent deformation. It represents the highest level of stress that can be applied to the fastener while ensuring that it remains within its elastic range—meaning it will return to its original dimensions once the load is removed. Beyond the proof load point, the material begins to deform plastically, leading to a permanent stretch or distortion that can compromise the fastener’s performance and integrity.
In practical terms, proof load serves as a safety benchmark used to verify that a fastener meets its specified strength requirements. During testing, the fastener is tightened or loaded up to its proof load (usually expressed as a specific percentage of its tensile strength, often around 85% to 95%) and then released. If it returns to its original shape and dimensions without yielding, it passes the proof test.

Proof load is usually specified in terms of force (N or lbf) or stress (MPa or ksi), depending on whether it’s defined for the entire fastener or for a particular cross-sectional area. The corresponding test ensures that the fastener can handle expected service loads without stretching, loosening, or losing clamping force.
For example, in high-strength steel bolts such as property class 8.8, the proof load is approximately 80% of the minimum tensile strength. This ensures that in normal service conditions, the bolt remains in the elastic range even when fully tightened, providing consistent and reliable clamping without risk of permanent deformation.
In summary, proof load defines the upper limit of safe, elastic loading for a fastener, ensuring it can perform reliably under tension without suffering permanent damage. It is a critical parameter in fastener design, testing, and quality assurance—helping engineers select the right fastener grade and tightening torque for each application.
Prop 65
A law that requires products sold to consumers in the state of California to carry a warning label if they contain chemicals known to cause cancer or reproductive harm. The law applies only to products sold in California and covers nearly 900 listed substances. It does not restrict the sale of products that contain these substances but is intended to raise awareness so consumers can use them safely. For fastener suppliers, Prop 65 labeling requirements typically apply to platings and coatings such as cadmium or zinc with hexavalent chromate.
Blog Post: Understanding Prop 65 and Its Impact on Suppliers
Property Class
A term used to describe a fastener’s material properties and strength level. Used primarily for metric fasteners, property classes are defined by standards organizations such as ISO or DIN, and help determine appropriate applications based on tensile strength, hardness, and overall performance. Higher property class numbers typically indicate stronger, more durable fasteners.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a synthetic fluoropolymer composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms, with the chemical formula (C₂F₄)ₙ. It is best known by the trade name Teflon®, originally developed by DuPont in 1938. PTFE is prized for its exceptional chemical resistance, low friction, high temperature tolerance, and non-stick properties, making it one of the most versatile and valuable plastics in industrial, chemical, and consumer applications.
Structurally, PTFE consists of long chains of carbon atoms fully surrounded by fluorine atoms. The strong carbon–fluorine bonds give it extraordinary chemical inertness and thermal stability—it doesn’t react with most chemicals, and it can withstand continuous use at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F). It remains stable in both extremely cold and hot environments, making it ideal for use in chemical processing equipment, seals, gaskets, valves, and electrical insulation.
PTFE’s low coefficient of friction makes it one of the most slippery solid materials known, which is why it’s used as the non-stick coating on cookware and in bearings, bushings, and fasteners that require reduced wear or resistance. It’s also an excellent electrical insulator, commonly used in wiring for aerospace, telecommunications, and high-frequency electronics due to its dielectric strength and resistance to moisture.
Additionally, PTFE is hydrophobic (repels water) and non-reactive to acids, bases, and solvents, which makes it useful in harsh environments like chemical plants, laboratories, and medical devices. However, it is soft and easily deformed under load (a property known as creep), so it’s often combined with fillers such as glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance its strength and wear resistance.
AKA: Teflon®
Push Button Ring Nut
A Push Button Ring Nut is a round, threaded nut, typically made of plastic or metal, that is an accessory for industrial-grade control components. Its primary function is to mechanically lock and fasten a push button or similar operator through a cutout hole in a mounting surface (like a control panel). The nut is threaded onto the body of the operator from behind the panel and tightened to press the operator's bezel firmly against the panel face, ensuring a secure mounting and, often, maintaining the seal of the assembly. It is essential for the reliable installation of 22mm or 30mm control devices.

