Resources
Glossary
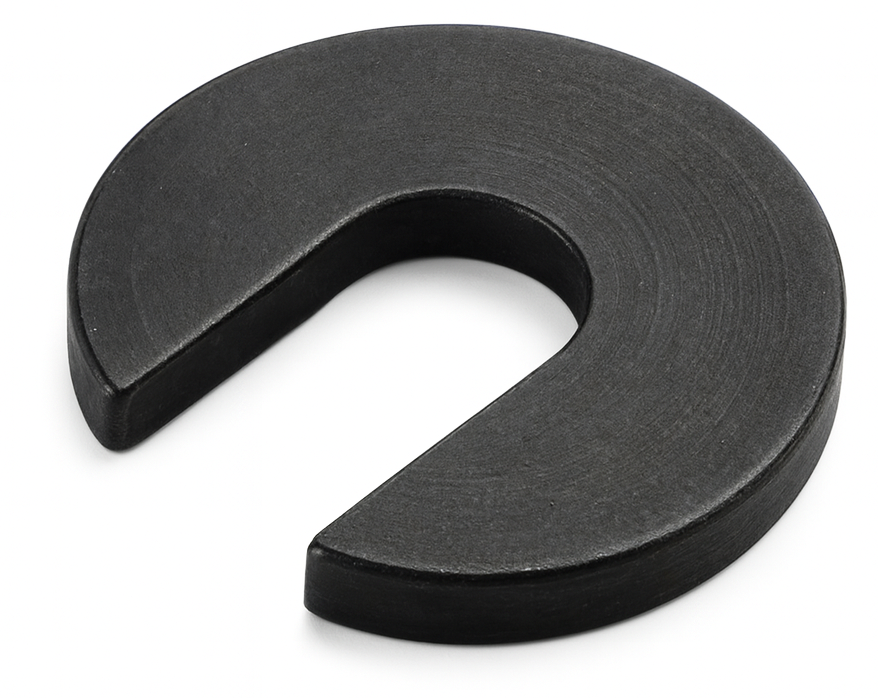
C Type Washer
A C-type washer (also called a C-washer, slotted washer, or horseshoe washer) is a flat washer with a side opening so it looks like the letter “C.” The slot lets you slide the washer in or out without removing the nut or bolt—useful when a part is already assembled, the stud is fixed, or you’re working in a slot.
What it does: like a standard flat washer, it spreads load under a nut/bolt head and protects the surface; it’s also used as a shim/spacer for quick thickness adjustments and for positioning/retention on studs, pins, or in slotted holes.
Where it’s used: equipment setup and alignment (shim packs), automotive brackets and strut alignments, fabrication fixtures, conveyor and racking systems, and anywhere you need fast, repeatable adjustments without fully disassembling hardware.
Materials & options: carbon steel (often zinc-plated), stainless steel, and spring steel; available in assorted thicknesses (shim sets) and by nominal bolt size with various slot widths.
Good practice: orient the slot away from the primary load direction or capture it in a slot/shoulder so it can’t slip out; don’t rely on C-washers alone for high-shear retention where a closed washer or proper shoulder is required.
AKA: C-Washer, Slotted Washer, Horseshoe Washer

Cadmium (Cd)
Cadmium (chemical symbol Cd) is a soft, bluish-white metallic element with the atomic number 48 and an atomic mass of 112.41. It is located in Group 12 of the periodic table, directly below zinc and above mercury, sharing several chemical similarities with those elements. Cadmium is relatively ductile and malleable, meaning it can be easily shaped, and it has a low melting point of 321°C (610°F) and a boiling point of 767°C (1413°F).
Cadmium is most commonly found in nature associated with zinc ores, particularly sphalerite (zinc sulfide, ZnS). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of zinc refining. Because it rarely occurs in concentrated deposits, cadmium’s availability depends largely on zinc production levels.
Chemically, cadmium is quite reactive. It slowly oxidizes in moist air, forming cadmium oxide (CdO), a compound that can release toxic fumes when heated. It also forms various salts, including cadmium chloride (CdCl₂) and cadmium sulfate (CdSO₄), which are highly soluble and toxic. Cadmium is divalent in nearly all its compounds, meaning it typically exhibits a +2 oxidation state (Cd²⁺).
Historically, cadmium has been valued for several key industrial uses. It was widely used in nickel-cadmium (NiCd) rechargeable batteries, electroplating, pigments, and stabilizers for plastics. Its corrosion resistance made cadmium plating particularly useful for protecting steel fasteners and aerospace components in marine or harsh environments. Cadmium pigments, producing bright yellows, oranges, and reds, were prized for their stability and brilliance in paints, plastics, and ceramics.
However, cadmium and its compounds are now recognized as highly toxic to humans and the environment. Prolonged exposure can cause kidney damage, bone demineralization, and respiratory illness, and cadmium is classified as a Group 1 human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Because of these dangers, cadmium use has been heavily restricted or banned in most consumer applications. NiCd batteries, once common, are being replaced by safer lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride alternatives, and cadmium pigments have been largely phased out.
In modern applications, cadmium still finds limited, specialized use in aerospace, nuclear, and electronics industries—for instance, in control rods of nuclear reactors due to its strong neutron-absorbing properties, and in infrared detectors and semiconductors.

Cadmium Plating
Cadmium plating is a metallic finish applied to fasteners through electrodeposition (also known as electroplating). This finish offers excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine and aerospace environments, and provides good lubricity for consistent torque-tension performance. However, cadmium is toxic and environmentally hazardous, leading to its highly restricted use and replacement by safer alternatives.

Appearance - Cadmium typically has a bright silver or dull gray appearance.
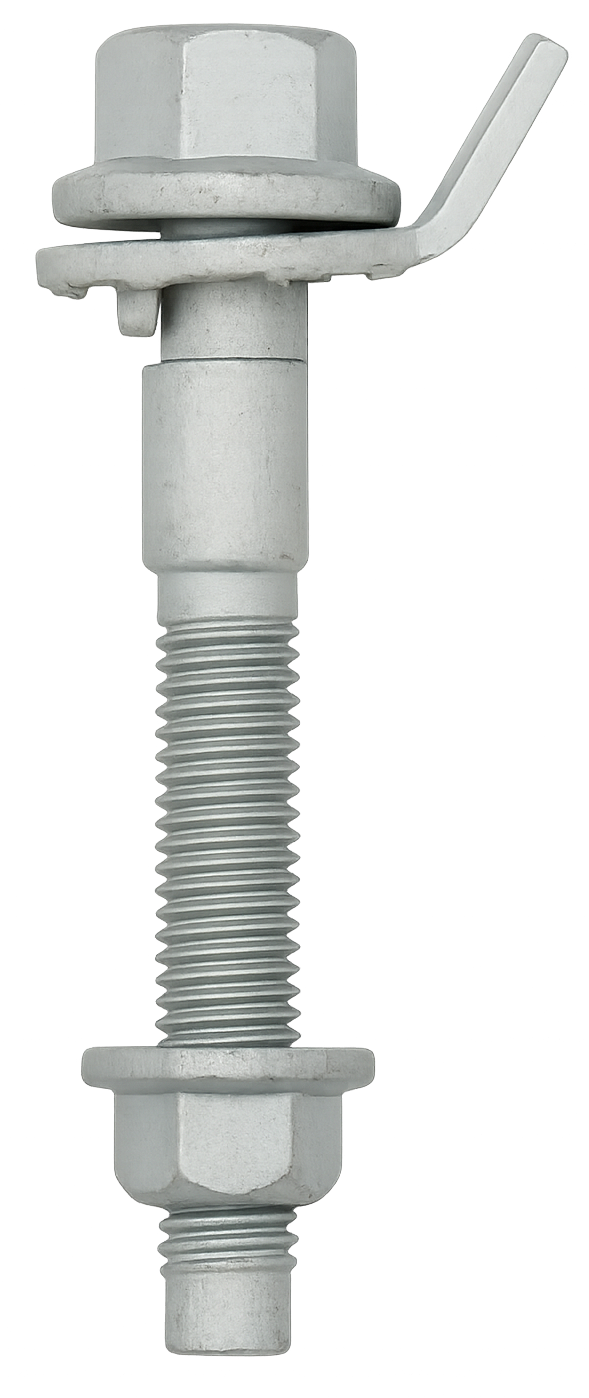
Cam Bolt
A cam bolt is a specialized fastener designed with an eccentric (off-center) lobe or cam-shaped washer incorporated into its head or shank, which allows for fine adjustment of alignment or position when the bolt is rotated. Unlike standard bolts that only clamp materials together, a cam bolt functions both as a fastening element and as an adjustment mechanism, making it especially useful in applications where precise positioning or alignment is required.
The key feature of a cam bolt is its eccentric cam, which is offset from the bolt’s central axis. As the bolt is turned, this offset causes the connected component—such as a suspension arm, bracket, or plate—to shift slightly relative to the mounting surface. Once the desired alignment is reached, the bolt can be tightened to lock the assembly in place. To improve stability, cam bolts are often paired with matching cam nuts or eccentric washers that help prevent slippage after tightening. This unique design eliminates the need for additional shims or spacers while still allowing for precise adjustment.
Cam bolts provide several important advantages. They allow for precise, incremental adjustments without requiring major disassembly or part replacement. Their compact design makes them space-saving, and they provide strong locking security once torqued, resisting unwanted movement under stress. Because they are usually made from durable steels and often heat-treated, cam bolts can withstand repeated adjustments and maintain high clamping loads even in demanding environments.
These bolts are widely used across industries. In automotive suspension systems, they are crucial for wheel alignment adjustments, particularly for setting camber and caster angles in control arms, struts, or subframes. By simply rotating the cam bolt, mechanics can fine-tune alignment to improve tire wear, vehicle handling, and steering response. In heavy machinery and industrial equipment, cam bolts are used for adjusting large components that need precise alignment under high loads. In construction and structural applications, they sometimes appear in anchor systems or adjustable joints. A different type of cam bolt is also common in furniture assembly, where lightweight cam bolts work with cam locks to secure panels in flat-pack furniture, though these serve a lower-strength, locking purpose compared to industrial or automotive cam bolts.
Cam bolts may vary depending on their intended application. Automotive cam bolts are typically manufactured to OEM or aftermarket suspension specifications, while industrial versions may be custom-made to suit specific equipment or machinery. Despite these differences, the principle remains the same: cam bolts act as both a fastening and alignment tool, combining strength, durability, and precision adjustment in one compact component.
AKA: Camber Bolt

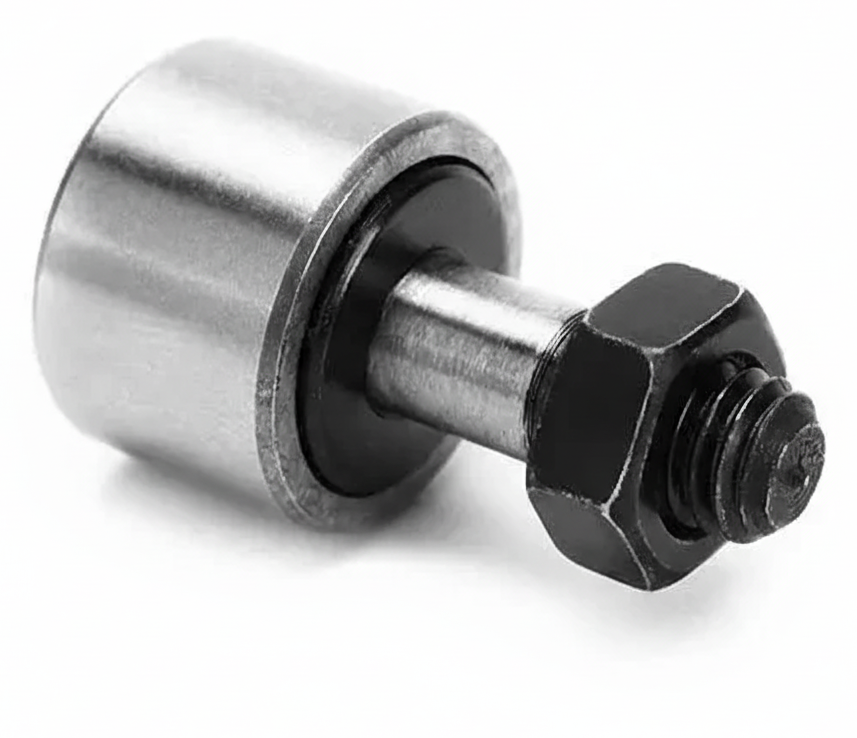
Cam Follower Bolt
A cam follower bolt is an integrated bearing assembly designed to convert rotary motion into linear or oscillating motion by following the profile of a cam or moving along a track. Also known as a stud-type cam follower or track roller, this component is characterized by a threaded stud that serves as both the inner bearing race and the mounting shaft. This integrated design allows for direct installation into a tapped or through-hole in a machine part, which is convenient for compact and efficient machine layouts.
The key features of this integrated assembly include a heavy-duty, thick-walled outer ring that resists deformation from the high radial and shock loads experienced while rolling along a track. It typically uses needle rollers as rolling elements, which provide high load-bearing capacity in a small space. For handling minor misalignment, variations with crowned outer rings are available. Many cam follower bolts are also sealed to protect the internal bearing and are pre-lubricated for low-maintenance operation. An eccentric stud variation allows for radial adjustment to eliminate backlash during installation.
Cam follower bolts differ from yoke-type followers primarily in their mounting style and load capacity. While the stud-type is mounted cantilever-style by its built-in threaded stud, the yoke-type requires a separate pin or shaft and support on both sides. The two-sided support of yoke followers makes them more suitable for extremely heavy loads and shock loading applications, whereas the stud-type is well-suited for moderate to heavy loads in applications where space is limited on the mounting side. This specialized bearing is used in various industrial machines, including conveyor systems, automotive engines, automated equipment, and robotics, to guide and control motion.

Cam Lever
A cam lever is a quick-acting mechanical clamping device that uses an eccentric cam (an off-center rotating surface) to apply or release clamping force with a simple flip of a lever—no tools required. Instead of tightening a screw or bolt by turning threads, a cam lever locks by rotating its cam-shaped body, which converts a small lever motion into a strong, controllable clamping action.
When the lever is pushed downward, the eccentric cam rotates into a position where its thickest portion presses against a surface or pulls on a stud, generating significant clamping force. When the lever is lifted upward, the cam rotates back to its thinnest position, instantly releasing tension. This makes cam levers ideal for frequent adjustments, quick setups, and tool-free clamping.
Cam levers are commonly used in:
- Machine setups and fixtures
- 3D printers and CNC equipment
- Camera mounts and tripods
- Bicycles and sporting equipment (quick-release systems)
- Furniture, jigs, and adjustable assemblies
- Industrial machinery where operators reposition parts repeatedly
They may clamp directly onto a surface or operate in combination with a threaded stud or bolt. Most cam levers are made from aluminum, steel, or reinforced plastics, and they come in various styles such as adjustable tension levers, stud-mounted levers, or cam-action knobs.
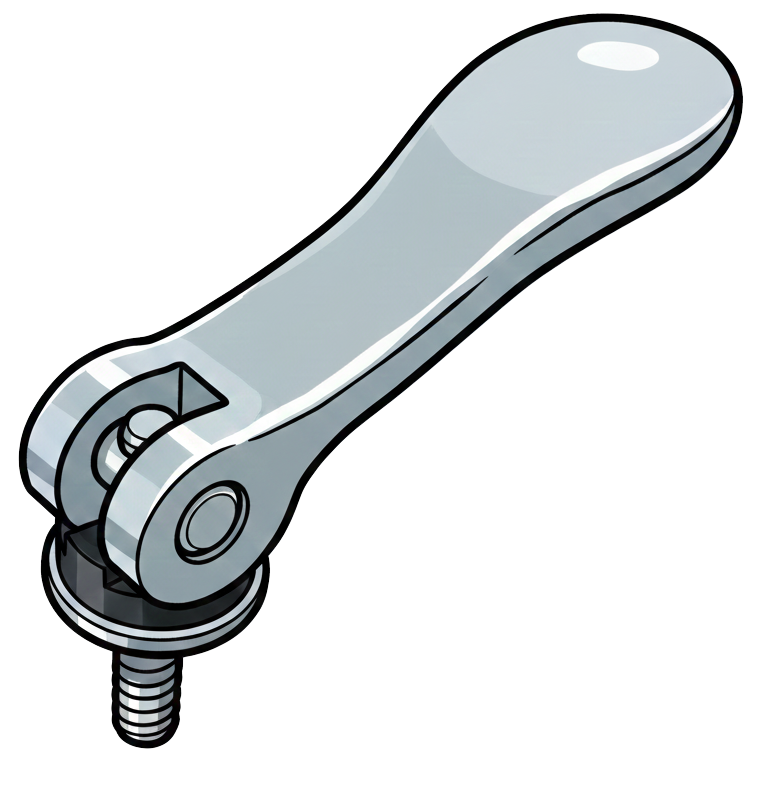

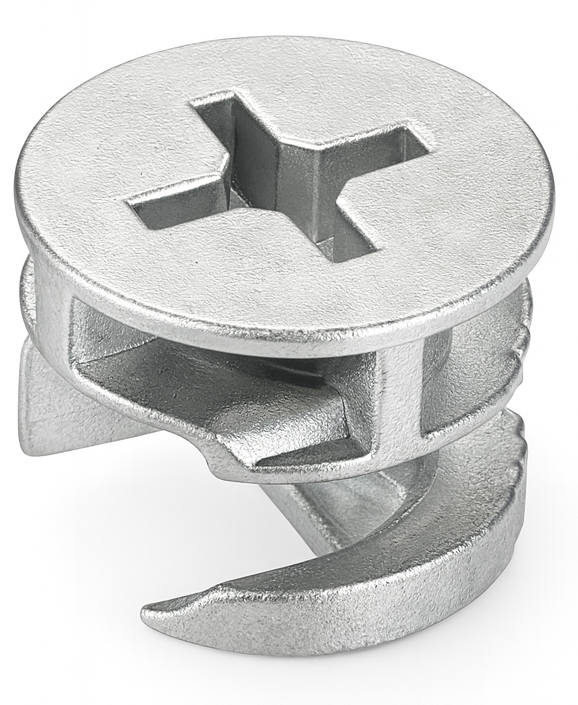
Cam Lock nut
A cam lock nut (part of a cam-and-dowel or cam connector system) is a round, barrel-shaped nut used to make knock-down furniture joints that can be tightened from one side and taken apart again. It sits in a shallow, large-diameter hole in one panel and locks onto a mating cam screw/dowel installed in the adjoining panel.
How it works: the cam screw’s head/neck projects into the cam nut’s keyhole. Turning the cam nut about 90° with a screwdriver (slot, Phillips/Pozi, or hex) rotates an eccentric cam that hooks the screw head and pulls the panels tightly together. The result is high clamping force with a flush, hidden fastener.
Where it’s used: ready-to-assemble furniture, cabinets, shelving, and millwork—any application needing strong, repeatable assembly without visible screws or through-bolts.
Common details: zinc die-cast or steel bodies, usually 12–20 mm diameter (15 mm is typical), various head recess styles and arrows/marks for alignment. The cam screw length is chosen for panel thickness so the cam engages fully without breaking out.
Installation tips: drill clean, perpendicular holes; align the cam’s arrow toward the approaching screw; insert the screw fully first, then rotate the cam only until snug (over-rotation can strip the cam or crush the board). For particleboard/MDF, avoid overtightening, and consider caps or covers if the cam face will be visible.
Cam Out
In mechanics, cam-out is when a driver bit slips out of a screw head while torque is applied. It usually happens because of excess torque, poor bit seating, or drive designs that encourage slipping (like Phillips). Cam-out wastes torque, damages fasteners and tools, and is why drive styles like Torx or hex are often preferred for higher torque applications.

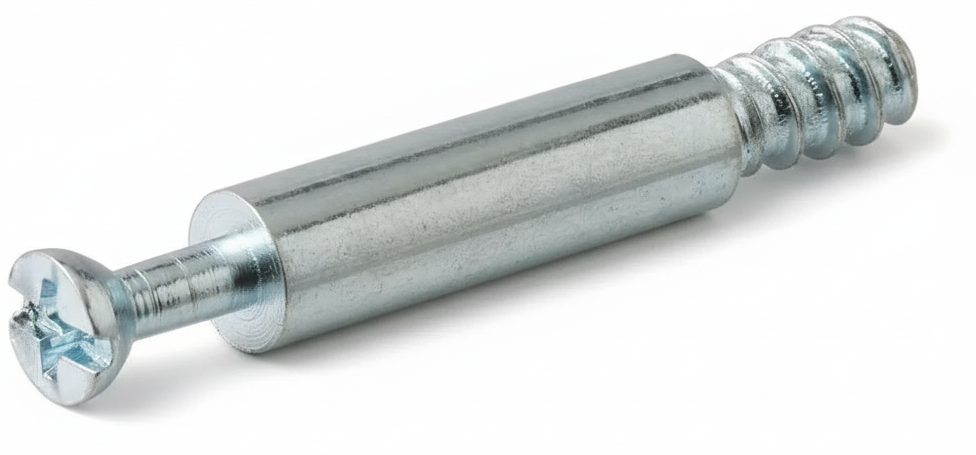
Cam Screw
A cam screw (also called a cam dowel, connector screw, or cam bolt) is the mating fastener used with a cam lock nut in knock-down furniture and casework. One end of the screw anchors in or passes through one panel, while a short shouldered neck near the head projects into the neighboring panel and engages the cam nut. When the cam nut is turned about 90°, its eccentric lobe hooks that neck and pulls the two panels tightly together.
Cam screws are made in several patterns. There is a threaded anchor style that screws into a pilot hole or insert in particleboard, MDF, or solid wood, and a through-bolt style that passes through a clearance hole to the cam on the far side. Variants also include Euro/confirmat-type threads, machine threads (with M6 very common), and double-ended studs to suit different substrates and thicknesses.
Typical materials are zinc-plated steel for strength or, less often, brass. The heads are low-profile with a shaped under-cut or neck sized to match the cam nut’s bite height. Correct sizing ensures the neck sits at the cam’s centerline for full pull-up.
For best results, drill straight, accurate holes; set the cam screw fully before turning the cam; align the cam’s arrow toward the screw; and tighten only until snug to avoid crushing low-density boards. The outcome is a strong, releasable joint with no visible through-bolts—ideal for RTA furniture, cabinetry, shelving, and fixtures.

Cantilever Beam
A cantilever beam is a structural beam that is fixed rigidly at one end and free at the other, meaning it extends outward without external support along its length. Unlike simply supported beams, which are held at both ends, a cantilever relies entirely on its fixed end to resist bending, shear forces, and rotational moments. This makes it ideal for structures where supports can’t be placed at both ends—such as balconies, diving boards, overhead signs, crane arms, and many bridge designs.

When a load is applied to a cantilever, the beam experiences tension on one side and compression on the other. At the fixed end, the structure must resist a bending moment equal to the applied load multiplied by its distance from the support. For example, a downward force F applied at the free end creates a bending moment M = F × L at the support, where L is the beam length. Engineers design cantilevers so that material strength, stiffness, and allowable deflection are balanced for the expected loads.
Because the supported end must resist torque, cantilever beams require strong joining methods such as welding, bolting to a rigid foundation, or embedding into concrete. They’re heavily used in civil, mechanical, and architectural engineering where space, aesthetics, or structural function demand an open span with only one support point.
Capstan Nut
A capstan nut is a cylindrical nut operated by inserting a bar or pin into one of the radial holes on its outer surface, which is how it gets its name. This design is practical in situations where using a traditional wrench is difficult or impossible. Because the nut's exterior is smooth and round with no hexagonal or other wrenching features, it provides a clean, finished appearance and is often used in marine and heavy engineering applications that require high torque.
The capstan nut's functionality relies on a simple lever principle. A tool, like a tommy bar, is inserted into one of the holes to provide the necessary leverage for tightening or loosening the nut. This method allows for the application of strong, controlled torque. Some versions may also feature a slotted drive, offering an alternative way to turn the nut with a bit. For example, the related slotted capstan screw is used in applications that demand very fine, incremental adjustments, such as in musical instruments like pianos or in metrology equipment.
It is important not to confuse a capstan nut with a "cap nut," which is sometimes also called an acorn nut. A cap nut has a domed end that covers and protects the bolt's threads, serving a decorative or protective function. In contrast, a capstan nut's defining characteristic is its method of operation using a bar inserted into its peripheral holes. The capstan nut's specialized design and operating method distinguish it from other fasteners, making it suitable for specific, heavy-duty applications where standard tools are ineffective.

Capstan Screw
A capstan screw is a specialized fastener distinguished by its broad, cylindrical head featuring multiple radial holes. This design allows for precise, incremental adjustments by inserting a lever, or a special capstan regulating tool, into one of the radial holes. Some variations, like DIN 404 standard screws, also include a slotted top, which offers the alternative option of using a standard flathead screwdriver for turning. The radial holes can also be used to wind a cable or wire around the screw to adjust tension.
Capstan screws are commonly used in applications that require very fine, controlled adjustments. They are notably prevalent in the mechanisms of both grand and upright pianos for regulating the height of hammers, adjusting lost motion, and timing various parts of the action. Beyond musical instruments, these screws are utilized in precision metrology and other equipment where incremental adjustment is necessary. The unique ability to be driven from the side is particularly useful when access to the top of the screw head is restricted. Certain types, specifically some DIN 404 models, are also designed for sealing purposes in electric or water meters, where a sealing wire can be passed through the head's holes to prevent tampering.
A capstan screw differs significantly from a standard set screw. A capstan screw is a headed fastener used for making fine adjustments and is typically visible on the surface of an assembly. In contrast, a standard set screw, or grub screw, is a headless fastener designed to secure an object against or inside another by pressure and/or friction, and it is almost always fully recessed within a threaded hole. While set screws are used for locking components in place, capstan screws are used for regulation and can be adjusted to sit at different heights to change the timing or tension of a mechanism.
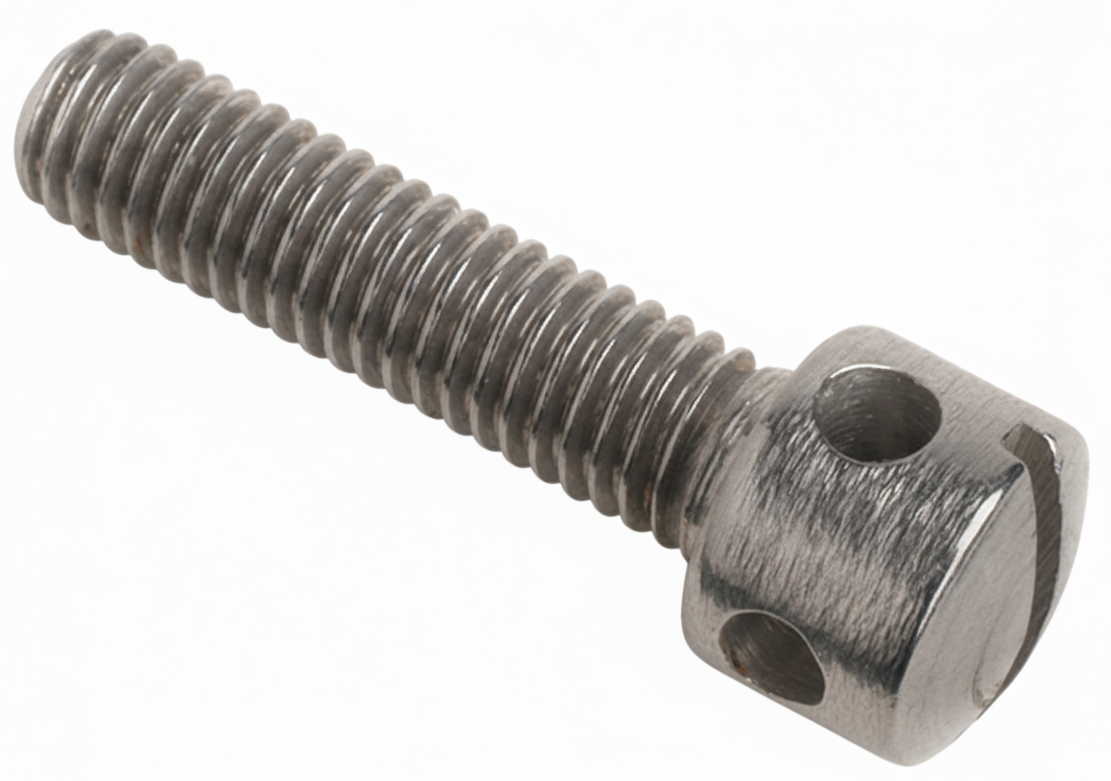

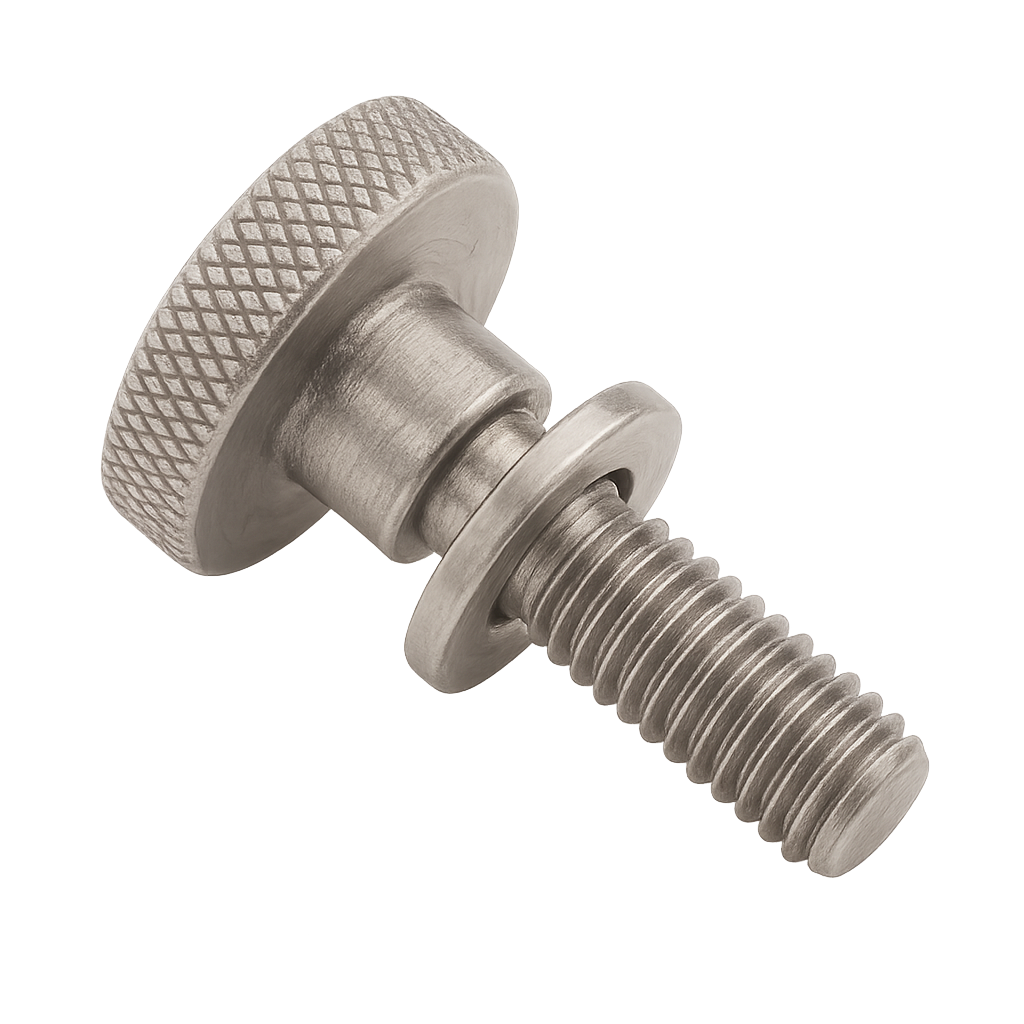
Captive Panel Screw
A captive panel screw is a type of fastener designed to remain attached to a panel, door, or equipment cover—even when loosened. Unlike a standard screw that comes free once unthreaded, a captive screw is secured by a retainer (such as a shoulder, clip, or spring) so it doesn’t fall out or get lost during use.
These screws are often used in equipment that needs frequent servicing—like electronics enclosures, server racks, machinery guards, or access panels—where losing a screw could cause downtime, safety issues, or foreign object damage (FOD). Captive screws speed up maintenance because you don’t have to fully remove and keep track of them.
Common in aerospace, automotive, medical devices, and IT hardware. They can have knurled heads for tool-free use, or be designed with Phillips, Torx, or hex drive styles for added torque. Some even integrate with captive washers to spread load and resist loosening.
Captive Thimble
A captive thimble is a specialized rigging component used in wire rope, cable, and lifting assemblies to reinforce and protect the eye, or loop, of a wire rope while keeping the thimble securely fixed in place. Unlike a standard thimble, which can slip out of the eye if the rope loosens, a captive thimble is designed to remain permanently retained, which ensures greater safety, durability, and reliability in demanding applications.
In terms of design and construction, a captive thimble usually has a teardrop or U-shaped body with a deep groove along its inner surface that guides and supports the wire rope. What distinguishes it as “captive” is an added retention feature such as extended lugs, tabs, or an integrated locking system that prevents it from shifting or falling out during use. These thimbles are manufactured from high-strength steel, stainless steel, or other durable alloys, and they are often galvanized or coated to provide corrosion resistance for marine or industrial environments.
The purpose and function of a captive thimble are to preserve the proper shape and integrity of a wire rope eye while reducing kinking, crushing, and wear at the loop. Because the thimble is fixed in place, it not only protects the rope but also distributes loads more evenly, increasing the strength and reliability of the termination. This leads to improved safety and longer service life for both the rope and the thimble.
Captive thimbles have a wide range of applications. In marine and offshore operations, they are used in mooring lines, towing hawsers, and lifting slings where secure thimble retention is critical. In construction and lifting, they ensure safe rope terminations in cranes, hoists, and heavy rigging systems. In industrial and utility work, they provide long-lasting protection for cable assemblies that undergo frequent loading. They are also used in the theatrical rigging and entertainment industry to secure overhead lifting cables where reliability and safety cannot be compromised.
There are several advantages to using captive thimbles. They prevent loss or misalignment of the thimble within rope assemblies, protect rope eyes from abrasion and deformation, improve load distribution, and extend the service life of the rope and thimble. However, they also have limitations. Captive thimbles tend to be heavier and more expensive than standard thimbles, and installation may require special tools or fittings to secure them in place. They are also less flexible in applications where a removable or adjustable thimble is desired.
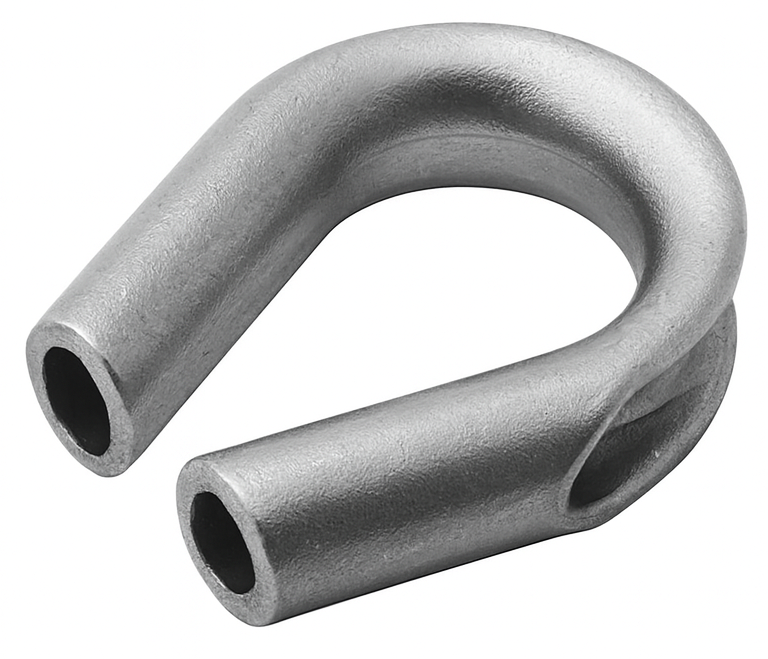

Car Alignment Reamer
A car alignment reamer (often just called an alignment or bridge reamer) is a tapered-lead reamer used in automotive chassis and body work to bring slightly misaligned bolt holes into register and then size them round to a precise, straight-through diameter. The long taper (“lead”) draws two parts into alignment as it enters both holes; the parallel section behind the taper reams the pair to the final size so bolts, pins, or sleeves fit correctly without forcing or galling.
These reamers are typically HSS with straight or spiral flutes and a 3/8"–1/2" shank for use in hand drills or drill presses. Techs use them on subframes, control-arm brackets, crossmembers, bumper/impact-bar brackets, strut/knuckle interfaces, and exhaust flanges—anywhere collision repair or assembly tolerances leave holes slightly off. They’re also used when installing camber/caster kits, where a hole may be precisely opened to accept an eccentric bolt or sleeve.
It’s not the same tool as a tie-rod/ball-joint taper reamer (which cuts a standardized tapered seat). An alignment reamer finishes straight bolt holes.
Best practice: clamp the work, run low RPM with cutting oil, keep the tool square to the surface, and remove only what’s needed (typically the last few thousandths). If significant material must be removed, plan for an oversize fastener or repair sleeve, and follow OEM procedures for structural locations.
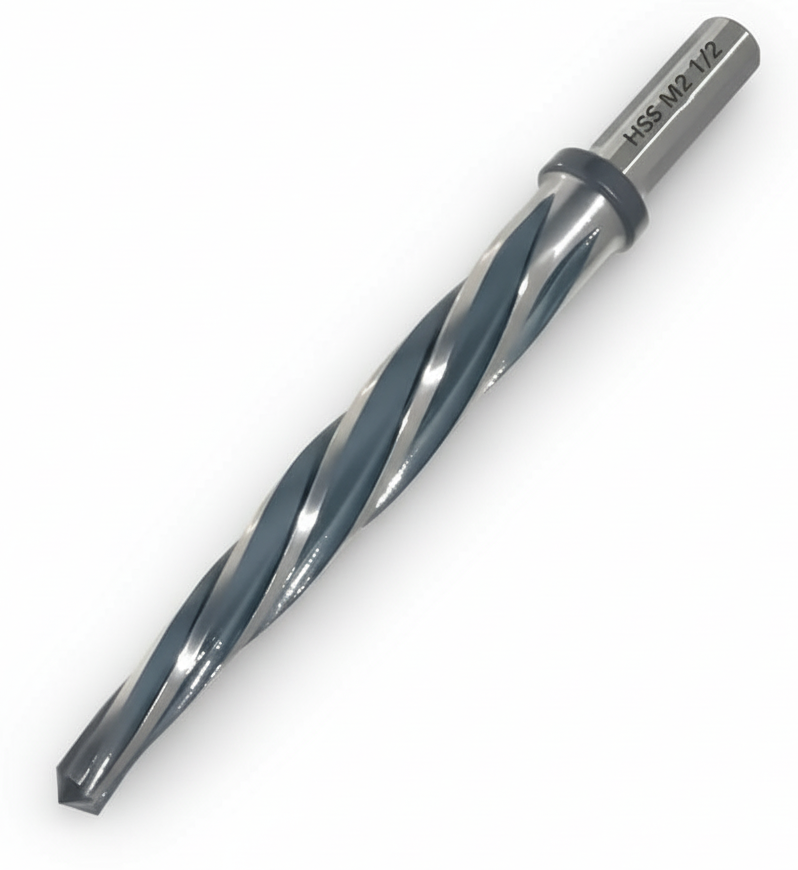

Carbide
Carbide refers to a class of very hard compounds composed of carbon and a metal or metalloid element. The most well-known type is tungsten carbide (WC), which is formed by combining tungsten and carbon, but there are many others such as silicon carbide (SiC), titanium carbide (TiC), and boron carbide (B₄C). These materials are prized for their extreme hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures, which makes them essential in many industrial applications.
Structure and Properties
Carbides typically have a crystalline structure where carbon atoms bond tightly with metal atoms. This gives them unique mechanical properties:
Extreme hardness: Many carbides are harder than steel, and some approach the hardness of diamond.
Wear resistance: They resist abrasion, erosion, and deformation under high stress.
High melting points: Carbides remain stable at very high temperatures.
Brittleness: While extremely hard, carbides can also be brittle, making them prone to cracking under impact or shock loading.
Common Types of Carbide
Tungsten Carbide (WC): The most widely used, known for exceptional hardness and toughness; often combined with cobalt as a binder.
Silicon Carbide (SiC): Lightweight, highly heat-resistant, and often used as an abrasive or in high-temperature applications.
Boron Carbide (B₄C): Extremely hard and lightweight, used in armor and cutting tools.
Titanium Carbide (TiC): Known for high hardness and resistance to oxidation, often used in coatings.
Applications
Carbides are used across industries where strength, durability, and resistance to wear are essential:
Cutting tools: Drill bits, milling cutters, lathe tools, and saw tips are often made with tungsten carbide.
Mining and drilling: Carbide-tipped equipment is used for rock drilling and excavation.
Abrasives: Silicon carbide is used in sandpapers, grinding wheels, and polishing compounds.
Armor: Boron carbide is used in body armor, tank armor, and bulletproof vests.
Mechanical components: Bearings, seals, and nozzles made from carbides handle high wear and corrosive environments.
Advantages
- Exceptional hardness and durability.
- Long service life compared to steel in abrasive conditions.
- High temperature and corrosion resistance.
Limitations
- Brittle compared to steels or alloys; prone to fracture under shock.
- More expensive to produce and machine.
- Typically requires specialized equipment for shaping or bonding.
Carbon (C)
Carbon is a nonmetallic chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is one of the most fundamental elements in the universe—forming the backbone of all known life and serving as a key building block in materials, fuels, and industrial compounds.
In its pure form, carbon exists in several allotropes, meaning it can take different structural forms with distinct physical properties. The three best-known are:
- Diamond – each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a tetrahedral lattice, making it the hardest natural material known. Diamonds are transparent, excellent electrical insulators, and extremely thermally conductive.
- Graphite – carbon atoms are arranged in flat hexagonal layers, with weak forces between the sheets. This gives graphite its slippery texture (used in lubricants and pencils) and makes it an excellent electrical conductor.
- Amorphous carbon – includes coal, charcoal, soot, and carbon black, where atoms lack long-range order but still form strong covalent networks.
Modern discoveries have revealed additional allotropes, such as graphene (a single layer of graphite atoms with extraordinary electrical and mechanical strength), fullerenes (C₆₀ “buckyballs”), and carbon nanotubes, all of which have revolutionized nanotechnology and materials science.
Carbon’s atomic structure—four valence electrons—allows it to form strong covalent bonds with many elements, including itself. This bonding flexibility enables carbon to create millions of compounds, more than any other element. These include organic molecules such as hydrocarbons, proteins, DNA, and polymers, making carbon the basis of organic chemistry and, by extension, life itself.
In industry, carbon is used in countless ways. It appears in steelmaking (as a strengthening alloying element), graphite electrodes, activated carbon filters, composite materials, carbon fiber, inks, and electrodes for batteries and fuel cells. Carbon compounds also form the foundation of the petrochemical industry—fuels like methane, gasoline, and propane are all carbon-based hydrocarbons.
Carbon is an essential part of Earth’s biosphere and atmosphere. It circulates through the carbon cycle, moving between the air (as carbon dioxide, CO₂), oceans, plants, animals, and fossil fuels. This cycle regulates global climate and supports life through photosynthesis and respiration.

Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is an iron–carbon alloy in which carbon is the primary hardening element, typically ranging from about 0.05% to 1.0% carbon and up to roughly 2.1% by definition, with only small amounts of other elements present—about ≤1.65% manganese, ≤0.60% silicon, and ≤0.60% copper. When alloying elements exceed those limits the steel is classified as an alloy steel rather than plain carbon steel. Increasing carbon content raises strength and hardness but reduces ductility, toughness, and weldability. As carbon rises, the microstructure shifts from mostly ferrite/pearlite at low carbon to finer pearlite and, when heat treated, martensite at higher carbon levels.
Within this family, low-carbon (mild) steels at about 0.05–0.30% carbon are easily formed and welded but cannot be through-hardened by quenching; they are often strengthened by cold work or given a hard surface by case hardening. Common examples include AISI 1008, 1018, and 1020, used for sheet, plate, brackets, and low-strength fasteners such as A307/Grade 2-type bolts. Medium-carbon steels at roughly 0.30–0.60% carbon respond well to quench-and-temper heat treatment for higher strength while retaining moderate weldability; AISI 1045 is typical, used for shafts, gears, and many higher-strength fasteners (for example, many Grade 5-type bolts are medium-carbon and quenched and tempered). High-carbon steels around 0.60–1.0% carbon (up to about 1.2% in some specifications) can be made very hard and wear-resistant after heat treatment but have lower toughness and weldability; examples include 1060, 1080, and 1095, used for springs, cutting edges, and wear parts.
Heat treatment is central to tuning properties. Annealing or normalizing is used to soften material and refine grain. Quenching and tempering of medium- and high-carbon grades produce a martensitic structure that is then tempered to balance strength and toughness. Low-carbon grades generally are not through-hardened; when a hard surface is needed they are case-hardened (e.g., carburized or nitrided) so the core remains tough while the surface gains wear resistance.
Because plain carbon steels rust readily, they are commonly protected with finishes such as paint, oil, phosphate, electro-zinc, zinc-flake, and hot-dip galvanizing. Care is required when plating high-strength fasteners (approximately ≥1000 MPa tensile strength) to avoid hydrogen embrittlement.
In fastener terms, A307/SAE Grade 2 hardware is typically low-carbon steel and low strength; SAE Grade 5 fasteners are typically medium-carbon steel that has been quenched and tempered for higher strength; and SAE Grade 8 fasteners are usually alloy steel rather than plain carbon steel, even though they are also quenched and tempered. In short, carbon steel is the workhorse of steels—cost-effective, versatile, and highly tunable via carbon content and heat treatment—chosen when strength and formability at low cost are priorities, with surface protection applied wherever corrosion resistance is required.
Carburizing
Carburizing is a thermochemical heat treatment process used to increase the carbon content of the surface layer of low-carbon steel or iron. During this process, a metal part is heated to the austenitizing temperature—typically 900–950°C (1650–1750°F)—in the presence of a carbon-rich environment, such as a gas (e.g., methane or carbon monoxide), liquid (molten salt bath), or solid (charcoal or carbon powder).
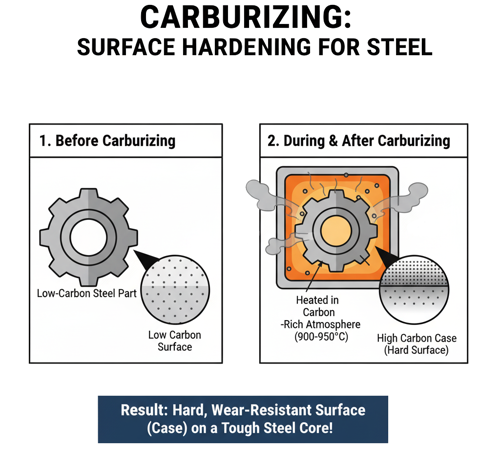
At this temperature, the steel’s crystal structure transforms into austenite, which has a high solubility for carbon. Carbon atoms diffuse into the surface layer of the metal over time, gradually forming a carbon-enriched zone known as the carburized case. The depth of this case depends on how long the metal is exposed to the carbon-rich atmosphere—typically ranging from a few tenths of a millimeter to several millimeters.
After the desired carbon diffusion is achieved, the part is quenched (rapidly cooled) to transform the carbon-rich austenitic surface into martensite, a hard, wear-resistant microstructure. The result is a component with a hard, high-carbon surface and a tough, low-carbon core. This dual property makes carburized parts highly resistant to wear, fatigue, and surface deformation while maintaining resistance to shock and impact.
Carburizing is just one method within the broader category of case hardening, which includes other surface-hardening processes such as nitriding, carbonitriding, cyaniding, and flame or induction hardening. While all case hardening techniques create a hardened outer layer over a softer interior, carburizing specifically relies on carbon diffusion at high temperature to form the case.
Cardan Bolt
A Cardan bolt is a specialized fastener used in Cardan joints (also called universal joints) that transmit torque between two shafts at an angle. These bolts secure the yoke or flange of the Cardan joint to its mating component, such as a driveshaft, gearbox flange, or differential. Because Cardan joints are used in power transmission systems where rotational loads and vibrations are high, Cardan bolts are designed to be extremely strong, secure, and resistant to loosening.
Unlike ordinary bolts, Cardan bolts often feature special head or shank designs to withstand shear forces and maintain alignment under continuous rotation. In some cases, they are manufactured with precise shoulders, splines, or fit tolerances so they locate the joint components accurately, not just hold them together. They are typically paired with hardened washers and self-locking nuts to ensure the joint remains secure during operation, even under heavy vibration and dynamic loading.
Cardan bolts are most commonly found in automotive driveshafts, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and other mechanical systems where universal joints are used. Their role is critical: if a Cardan bolt loosens or fails, the universal joint can separate, leading to catastrophic equipment damage or loss of power transmission.
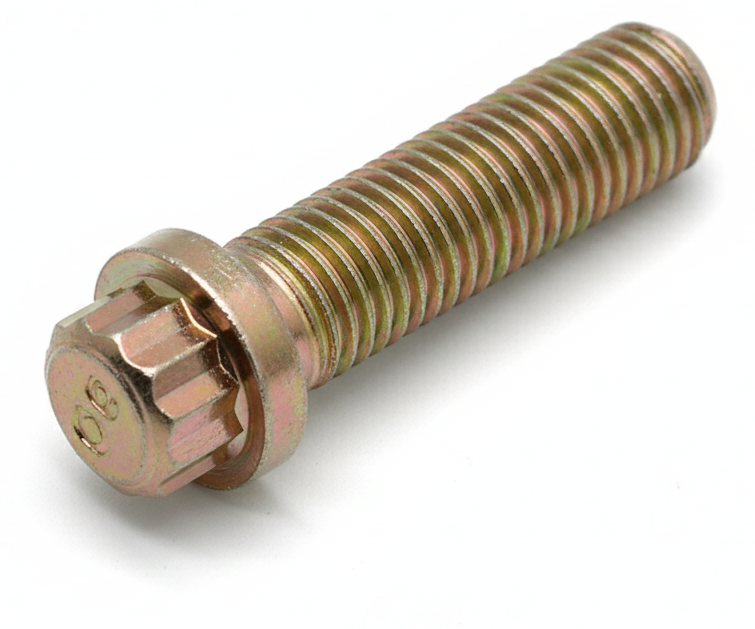

Carriage Bolt (also called Shaker Screen Bolt)
A carriage bolt, also known as a shaker screen bolt, is a fastener featuring a rounded, dome-shaped head and a square neck directly beneath it, designed to fit into a corresponding square hole or embed into wood or metal to prevent rotation during tightening. These bolts are typically used with a nut and washer to secure materials together. The smooth, rounded head provides a clean, tamper-resistant finish while the square neck locks the bolt in place as torque is applied. Commonly used in wood-to-metal connections, shaker screens, agricultural equipment, and structural assemblies, these bolts are valued for their strength, vibration resistance, and ability to maintain a secure, flush appearance.

Carriage Bolt DIN 603
A Carriage Bolt DIN 603 is a metric standard fastener defined by the DIN 603 specification from the German Institute for Standardization (Deutsches Institut für Normung). It is commonly used in woodworking, construction, and metal-to-wood connections where a smooth, finished appearance on one side is desired.

Carrier or Bearing Cap Bolt
A carrier or bearing cap bolt is a high-strength fastener used in differentials and transmissions to secure the bearing caps (also called carrier caps) that hold the differential carrier bearings in place. These bolts are critical to maintaining proper bearing preload, gear alignment, and structural stability within the axle housing.
Inside a differential, the carrier (or differential case) supports the ring gear and spider gear assembly. On each side of the carrier are tapered roller bearings that allow it to rotate smoothly inside the axle housing. These bearings are clamped in place by bearing caps, which are bolted to the housing using carrier or bearing cap bolts. The precision and torque of these bolts directly affect how well the gears mesh and how long the bearings last.
Because of the stresses involved, bearing cap bolts are typically made from hardened alloy steels such as 4140 or 8740 chromoly, with tensile strengths often exceeding 150,000 psi. They are usually fine-threaded to allow precise torque application and to resist loosening under vibration. Many designs also use shouldered bolts for perfect alignment and may include threadlocker or safety wire holes to prevent backing out under load.
If a bearing cap bolt fails or loosens, the carrier bearings can shift, causing gear misalignment, premature wear, or even catastrophic failure of the differential. That’s why manufacturers specify exact torque values and tightening sequences during assembly.

Case Hardening
A heat treatment process that hardens the outer surface of a fastener to resist wear and abrasion while keeping the core softer and more ductile (flexible). This combination provides a hardened, wear-resistant exterior and a flexible core that helps absorb impacts and resist cracking or breaking under stress. This balance improves overall durability by combining hardness with some internal flexibility.

Article: Case Hardening Explained
Cast Alloy Nut
A cast alloy nut is a fastener created by pouring a molten metal alloy into a mold. Two of the most commonly used types are made from zinc and aluminum, each having distinct properties for specific applications. The general manufacturing process involves melting the metal and then casting it into a mold, such as through die casting or sand casting. Die casting is a high-pressure, high-volume method that produces accurate parts with smooth finishes, while sand casting is a lower-cost, more versatile method often used for complex shapes. Following casting, the nuts may undergo further processes, like threading and machining, to achieve their final specifications.
Zinc alloy nuts, which are often die-cast, offer cost-effectiveness and good corrosion resistance. Their properties prevent them from galling or "freezing" onto mating threads, a significant advantage in many fastening applications. They are frequently used for panel mounting and as thumb or wing nuts in various consumer and hardware products.
Alternatively, aluminum alloy nuts are valued for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them significantly lighter than their steel counterparts. They naturally form a protective oxide layer that gives them excellent corrosion resistance. Although not as strong as steel, they are highly durable and reliable for many uses. Their applications range from weight-sensitive items like automotive wheel lug nuts and aerospace components to consumer goods and electronics where light weight and corrosion resistance are needed.
The applications for cast alloy nuts are diverse due to their combination of strength, light weight, and corrosion resistance. In the automotive industry, lightweight aluminum wheel lug nuts can improve a vehicle's performance by reducing unsprung weight. The electronics sector benefits from cast aluminum nuts' high thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat in connectors and other components. Furthermore, cast alloy barrel nuts are a popular choice in the furniture industry for assembly, while corrosion-resistant zinc alloy nuts are commonly used in appliances and general hardware.
Cast Iron
Cast iron is a group of iron-carbon alloys containing more than 2% carbon, along with varying amounts of silicon, manganese, and trace impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus. It is produced by melting pig iron (a crude form of iron extracted from a blast furnace) and then casting the molten metal into molds, rather than shaping it through forging or rolling. The high carbon content gives cast iron its characteristic hardness, wear resistance, and excellent fluidity when molten, but it also makes the material brittle compared to steel.

The structure of cast iron depends on how carbon solidifies in the alloy. Carbon can appear either as graphite flakes, nodules, or iron carbides (cementite), and these different forms define the main types of cast iron:
- Gray cast iron: The most common type, in which carbon forms as graphite flakes. These flakes interrupt the metal matrix, giving gray iron its characteristic dull gray fracture surface. It has excellent machinability, vibration damping, and compressive strength, making it ideal for engine blocks, machinery bases, and pipe fittings.
- Ductile (nodular) cast iron: Also called spheroidal graphite iron, this type is treated with magnesium or cerium to make the graphite form into spherical nodules instead of flakes. This structure significantly improves tensile strength and ductility, allowing it to behave more like steel while retaining cast iron’s wear resistance.
- White cast iron: Here, carbon remains combined as iron carbide (Fe₃C), giving the metal a white fracture surface. It is extremely hard and wear-resistant but very brittle, often used for crusher liners, grinding balls, and abrasion-resistant surfaces.
- Malleable cast iron: Produced by heat-treating white cast iron, which decomposes the carbides into small graphite particles. The result is a more ductile and tough material suitable for pipe fittings, brackets, and automotive parts.
Cast iron has a lower melting point (around 1150–1200°C) than pure iron, which makes it easy to pour into intricate molds—a major reason it’s favored for complex or detailed castings. However, its brittleness means it cannot absorb much tensile stress or bending without fracturing.
Because of its combination of strength, castability, vibration damping, and heat retention, cast iron remains one of the most widely used materials in engineering. It’s found in everything from machine tools and cookware to engine components, heavy-duty pipes, and architectural structures—a testament to its versatility despite being one of the oldest known engineering materials.
Cast Iron Fastener
A cast iron fastener is a piece of hardware whose main body is made from cast iron—most commonly gray iron, ductile (nodular) iron, or malleable iron—formed by pouring molten iron into a mold and then machining features such as threads. Unlike the vast majority of modern bolts and screws, which are wrought (rolled) steel, cast iron fasteners rely on the cast microstructure of iron. This makes them suitable for parts where the geometry is complex and casting is economical (clamps, hangers, brackets, decorative hardware, certain rail clips, and some thumb/wing-style nuts), but it also means they are rarely used for high-tension, safety-critical bolting.
Performance depends on the iron type. Gray iron (ASTM A48) contains flake graphite that gives excellent compressive strength, vibration damping, and machinability, but it is brittle in tension and notch-sensitive, so it is generally poor for highly stressed threaded fasteners. Ductile iron (ASTM A536; grades such as 60-40-18, 65-45-12, 80-55-06) has spheroidal graphite that markedly improves tensile strength and elongation; it can handle moderate service loads and is common for cast components that include tapped holes or integral studs, though it still does not match the fatigue and impact resistance of quenched-and-tempered alloy steel bolts. Malleable iron (ASTM A197/A197M) is heat-treated white iron that attains reasonable ductility and has long been used in pipe fittings, beam and conduit clamps, and other hardware with threads, but it is likewise intended for relatively low to moderate stresses.
Manufacturing and design constraints follow from the material. Because cast iron cannot be cold-formed, the part’s shape is created in the mold and then finished by machining. Threads in cast iron are cut or chased, not roll-formed, and coarse pitches with generous root radii are preferred to reduce stress concentration. Good practice is to keep the iron component primarily in compression or shear, avoid shock and cyclic tension, provide generous fillets and section transitions, and size bosses and wall thicknesses to support threads. Where higher preload is required, the better solution is usually to cast the body from iron (for shape and cost) and use separate steel fasteners for the threaded elements, or to install steel inserts (helicoils/solid inserts) in tapped cast iron to increase thread strength and wear resistance.
In application, cast iron fasteners and fastener-like hardware appear in building hardware, pipe and conduit supports, rail and heavy-equipment castings, vintage machinery, and architectural pieces where casting enables complex geometry or an “as-cast” aesthetic. They are commonly zinc-plated, galvanized, painted, or powder-coated to mitigate corrosion, which is broadly similar to carbon steel. They are not appropriate substitutes for standardized structural or pressure-boundary bolting; for those uses, wrought steel fasteners to standards such as ASTM/SAE/ISO bolting specifications are required, with the cast iron component serving only as the clamped part or housing.
It is also worth distinguishing “cast iron fastener” from “fastening into cast iron.” When you are joining to a cast iron substrate (engine blocks, housings, machinery bases), the recommended practice is to use steel screws/bolts with adequate washer area to spread load, apply appropriate torque (often lower than for steel-on-steel to avoid cracking), use anti-seize to protect threads, and consider thread inserts for repeated service or higher loads. In short, cast iron can be used to make certain fastener bodies and fastener-like components when casting advantages outweigh mechanical limits, but for high-preload, fatigue- or impact-critical joints, the threaded fastener itself should be steel while the cast iron remains the part being clamped.
Cat Clamp Bolt
A Cat Clamp Bolt is a specialized fastener designed for use with the CatClamp® catalytic converter lock system. The CatClamp is an anti-theft device that secures a vehicle’s catalytic converter by clamping it to the exhaust system with high-strength aircraft-grade cables. The Cat Clamp Bolt is the bolt that anchors and tightens the clamp mechanism, holding the cables in place.
These bolts are typically made from hardened, corrosion-resistant steel and often feature tamper-resistant heads (such as proprietary drive styles or shear-off designs). This makes them extremely difficult to remove without the proper tool, preventing thieves from quickly unbolting or cutting away the clamp.
In practice, the Cat Clamp Bolt functions as the core fastener of the entire security system: once tightened, it locks the woven cables around the catalytic converter and vehicle frame or exhaust components, creating a cage-like barrier. Because catalytic converters are targeted for the valuable metals inside them (like platinum, palladium, and rhodium), these bolts are a critical part of theft-prevention strategies in automotive security.

Caustic Cleaning
Caustic cleaning is a chemical cleaning process used to remove organic contaminants, oils, greases, waxes, and dirt from the surface of steel and other metals before further processing—such as plating, painting, galvanizing, or heat treatment. It involves immersing or spraying the steel with a hot alkaline solution, typically containing sodium hydroxide (NaOH)—commonly called caustic soda—and other additives that enhance cleaning efficiency and prevent corrosion.

The process works through a combination of saponification, emulsification, and detergency. The strong alkali in the caustic solution reacts chemically with fats and oils (which are often esters) to form soap and glycerol—a reaction known as saponification. This breaks down greasy films and allows them to be lifted and dispersed into the cleaning solution. Surfactants and wetting agents are often added to reduce surface tension and help the solution penetrate into small crevices or rough surfaces, ensuring a uniform clean.
The cleaning bath typically contains sodium hydroxide (NaOH) concentrations between 5–15% and is maintained at temperatures around 80–95°C (175–200°F) to accelerate chemical activity. Sometimes, sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃), sodium silicate (Na₂SiO₃), or phosphate compounds are added as builders or corrosion inhibitors to stabilize the solution and protect the metal surface.
Caustic cleaning is commonly used in steel manufacturing and fabrication as a pre-treatment step before surface finishing processes like electroplating, phosphate coating, galvanizing, or painting, where any residual oil or dirt could prevent adhesion or cause defects. It’s also used in maintenance cleaning, such as removing grease from machinery parts or heat-treatment residues from steel components.
However, the process must be carefully controlled. Prolonged exposure or excessive concentrations can etch or dull the steel surface, and if aluminum, zinc, or other reactive metals are present in an assembly, the caustic solution can attack or dissolve them. After cleaning, the steel is usually rinsed thoroughly with water to remove all traces of alkali, followed by acid pickling or neutralizing rinse to eliminate any residual alkalinity and prepare the surface for finishing.
Cement Board Screw
A cement board screw is a purpose-made fastener for attaching cement backer board (CBU) to wood or metal framing/subfloors in wet areas like showers, tub surrounds, and floors. Cement board is alkaline, abrasive, and often damp; ordinary drywall or deck screws corrode quickly and can snap. Cement board screws solve that with a corrosion-resistant finish or stainless steel, a head and thread form that cuts cleanly into the board, and points tailored to the base material.
Most have a flat, countersinking head with small cutting “nibs” under the head so it seats flush without tearing the board’s face, plus a high/low or twin-lead thread that bites hard in brittle cement board. For wood framing they use a sharp Type-17–style cutting point; for steel studs they’re self-drilling with a fine thread and drill point sized for light-gauge steel. Materials are typically case-hardened steel with a heavy ceramic/polymer coating rated for cementitious/alkaline environments, or 410/305 stainless for maximum corrosion resistance. Drives vary by brand (Phillips, square, or star/Torx) to reduce cam-out.
Common lengths are about 1-1/4 in. for 1/4–1/2 in. board over wood subfloors and 1-5/8 in. for wall studs; choose a length that leaves at least ~3/4 in. embedment in wood or full thread engagement through light-gauge steel. Install screws flush—neither proud nor overdriven—at the spacing specified by the board maker (often ~6 in. on floors, ~8 in. on walls, with minimum edge distances), then tape joints with alkali-resistant mesh and thinset. In short, cement board screws are corrosion-resistant, self-countersinking fasteners engineered to hold brittle, abrasive backer board securely without rusting or crumbling the substrate.
Cemented Carbide
Cemented carbide is a composite material made by combining fine particles of a hard carbide compound—usually tungsten carbide—with a metallic binder, typically cobalt (Co) or sometimes nickel (Ni). The mixture is pressed into shape and then sintered at high temperatures (around 1400–1600 °C), causing the binder metal to melt slightly and bond the hard carbide grains together. The result is an exceptionally hard, wear-resistant material that retains strength even at very high temperatures.
The tungsten carbide grains provide extreme hardness and resistance to abrasion, while the cobalt binder gives the material toughness and impact resistance, preventing it from shattering under stress. The ratio between carbide and binder determines the final properties: a higher carbide content produces greater hardness but lower toughness, while more binder improves ductility at the cost of hardness.
Cemented carbide is widely used in cutting tools, drills, end mills, inserts, dies, and wear parts—anywhere that hardness, heat resistance, and durability are essential. In metalworking, it can cut hardened steels and superalloys that would quickly destroy ordinary high-speed steel tools. It’s also used in mining, oil and gas drilling, woodworking, and construction equipment, and for precision components such as valves, bearings, and nozzle tips.
Because of its extreme hardness (second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride), cemented carbide maintains sharp cutting edges and dimensional stability even under intense friction and pressure. However, it can be brittle—especially at low cobalt contents—and may fracture if subjected to sudden impacts. To overcome this, modern manufacturing often applies surface coatings like titanium nitride (TiN) or aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) using chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD) processes, further extending tool life.
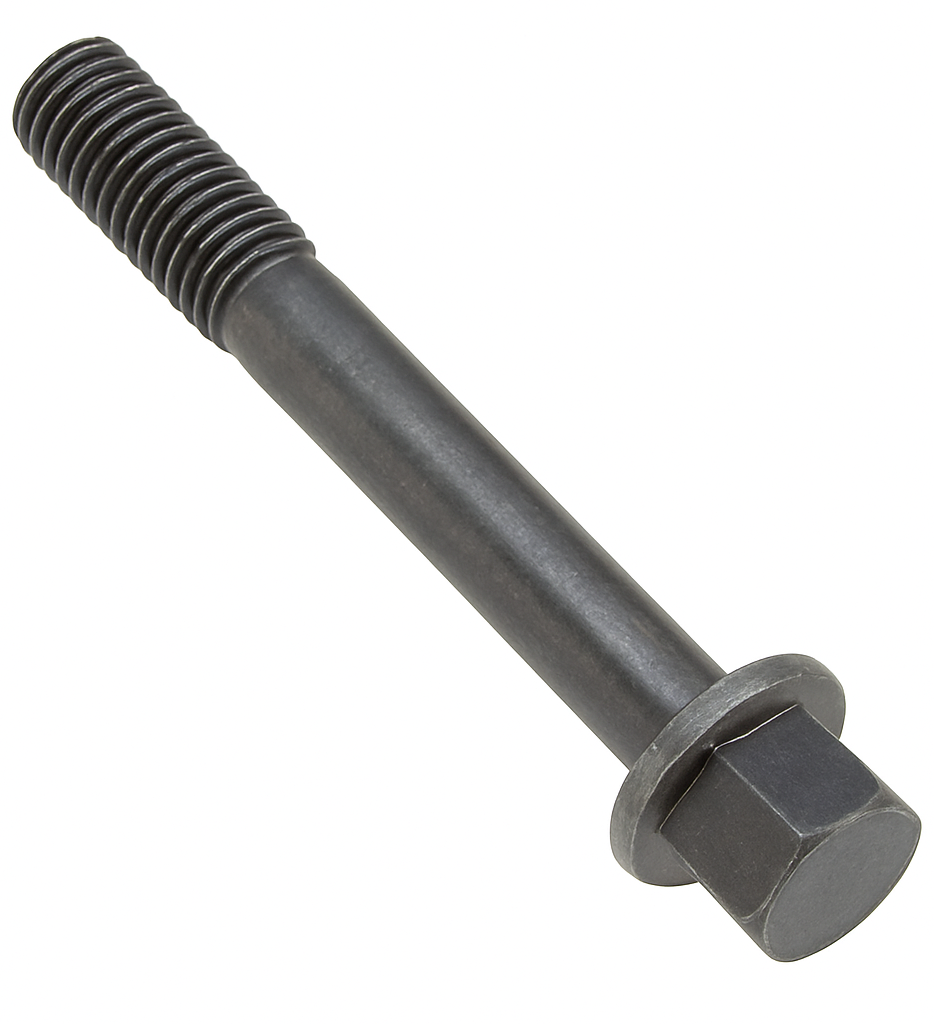
Center Bolt
A center bolt is the through-bolt that runs up the middle of a leaf-spring pack, clamping the individual leaves into one unit and locating that spring on the axle. The bolt’s small, round “button” head seats in a matching hole in the spring seat/perch and acts like a dowel so the axle can’t shift fore/aft on the spring. The threaded end passes through the stack and is tightened with a nut to squeeze the leaves together; U-bolts then clamp the spring to the axle. In service, the center bolt primarily provides alignment and clamping of the leaf pack and shear location at the perch—it isn’t the main load-carrying fastener for the axle joint (that’s the U-bolts).
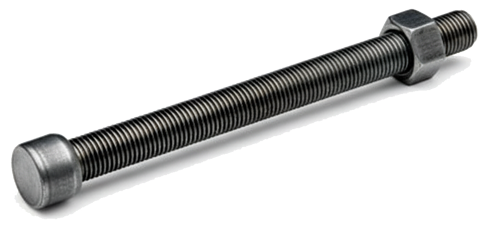
Center bolts are typically high-strength steel (often Grade 5 or Grade 8 in inch sizes) with a round, low-profile head and rolled or cut threads. Common diameters are about 5/16–1/2 in. (roughly M8–M12) with lengths chosen to match the total spring stack thickness. They’re single-use items: when a leaf pack is disassembled or a bolt is bent, rusty, or necked, you replace it. Installation is done with the spring clamped securely in alignment, the new bolt inserted from the perch side so the head can seat in the locating hole, and the nut tightened to clamp the leaves; excess thread is usually trimmed flush after tightening. Never grind or thin the head—the head’s full shape is what keys the spring to the perch.
Outside suspension work, people sometimes use “center bolt” more loosely for any bolt that runs through the center of a built-up assembly (for example, some timber or furniture connectors), but in fastener/vehicle contexts it almost always means the leaf-spring center bolt described above.
Ceramic-Coated Fastener
A ceramic-coated fastener is a bolt, screw, nut, or other fastening component that has been treated with a thin layer of ceramic-based coating to enhance its performance in demanding environments. The coating is typically applied through processes such as spraying, dipping, or electrostatic application, followed by curing to bond the ceramic material to the fastener’s surface. These coatings are engineered to improve corrosion resistance, reduce friction, and extend the service life of the fastener, especially in aggressive or high-temperature conditions.
The design and construction of ceramic-coated fasteners begin with a substrate material, usually carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, or other high-strength alloys. The ceramic coating, often composed of oxides, silicates, or ceramic-polymer composites, forms a protective barrier on the metal surface. This barrier is non-conductive, chemically inert, and highly resistant to heat, abrasion, and corrosive substances such as saltwater, acids, and industrial chemicals. In some cases, the coatings are designed to provide lubricity, which reduces friction during installation and ensures more accurate torque-tension relationships.
The purpose and function of ceramic coatings are to protect fasteners from environmental degradation and mechanical stress. They prevent rusting and surface oxidation, minimize galling (metal-to-metal sticking), and reduce the likelihood of fasteners seizing in place. The coatings also improve load consistency in bolted joints by lowering variability in friction, which is especially important in precision or high-performance assemblies.
Applications for ceramic-coated fasteners are widespread across industries where durability and resistance to harsh conditions are critical. In the automotive sector, they are commonly used in exhaust systems, engine components, and underbody assemblies exposed to heat and road salt. In aerospace, they protect fasteners from oxidation and extreme temperatures. In marine environments, ceramic coatings help fasteners withstand saltwater corrosion. In industrial and energy sectors, they are employed in chemical plants, oil and gas equipment, wind turbines, and offshore structures where corrosion and wear are major concerns.
The advantages of ceramic-coated fasteners include exceptional corrosion resistance, high-temperature stability, and improved torque control due to reduced friction. They can extend the lifespan of fasteners, reduce maintenance frequency, and improve safety and reliability in critical systems. Additionally, ceramic coatings are often environmentally friendlier than traditional plating processes that may use hazardous materials like hexavalent chromium.
However, there are limitations. Ceramic coatings, while durable, can be brittle and may chip or crack under extreme mechanical stress or impact. They may also be more expensive to produce compared to standard zinc or phosphate coatings. The thickness and uniformity of the coating are critical—if not applied properly, performance can be inconsistent. Furthermore, once the coating is damaged, the exposed metal can corrode rapidly if not maintained.

Chainring Nut Wrench
A chainring nut wrench is a specialized hand tool used in bicycle maintenance, specifically for installing and removing dual hex chainring bolts and nuts that secure the chainrings (sprockets) to the crankset. Chainring bolts typically consist of two parts — a bolt and a slotted nut — and during tightening or loosening, the nut can easily spin in place unless held securely.
The chainring nut wrench has a thin, flat blade or prong that fits perfectly into the slot on the chainring nut, preventing it from turning while the bolt is tightened or removed with a hex key, Torx wrench, or Allen wrench on the opposite side. Most versions are small and compact, often made of steel or hardened alloy, and designed to fit a range of chainring nut sizes.

Chamfer
A chamfer is a transitional edge between two surfaces, typically created by cutting or grinding the corner at an angle, most commonly 45 degrees. Chamfers are used to remove sharp edges, improve aesthetics, facilitate assembly, and reduce stress concentrations. For fasteners, chamfers are often applied to the ends of bolts or screws to help guide the part into a hole or make it easier to start threading a nut onto the fastener.

Chamfer Angle
The angle at which the edge or corner of a part is cut or ground to create a beveled surface, commonly set at 45 degrees but varying based on design needs. In fasteners, this angle helps facilitate easier installation by providing a smooth lead-in edge.
Channel Nut
A channel nut (also called a strut nut or spring nut) is the threaded insert that locks into the lips of metal strut channel (e.g., Unistrut-type framing) to create a movable attachment point. The nut has side grooves that hook under the channel’s inward-turned edges; you insert it through the slot at an angle and twist 90° so the grooves seat. On “spring” versions, a captive spring pushes the nut up against the slot to hold position while you line up parts and start the bolt.
Channel nuts come in sizes that match common strut systems and bolt threads—typically 1/4-20 through 3/4-10 (metric M6–M12) for 1-5/8 in. (41 mm) channel, with smaller nuts for shallow “mini-strut.” Materials and finishes include zinc-plated steel for general use, hot-dip galvanized for outdoors, and stainless for corrosive environments. Variants include long or short springs, serrated/teeth (“conical” or “top hat”) for extra bite, flat or cone washers pre-assembled, and “without spring” nuts for tight spaces or back-to-back channel.
They’re used to mount pipe hangers, conduit, cable tray, HVAC supports, trapeze racks, and solar or equipment frames—anywhere you want strong, adjustable fastening without drilling. For safety and performance, match the nut to the channel series, seat it fully with the grooves under both lips, use the manufacturer’s torque guidance, and check load tables—ultimate capacity is limited by both the nut threads and the channel’s lip strength.
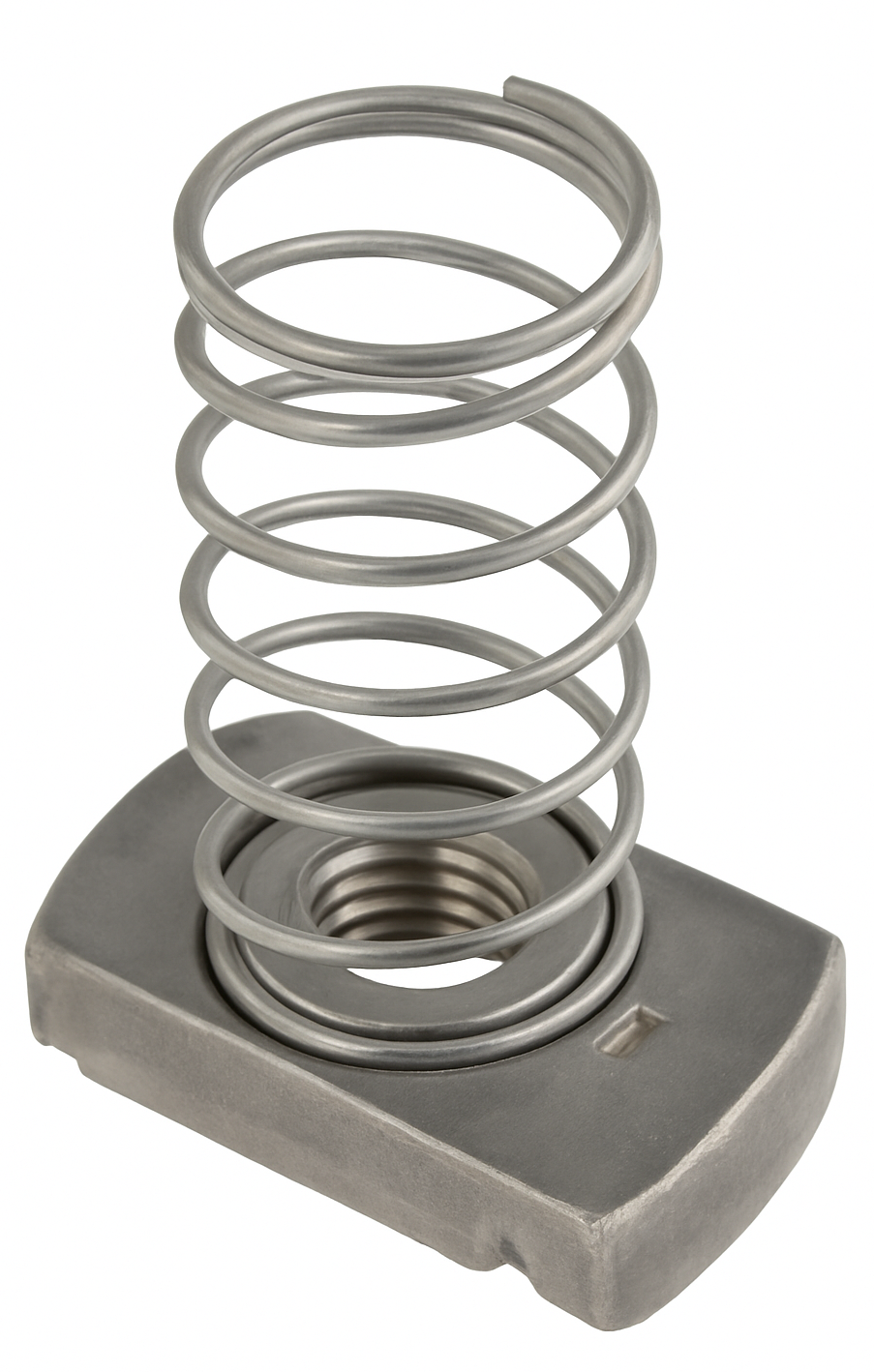

Check Nut
A check nut is a thin nut used to lock another nut in place on a threaded fastener, preventing loosening caused by vibration, rotation, or dynamic loads. It is sometimes referred to as a jam nut or lock nut, though those terms may also apply to other locking designs. By working in tandem with a primary nut, the check nut provides added security and stability in threaded assemblies.
In terms of design and construction, check nuts are thinner than standard hex nuts, making them lighter and easier to pair without adding significant bulk. They are typically manufactured from the same materials as the primary fastener, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or brass, and may be plated or coated for improved corrosion resistance. Their reduced thickness allows them to be tightened securely against the main nut, maintaining compactness while ensuring functionality.
The purpose and function of a check nut is to stop loosening by creating friction between two nuts. After the primary nut has been tightened to the correct torque, the check nut is tightened against it. This “jamming” effect holds both nuts in place and resists loosening from vibration, thermal expansion, or other external forces. This makes them particularly useful in applications where joint security is critical.
Common applications of check nuts include machinery and equipment, where they are used to withstand vibrations in engines, pumps, and rotating systems. They are also employed in automotive and transportation settings, such as suspension systems and steering linkages, where reliability is essential. In construction and structural connections, check nuts secure fasteners in steel frameworks, towers, and other heavy-duty assemblies. More generally, they are found in fastening tasks where consistent reliability and resistance to loosening are needed.
The advantages of check nuts are their simplicity and cost-effectiveness as a locking method. They are reusable if undamaged, work with standard threads, and require no specialized hardware. However, they also have limitations. They require sufficient thread length to accommodate two nuts, which adds to assembly complexity and space requirements. Additionally, they are not as strong or fail-safe as specialized lock nuts with built-in locking features.

Chemical Patch
A chemical patch is an anaerobic adhesive applied to the threads of a fastener. Anaerobic adhesives cure (harden) when confined between metal surfaces and sealed from air. When the patched fastener is assembled with a mating part, the adhesive activates and locks the threads together, helping prevent loosening caused by vibration or movement. Chemical patches offer consistent thread locking, eliminating the need for additional liquid adhesives during assembly.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a materials-processing technique used to produce thin films, coatings, and high-purity solid materials on a substrate through chemical reactions of vapor-phase precursors. Unlike physical coating methods that rely on melting or sputtering, CVD works by introducing volatile chemical compounds into a heated reaction chamber, where they decompose or react at the surface of the substrate. The reaction leaves behind a thin solid layer while gaseous byproducts are removed from the chamber.
The process begins with a substrate—often silicon wafers, metals, or ceramics—placed inside a reaction chamber. A controlled mixture of precursor gases is introduced and then activated by heat, plasma, or light, depending on the specific type of CVD. At the substrate’s surface, the gases undergo chemical reactions that deposit a thin, uniform film of the desired material. This film can be extremely pure and tightly bonded to the substrate, making it highly durable.

CVD is widely used for depositing materials like silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, titanium nitride, diamond-like carbon, and various metal or ceramic coatings. Variants of the process include Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) for uniform semiconductor coatings, Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) which uses plasma at lower temperatures, and Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD) commonly used in the production of LEDs and optoelectronic devices.
The advantages of CVD include excellent control over film thickness and composition, high-quality and high-purity coatings, uniform coverage even on complex geometries, and strong adhesion to substrates. This makes it vital in industries such as semiconductors, aerospace, optics, energy, and cutting tools. However, it also has disadvantages: the process often requires high temperatures, which may limit the choice of substrates; the precursor chemicals can be expensive or hazardous; and equipment costs can be significant.
In the context of fasteners and industrial components, CVD is often used to apply wear-resistant, anti-corrosion, or friction-reducing coatings. For example, titanium nitride or diamond-like carbon layers deposited via CVD can extend the life of cutting tools, improve fastener performance, and protect components operating in harsh environments.
Chipbreaker Screw
A chipbreaker screw is the screw that fastens the chipbreaker (cap iron) to the cutting iron on a hand plane. The chipbreaker sits on top of the blade and its leading edge is set close to the cutting edge; tightening the chipbreaker screw clamps the two together so they act as one unit. This helps curl and break shavings, reduces tear-out, stiffens the iron to limit chatter, and seals the tiny gap where shavings might jam.
On most bench planes it’s a single, relatively large screw—typically steel, with a wide slotted head—threading into the chipbreaker and bearing on a countersink in the blade slot. Some block/specialty planes use a different layout, but the job is the same: provide a rigid, adjustable connection that can be loosened to shift the breaker’s set and re-tightened to lock it.
You’ll also hear “chipbreaker screws” mentioned on planers/jointers: those are the small screws that secure the machine’s chipbreaker bar in front of the cutterhead. Different hardware, same idea—holding the chipbreaker in its working position.
Good practice: keep threads clean, the screw head undamaged, and tighten firmly but not so hard that you distort the chipbreaker or make later adjustments difficult. If the screw won’t hold, check for burrs on the blade slot or a bowed chipbreaker before blaming the fastener.

Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking
Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking (Cl-SCC) is a type of environmentally assisted cracking that occurs when certain metals—especially austenitic stainless steels—are exposed simultaneously to tensile stress and chloride-containing environments (such as saltwater, seawater mist, or de-icing solutions). It is one of the most insidious forms of corrosion because it can cause sudden and catastrophic failure with little or no visible warning.
This phenomenon arises from a combination of three key factors: a susceptible material, a chloride-rich environment, and tensile stress (either from external loads or residual stresses from welding, cold working, or assembly). When all three are present, microscopic cracks can initiate at points of stress concentration—such as welds, notches, or pits—and then grow over time under relatively low stress levels.

Chloride ions are particularly aggressive because they can penetrate and locally destroy the passive oxide film that normally protects stainless steels. Once this film breaks down, localized anodic dissolution begins at the crack tip, while the surrounding metal remains cathodic. The crack then propagates through repeated cycles of film breakdown and repassivation, driven by the tensile stress. This process often produces branching, brittle-looking cracks that can penetrate deep into the metal.
Cl-SCC is most severe at elevated temperatures (typically above 50°C or 120°F) and in environments with high chloride concentrations, such as marine atmospheres, chemical plants, and desalination systems. It is a major concern in stainless steel piping, pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and fasteners.
Prevention strategies include reducing tensile stress (via stress relief or redesign), controlling chloride exposure, using more resistant materials (such as duplex or ferritic stainless steels, or nickel-based alloys), and maintaining lower operating temperatures.
In summary, chloride stress corrosion cracking is a localized, brittle fracture mechanism caused by the combined action of tensile stress and chloride attack on metals—most notably stainless steels—resulting in rapid, often unexpected failure even in materials that otherwise appear corrosion-resistant.
Chrome-Plated Bolt
A chrome-plated bolt is a type of fastener coated with a thin layer of chromium through an electroplating process. The purpose of this coating is mainly to enhance appearance while adding a degree of corrosion resistance, all while maintaining the underlying strength and functionality of the bolt, which is typically made from steel.
In terms of design and construction, the core of a chrome-plated bolt is usually medium- to high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel. During the plating process, a thin layer of chromium is applied to the surface, creating a shiny, mirror-like finish that is visually appealing and more resistant to tarnishing. While this layer does provide some corrosion resistance, it is relatively thin and less durable than specialized coatings like zinc-nickel, phosphate, or ceramic finishes, which are better suited for harsher environments.
The purpose and function of chrome plating are primarily aesthetic, making these fasteners suitable for visible or decorative applications. The plating also provides some protection against oxidation, rust, and wear. However, chrome-plated bolts are not designed for high-corrosion or heavy industrial environments, as the plating can crack, chip, or peel if subjected to excessive stress, which exposes the base metal underneath.
Common applications include the automotive and motorcycle industries, where they are used in engine bays, trim, and other exposed fasteners for a polished look. They are also popular in furniture and appliances for their reflective finish, in architectural and decorative hardware such as fixtures and railing assemblies, and in consumer products where both functionality and appearance matter.
The advantages of chrome-plated bolts are that they provide an attractive, shiny appearance for decorative use, offer light to moderate corrosion resistance, have a smooth surface that is easy to clean, and provide better wear resistance than uncoated steel.
There are also limitations. Chrome plating is not suitable for harsh or marine environments since the coating can chip or peel away. Chrome-plated bolts are more expensive than standard fasteners due to the electroplating process. Over-tightening can damage the chrome layer, and compared to other coatings, they provide less reliable corrosion protection in demanding conditions.

Chromium (Cr)
Chromium is a hard, lustrous metallic element (chemical symbol Cr, atomic number 24) known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, hardness, and shiny, silvery appearance. It is one of the key alloying elements in many steels—especially stainless steel and chromoly (chromium-molybdenum) alloys—and plays a vital role in improving strength, surface durability, and oxidation resistance.
In metallurgy, chromium serves several important functions:
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance:
When chromium is added to steel (usually at least 10.5%), it reacts with oxygen in the air to form a thin, stable layer of chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃). This invisible film protects the underlying metal from rusting, which is why stainless steel doesn’t corrode easily.
Hardness and Wear Resistance:
Chromium increases a metal’s surface hardness and resistance to abrasion. This makes it useful for tool steels, bearings, and fasteners that experience friction, impact, or wear.
High-Temperature Strength:
Chromium helps metals maintain their strength and oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures—important for exhaust systems, turbines, and high-heat industrial equipment.
Aesthetic and Protective Coatings:
Chrome plating (electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto another metal) gives parts a mirror-like finish while improving wear and corrosion resistance. This is common on decorative hardware, automotive trim, and tools.
In its pure form, chromium is steel-gray, brittle, and highly polished. Industrially, it’s produced from chromite ore (FeCr₂O₄) and is used not only in metal alloys but also in pigments, refractory materials, and catalysts.

Chromium Ore
Chromium ore is the natural mineral source of chromium, an essential metallic element used to make stainless steel, superalloys, and industrial coatings. The main chromium ore is chromite, with the chemical formula FeCr₂O₄—an iron chromium oxide. It’s the only commercially significant ore of chromium and the raw material from which nearly all chromium-based metals, chemicals, and alloys are derived.

Composition and Structure
Chromite is a hard, dense, black-to-brownish-black mineral belonging to the spinel group. Its structure consists of:
- Iron (Fe²⁺) ions occupying one set of sites,
- Chromium (Cr³⁺) ions occupying another,
- and oxygen (O²⁻) forming the lattice.
The general chemical formula can vary slightly due to natural substitutions—magnesium, aluminum, and other elements often replace some of the iron and chromium atoms, resulting in slight compositional differences depending on the deposit.
Processing and Production
After mining, chromite ore is refined through several steps:
- Concentration: Crushing, grinding, and separating the chromite from gangue minerals.
- Smelting: In a ferrochrome furnace, chromite is combined with carbon (usually coke) and fluxes to produce ferrochrome (FeCr)—an alloy of iron and chromium.
- Refining: The ferrochrome is then used in stainless steel and other chromium-containing alloys.
Industrial Uses of Chromium Derived from Ore
- Stainless steel: Chromium gives steel its corrosion resistance and shiny finish.
- Alloy steels: Improves hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature strength.
- Electroplating (chrome plating): For decorative and protective coatings.
- Pigments: Produces vivid green, yellow, and red colors in paints, ceramics, and glass.
- Refractory materials: Used to line furnaces because of its heat resistance.
Chromium Oxide
Chromium oxide refers primarily to chromium(III) oxide, with the chemical formula Cr₂O₃. It’s a dark green, extremely stable compound that forms when chromium reacts with oxygen. This oxide is one of the most important and naturally occurring compounds of chromium—it’s the same protective film that makes stainless steel “stainless.”

Formation and Structure
When chromium in an alloy (like stainless steel or chromoly) is exposed to air, it reacts with oxygen to form a thin, dense, self-healing layer of Cr₂O₃ on the metal’s surface. This layer is only a few atoms thick, but it’s chemically inert and adheres tightly, preventing oxygen and moisture from reaching the metal beneath.
This process is known as passivation, and it’s why stainless steels and chromium-plated parts resist rust and corrosion far better than carbon steel.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Cr₂O₃
- Color: Deep green (also used as a pigment known as chromium green or chrome oxide green)
- Melting point: ~2,435°C (4,415°F)
- Hardness: Very high—used as an abrasive and in polishing compounds
- Chemical stability: Resistant to acids, bases, and oxidation
Industrial and Engineering Uses
Corrosion Protection:
The protective oxide film on chromium-bearing metals shields fasteners, tools, and machinery from rust.
Pigments and Coatings:
Used in paints, ceramics, and glass as a durable green pigment.
Polishing and Abrasives:
Finely ground chromium oxide is used in metal polishing compounds (“green rouge”).
Refractory Applications:
Its heat resistance makes it ideal for furnace linings and ceramics.
In Fasteners and Alloys
In fastener materials like stainless steel, chromium-molybdenum (chromoly) steel, and plated bolts, chromium oxide is what prevents corrosion. If the surface is scratched, the oxide layer re-forms automatically, sealing the exposed metal—making it a key reason why chromium-alloyed steels have such long service lives.
Chromoly
Chromoly—short for chromium-molybdenum steel—is a high-strength alloy steel that combines iron with small amounts of chromium (Cr) and molybdenum (Mo). These alloying elements dramatically improve the material’s tensile strength, toughness, and resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion compared to standard carbon steel.
The most common grades are AISI 4130 and AISI 4140, which differ slightly in their carbon content (and thus hardness and machinability). 4130 is easier to weld and form, while 4140 is stronger and used in applications that require higher fatigue resistance.
Chromoly’s key characteristics include:
High tensile strength: It can handle heavy loads and torque without stretching or breaking.
Excellent toughness and ductility: It can deform slightly under stress without cracking, making it ideal for structural and automotive applications.
Good machinability and weldability: Especially in the normalized or annealed condition.
Resistance to fatigue and impact: It holds up under repeated cyclic stresses (important for rotating fasteners and suspension components).
Moderate corrosion resistance: Better than plain carbon steel but not as good as stainless steel—often used with protective coatings.
Because of these properties, chromoly is widely used in aircraft parts, roll cages, bicycle frames, racing car chassis, shafts, and high-performance fasteners such as bolts, studs, and connecting rods.
In the fastener world, chromoly bolts are prized for their high yield and tensile strength, typically exceeding 150,000 psi, allowing them to provide reliable clamping force under extreme loads without failure.
AKA: Chromium-Molybdenum Steel
Circumferential Lines
Markings or grooves that run around the outer edge or face of a nut, following its circumference. These lines often appear as curved or half-moon-shaped grade markings used to indicate the strength classification of nuts, such as those specified in the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts.
Clad Pipe
A clad pipe is a composite steel pipe that combines two different metals — typically a carbon steel or low-alloy steel base for structural strength and an inner corrosion-resistant alloy (CRA) layer such as stainless steel, nickel, or titanium. The goal is to take advantage of both materials: the mechanical strength and low cost of carbon steel with the chemical resistance and durability of high-performance alloys.
In essence, a clad pipe provides the best of both worlds — the outer layer (called the backing or substrate) gives the pipe its ability to withstand pressure, impact, and load, while the inner layer (the cladding) protects against corrosion, erosion, or chemical attack from the fluid being transported.

Manufacturing Process
There are several ways to create clad pipe, depending on the application and required performance:
- Metallurgical bonding (mechanical + heat fusion): The corrosion-resistant alloy layer is bonded to the carbon steel plate using processes such as explosion bonding, hot rolling, or weld overlay. This ensures the two metals are fused at the atomic level, not just mechanically joined.
- Weld overlay cladding: A CRA layer is welded onto the internal surface of a carbon steel pipe using automated welding (e.g., GTAW or SAW), forming a metallurgically bonded corrosion-resistant lining.
- Co-extrusion or roll bonding: Involves hot rolling two metals together into a single billet or sheet that’s then formed into pipe through extrusion or welding.
Typical Materials
- Base material (outer): Carbon steel (A106, A516, or similar) for strength and cost efficiency.
- Cladding material (inner): Stainless steels (304L, 316L), nickel alloys (Inconel 625, Monel 400), titanium, or even copper-nickel, depending on the environment.
Applications
Clad pipes are widely used in industries where corrosion, temperature, or chemical attack are major concerns — especially where solid CRA pipes would be too expensive. Examples include:
- Oil and gas pipelines: Transporting sour gas, crude oil, and seawater injection lines.
- Chemical processing plants: Handling acids, chlorides, and other corrosive media.
- Power generation: Steam lines, desalination plants, and flue gas desulfurization systems.
- Marine environments: Offshore platforms and subsea piping exposed to seawater.
Clamp
An industrial clamp is a mechanical device used to hold, secure, or position objects tightly together to prevent movement or separation. They are essential tools in manufacturing, construction, welding, woodworking, and many other industrial settings. Industrial clamps come in many types, each suited for specific applications, and they are often designed to withstand high pressure, vibration, or heat.
Clamp Load (or Preload) and Clamping Force
The terms clamp load and clamping force are closely related and often used interchangeably, but there’s a subtle distinction in how they’re defined and measured within fastener mechanics.
Clamp load refers to the tensile force generated in a fastener (such as a bolt or screw) when it is tightened. It is the internal tension that develops as the bolt stretches elastically, much like a spring being pulled. This stored tension is what creates the compressive force between the joined parts. In other words, clamp load is the result of tightening torque applied to the fastener.

Clamping force, on the other hand, refers to the compressive force acting on the joint members themselves—the pressure that holds the components together. It’s the external manifestation of the bolt’s internal clamp load. In a properly designed joint, the clamp load and clamping force are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction: the bolt is in tension, while the joint is under compression.
To put it simply:
- Clamp load = the tension inside the bolt created during tightening.
- Clamping force = the compression applied to the joint as a result of that tension.
In an ideal system, these forces balance each other exactly. However, factors like friction, material deformation, surface roughness, and joint flexibility can cause minor differences between the two in real-world applications.
In summary, clamp load is the internal tensile force within the fastener, while clamping force is the external compressive force applied to the jointed parts—two sides of the same mechanical interaction that ensures the joint remains tight and secure.
Clear O-Rings
A clear O-ring is a type of sealing ring made from transparent or translucent elastomeric material, rather than the typical black or colored rubber compounds. These O-rings are functionally identical to standard O-rings—they seal against the passage of liquids or gases—but are made from materials that allow light to pass through, giving them a clear or glass-like appearance.
Clear O-rings are most commonly manufactured from materials such as silicone, polyurethane, or fluorosilicone, which can be formulated for transparency while still maintaining flexibility, resilience, and chemical resistance. They are particularly useful in applications where visual inspection, cleanliness, or aesthetic appearance is important—such as medical devices, laboratory instruments, food processing equipment, and beverage systems. The transparency makes it easy to detect contamination, cracks, or improper seating during assembly or maintenance.
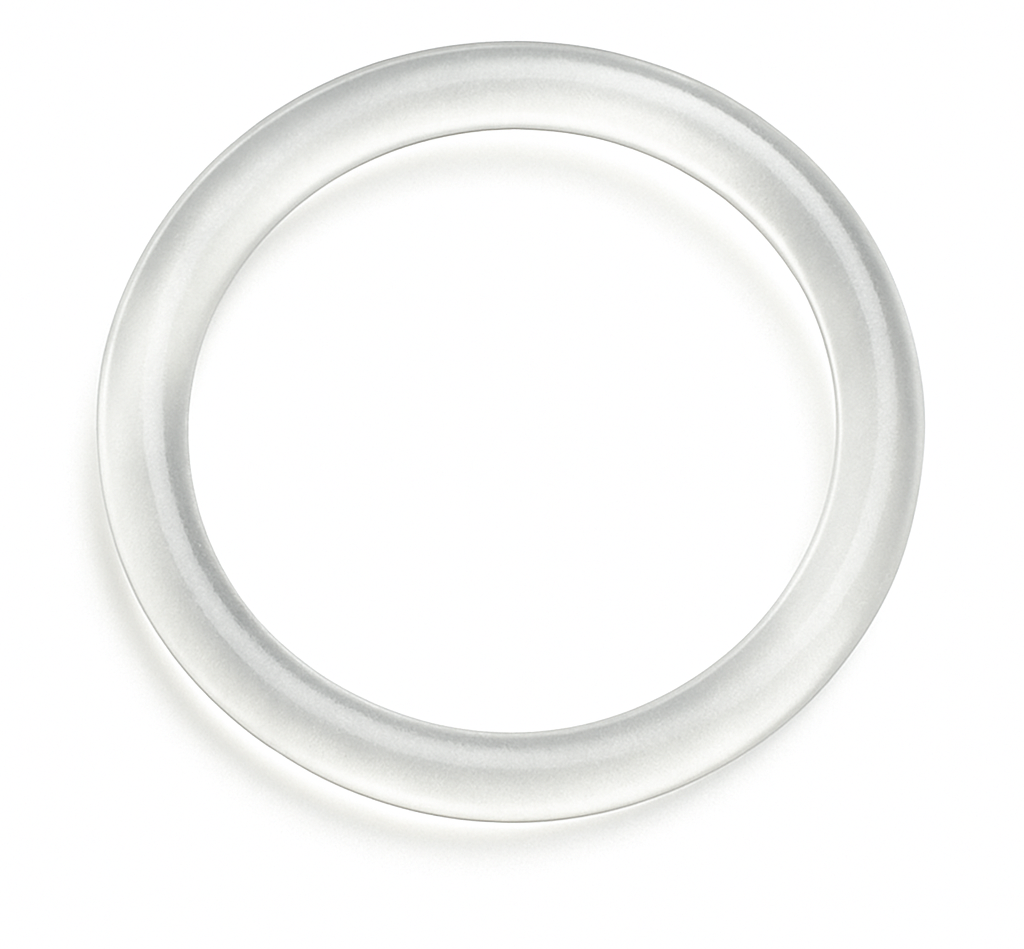

Cleveloc® Nut
A Cleveloc® nut is a type of all-metal self-locking nut designed to resist loosening under vibration, thermal cycling, or heavy loads. Unlike nylon-insert locknuts, it achieves its locking action purely through its metallic design, making it suitable for high-temperature and high-stress environments.
The locking feature comes from a slightly deformed thread section near the top of the nut. As a bolt is threaded in, the interference fit between the nut and bolt threads creates friction, preventing the nut from backing off. Because it is all-metal, the Cleveloc® nut can be reused multiple times and maintains performance in conditions where polymer inserts would fail.
Cleveloc® nuts are commonly used in aerospace, defense, rail, and automotive industries, particularly in assemblies where reliability and vibration resistance are critical. They are valued for their durability, reusability, and ability to maintain secure fastening even in harsh operating environments.

Clevis Pin
A clevis pin is a cylindrical fastener with a head on one end and a cross-hole on the other, designed to be secured with a cotter pin or retaining clip. Unlike bolts, it isn’t threaded along its length and is mainly used to create a pivot or hinge connection.
These pins are common in agricultural machinery, construction equipment, vehicles, and general machinery, where parts need to rotate or move while staying securely connected. They’re valued for being strong, simple, and easy to install or remove.

Clinching Fastener
A clinching fastener is a fastener that locks permanently into thin sheet materials by being pressed into place. During installation, the fastener displaces the surrounding material into grooves on its body, securing it without the need for welding or adhesives.
These fasteners—such as self-clinching nuts, studs, and standoffs—are widely used in electronics, automotive, and sheet metal fabrication because they provide strong, reusable threads in thin materials that couldn’t otherwise support them.
Clip
An industrial clip is a broad term referring to any clamping, securing, or fastening device used in industrial settings to hold or position components, cables, pipes, panels, or other materials. Unlike traditional fasteners (like bolts or screws), clips often allow for quick attachment or removal without tools.
Clipped Head Plow Bolt
Popular in the agriculture industry, Clipped Head Plow Bolts have helped transform the agriculture industry. In many cases, these bolts are used to attach plow shears to agricultural plows, allowing the tractor to churn up dirt and break up the soil — burying crop residues and controlling weeds. The bolts are treated to Grade 5 standards to provide additional strength to get the job done.

Clutch Bolt
A clutch bolt is a specialized fastener used in mechanical clutches, especially in automotive, heavy equipment, and industrial machinery. Its primary function is to securely fasten clutch components—such as the pressure plate, clutch cover, or flywheel—while enduring the extreme torque, vibration, and heat that are generated during clutch engagement and disengagement. Because these bolts operate in one of the most demanding environments in a power transmission system, they are engineered to provide both strength and reliability under constant stress.
These bolts are typically manufactured from high-strength materials, most often alloy steel or other hardened grades, in order to withstand cyclic loading and extreme pressure. The threads are precisely machined to ensure dependable engagement that resists loosening under vibration. The head design varies depending on the application; clutch bolts may feature hex heads, flanged heads, or other configurations that allow a flush, secure fit against rotating clutch components. Another defining characteristic is their ability to resist heat and fatigue. Since clutches generate significant frictional heat during operation, clutch bolts are designed to maintain their clamping force even at elevated temperatures, preventing failure during prolonged use.

In terms of function, clutch bolts play a critical role in holding the clutch pressure plate to the flywheel. This creates the clamping force that allows torque to be transferred between the engine and the transmission. To ensure proper operation, they must be tightened in a precise sequence and to a specified torque value. In many cases, threadlocker compounds or lock washers are used alongside the bolts to prevent them from backing out. Proper tightening is essential because uneven pressure can cause warping, premature wear, or even complete clutch failure.
Clutch bolts are widely applied across industries. In the automotive sector, they are essential to the operation of manual transmission systems in cars, trucks, and motorcycles. Heavy machinery, such as construction equipment, agricultural vehicles, and industrial machines with large torque-transmitting clutches, also depend on clutch bolts for reliable performance. Beyond vehicles, clutch bolts are found in industrial power transmission systems, including presses, pumps, and other driven equipment where secure torque transfer and durability are required.
Clutch Hub Nut
A clutch hub nut is a specialized fastener used to secure the clutch hub to the transmission shaft or gearbox input shaft in vehicles and machinery equipped with a clutch system. The clutch hub itself is the central component that holds the clutch plates, allowing them to engage and disengage power between the engine and the transmission. The nut’s job is to lock this hub firmly onto the shaft so it can rotate in unison with the shaft and transfer torque reliably.
Clutch hub nuts are usually heavy-duty and may be larger in size compared to standard nuts, since they must withstand the constant stress of torque transmission, vibration, and rapid engagement and disengagement cycles. Many designs are self-locking or used with locking devices such as cotter pins, tab washers, or staking grooves to prevent the nut from loosening during operation. Some versions are castellated (slotted) to accommodate a cotter pin, while others are flanged or have special profiles that resist backing off under vibration.
These nuts are critical in motorcycles, cars, trucks, agricultural equipment, and industrial machinery where clutches are part of the drivetrain. If a clutch hub nut loosens or fails, the clutch assembly can lose alignment or disengage unexpectedly, leading to serious mechanical damage or loss of power transmission.
In essence, a clutch hub nut is not just a retaining nut but a safety-critical fastener designed to secure the clutch hub firmly to its shaft, ensuring smooth, reliable operation of the clutch system under demanding conditions.

CNC Lathe
A CNC lathe is a computer-controlled machine tool used to shape metal, plastic, and other materials by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool. “CNC” stands for Computer Numerical Control, meaning the machine’s movements, tool positions, spindle speeds, and cutting operations are all controlled by a programmed set of instructions rather than manual operation.
How a CNC Lathe Works
A cylindrical workpiece is clamped into a rotating spindle. As it spins, the CNC system moves cutting tools along precise, pre-programmed paths to remove material. This allows the machine to create symmetrical, round, or tapered parts with very high accuracy.
Common Parts Made on CNC Lathes
CNC lathes are widely used to manufacture:
- Bolts, screws, and threaded fasteners
- Pins, shafts, bushings, and spacers
- Fittings, couplings, and hydraulic components
- Automotive and aerospace parts
- Precision industrial components
Anything round, concentric, or cylindrical often comes off a CNC lathe.
Why CNC Lathes Are Important in Industrial Manufacturing
- Precision: Can hold extremely tight tolerances.
- Repeatability: Produces identical parts consistently in high volume.
- Speed & Efficiency: Automatic operation reduces labor and increases throughput.
- Complexity: Modern CNC lathes (turning centers) can perform drilling, tapping, milling, and even multi-axis machining in a single setup.
Turning Center vs. Basic CNC Lathe
A simple CNC lathe mainly turns and faces material.
A CNC turning center is more advanced, often featuring:
- Live tooling (milling + turning)
- Sub-spindles
- Automatic bar feeders
- Y-axis movement
- Tool turrets with multiple tools
These machines can produce finished, complex parts in one cycle.
Fastener Industry Tie-In
Many fasteners—especially custom bolts, studs, bushings, standoffs, precision shafts, and specialty components—are produced or finished on CNC lathes. The machine’s ability to produce exact diameters, threads, and surface finishes makes it a core tool in fastener manufacturing and the broader industrial machining world.
CNC Mill
A CNC mill (Computer Numerical Control milling machine) is a programmable machine tool that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a solid workpiece, creating precise shapes, cavities, surfaces, and features. Unlike a CNC lathe—which rotates the workpiece—a CNC mill keeps the part stationary (or moves it in controlled axes) while the cutting tool rotates and moves along multiple directions to carve out geometry.
How a CNC Mill Works
A CNC mill uses a high-speed rotating cutter to remove material as the tool moves along programmed paths called “toolpaths.” The CNC controller precisely manages:
- Tool movement (X, Y, Z axes and more)
- Spindle speed
- Tool changes
- Feed rate
- Depth of cut
This allows the machine to create both simple and extremely complex shapes with high accuracy.
What CNC Mills Make
CNC mills produce parts that require flat surfaces, slots, pockets, angles, contours, and detailed geometric shapes, such as:
- Brackets, housings, and mounting plates
- Mold cavities and dies
- Precision machine components
- Engine and transmission parts
- Fixtures, tooling, and jigs
- Custom fastener heads, sockets, and drive features
- Complex prismatic parts
Anything requiring 3D shaping or precise surface geometry is a candidate for CNC milling.
CNC Mill Types
Vertical CNC Mill (VMC)
- Most common
- Spindle is vertical
- Great for most machining tasks
Horizontal CNC Mill (HMC)
- Spindle is horizontal
- Better for deep cavities, chip evacuation, and production runs
5-Axis CNC Mill
- Can rotate and tilt the part or tool
- Allows machining from multiple angles in one setup
- Ideal for aerospace, molds, medical components, and complex geometry
Why CNC Mills Matter in Industrial Manufacturing
- Precision: Achieves exceptionally tight tolerances
- Versatility: Cuts metals, plastics, composites, and more
- Complexity: Creates features that lathes or manual machines cannot
- Automation: Multi-tool carousels allow complete machining in one cycle
- Repeatability: Perfect for production runs and prototypes
Fastener Industry Connection
CNC mills are used to machine:
- Custom bolt heads
- Socket drives (hex, Torx®, square)
- Washers and spacers
- Thread reliefs and undercuts
- Complex specialty fasteners and fittings
- Tooling and dies used to manufacture fasteners
While CNC lathes handle the “round” world of manufacturing, CNC mills create the flat, angled, contoured, or geometric features that lathes can’t produce.
Coarse Thread
A coarse thread is a screw or bolt thread with fewer, deeper, and more widely spaced threads compared to a fine thread of the same diameter. This design makes coarse threads easier to assemble, more resistant to stripping, and better suited for softer materials or rough conditions.
They are commonly used in general-purpose fasteners, construction, and automotive applications, where durability, speed of installation, and resistance to damage are more important than fine adjustment or maximum tensile strength.
Cobalt (Co)
Cobalt is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal with the chemical symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is a transition metal known for its magnetic properties, wear resistance, and ability to form strong, heat-resistant alloys. Cobalt is chemically similar to iron and nickel, and it plays an essential role in both industrial manufacturing and biological systems.
In metallurgy, cobalt is most valued for its use in superalloys—high-performance alloys that retain strength and stability at extreme temperatures. These alloys are used in jet engines, gas turbines, cutting tools, and space applications. Cobalt improves hardness, tensile strength, and resistance to oxidation and corrosion, especially under high stress and heat.
Cobalt compounds also have important uses. Cobalt oxide and cobalt aluminate provide vivid blue pigments known as cobalt blue, used in ceramics, glass, and paints since ancient times. Cobalt salts are used as catalysts in chemical industries and in electroplating, providing a hard, attractive, and corrosion-resistant surface finish.
In modern technology, cobalt is critical in rechargeable batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries, where it stabilizes the cathode and improves energy density and lifespan. This makes cobalt a key material for electric vehicles, smartphones, and renewable energy storage.
Biologically, cobalt is an essential trace element as part of vitamin B₁₂ (cobalamin), which is necessary for red blood cell production and neurological function. However, excessive exposure to cobalt (such as dust or fumes in industrial settings) can be toxic, leading to respiratory or cardiac issues.
Cobalt is typically obtained as a byproduct of nickel and copper mining, with major producers including the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Russia, Canada, and Australia.

Cobalt Oxide
Cobalt oxide refers to a group of chemical compounds composed of cobalt and oxygen, the most common being cobalt(II) oxide (CoO) and cobalt(III) oxide (Co₂O₃). These oxides are important industrial materials used in ceramics, batteries, catalysts, and pigments because of their unique color, magnetic, and chemical properties.

Cobalt(II) oxide (CoO) is a grayish or olive-green powder that forms when cobalt metal is heated in air at moderate temperatures. It has a cubic crystal structure and is slightly soluble in acids but insoluble in water. CoO is used primarily as a pigment (giving a bluish-green tint), in glass and enamel production, and as a precursor in making other cobalt salts and compounds. It’s also used in lithium-ion batteries as part of the cathode material, contributing to high energy density and stability.
Cobalt(III) oxide (Co₂O₃), on the other hand, is a black crystalline powder that forms when cobalt compounds are oxidized at higher temperatures or in strong oxidizing environments. It contains cobalt in the +3 oxidation state and is less stable than CoO. Co₂O₃ is used mainly as an oxidizing agent, in ceramic glazes, and in certain chemical catalysts, especially for hydrocarbon oxidation and hydrogenation reactions.
Another related compound is cobalt(II,III) oxide (Co₃O₄), which is actually the most stable and technologically important cobalt oxide. It appears as a black powder and contains both +2 and +3 oxidation states of cobalt. Co₃O₄ is widely used in rechargeable batteries, particularly in lithium-ion and sodium-ion cathodes, as well as in supercapacitors, solar cells, and gas sensors. It also functions as a catalyst in environmental and industrial processes such as CO oxidation and water splitting.
Coil Threaded Rod
A coil threaded rod is a type of metal rod that is fully threaded along its length and designed specifically for use in concrete formwork and construction applications. Unlike standard threaded rods, a coil threaded rod uses a specialized thread profile (coil threads) that is heavier and more durable to withstand the stresses of repetitive use, particularly in environments where frequent assembly and disassembly are required.
Cold Forming
Cold forming is a high-speed metalworking process used to manufacture fasteners and other components by plastically deforming metal at or near room temperature. Instead of heating the material to soften it, cold forming relies on powerful mechanical presses and precision dies to force the metal into the required shape. Because the process works the metal while it remains cold, it preserves and even enhances material strength through work hardening, making the finished fasteners stronger and more durable than those produced by machining or hot forming.
The process begins with wire or rod stock, which is drawn to the proper diameter for the fastener being produced. The stock is cut into blanks and then fed into a multi-station cold forming machine. The first major step is heading, where the end of the blank is upset or deformed to create the head of the fastener. The next step is often extrusion, which forces metal to flow into die cavities to shape the shank or special features of the fastener. Excess material may then be removed through trimming, ensuring precise geometry. Finally, thread rolling is performed by pressing the blank between dies that displace material to form threads rather than cutting them, producing stronger threads with excellent surface finish.
The advantages of cold forming are considerable. It is highly efficient, producing minimal waste since the metal is displaced rather than cut away. The process is extremely fast, capable of producing hundreds of parts per minute, making it well-suited for high-volume production. Because the material is work-hardened, the resulting fasteners have superior mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, and reliability. The process also achieves tight dimensional tolerances and smooth surface finishes, which reduces the need for secondary machining.
However, there are also disadvantages. The dies and tooling are costly to design and manufacture, which makes cold forming less economical for small production runs or prototypes. The process is best suited to parts with relatively simple geometries; very large fasteners or complex shapes are better made by hot forging or machining. Additionally, because cold forming strain-hardens the metal, secondary operations such as drilling or machining can be more challenging.
In terms of applications, cold forming is one of the most important processes in the fastener industry. It is used to produce bolts, screws, rivets, nuts, and specialty fasteners in massive volumes, with consistent quality and strength. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and general manufacturing depend on cold-formed fasteners for safety-critical and cost-sensitive applications.
Cold Heading
A specific type of cold-forming. This process is primarily used to create the head of a fastener, such as a bolt, screw, or rivet. The head is formed by rapidly striking or compressing a short piece of metal wire, known as a blank, at room temperature, forcing the material to flow into a desired shape within a die. Like all cold-forming processes, this method increases the fastener's strength and produces parts with minimal material waste.
Cold Rolling
Cold rolling is a metalworking process where a metal sheet, strip, or wire is passed through rollers at room temperature to reduce thickness, improve surface finish, and increase strength through strain hardening. In fasteners, wire stock is often cold rolled first to achieve the correct diameter and mechanical properties before further shaping.
Collar Bolt
A collar bolt is a specialized fastener that features a smooth, unthreaded section—known as the collar—beneath the head before the threaded portion begins. This collar provides a precise locating surface and allows the bolt to act not only as a clamping device but also as an alignment and shear-resisting element. Manufactured from high-strength steels or alloys, collar bolts are engineered for critical applications where both tensile and lateral loads are present. The collar is machined to tight tolerances so it can fit snugly into a drilled hole, helping to align parts while the threaded section secures them with a nut. They are commonly used in automotive assemblies, heavy machinery, aerospace structures, and industrial equipment where precision and durability are essential.
Collar bolts are also valued for their performance in environments with high vibration and thermal cycling. Because the collar fits tightly in its bore, it prevents the joint from shifting or loosening under vibration more effectively than a fully threaded bolt. In heat exchangers, turbines, and other pressure equipment, collar bolts are used to secure and align critical components such as tube sheets and baffles. Their ability to resist both shear forces and thermal stress makes them particularly suitable for these demanding conditions. Often paired with locking nuts, washers, or thread treatments, collar bolts maintain clamping force and structural integrity even in systems exposed to constant vibration and fluctuating temperatures.

Collar Nut
A collar nut is a type of fastener designed with an extended cylindrical section, or “collar,” beneath the hexagonal head. This collar provides additional surface area for load distribution, helping the nut secure components more effectively than a standard nut. It also ensures stability and alignment in applications where precise positioning of the nut is critical.
Collar nuts are commonly made from high-strength steel, stainless steel, or other durable alloys, and they may be plated or coated for corrosion resistance. The extended collar portion can be smooth, flanged, or threaded, depending on the specific application and required fit.
The primary function of a collar nut is to provide strong, secure fastening while reducing stress concentration on the mating surfaces. The collar acts as an integrated washer, preventing loosening from vibration and distributing clamping force more evenly across the joint. This makes them particularly effective in dynamic or high-load assemblies.
They are often used in automotive, aerospace, machinery, and construction applications, where both secure fastening and alignment are essential. Advantages of collar nuts include their added strength, improved stability, and resistance to loosening. However, they are typically more expensive than standard nuts and may require additional space for installation due to their larger dimensions.

Collet Nut
A collet nut is a fastening component used to secure a collet onto a spindle, tool holder, or chuck in machining and woodworking applications. The collet itself is a slotted, cone-shaped sleeve that grips a tool or workpiece when compressed, and the nut provides the force needed to clamp it in place. When the collet nut is tightened, it draws the collet into its tapered seat, causing it to contract and create uniform radial pressure around the tool or workpiece. This action allows the tool to be held firmly and precisely during operation.
In terms of design and construction, a collet nut has internal threads that match the spindle or tool holder, and an internal taper that corresponds to the taper of the collet. The outside of the nut is usually hexagonal or round with flats or grooves, so it can be tightened with a spanner wrench. These nuts are manufactured from hardened steel or alloy steel to withstand repeated tightening cycles, and they are often treated with coatings such as black oxide or nickel plating to resist wear and corrosion.
The purpose and function of a collet nut are to provide consistent clamping force and accuracy during machining. By evenly compressing the collet, the nut keeps the tool or workpiece centered, minimizes runout, and ensures stability even at high speeds. This precision is essential for producing accurate parts and for extending the life of both the tool and the machine spindle.
Common applications for collet nuts include CNC machining centers and milling machines, where they are used to hold drills, end mills, and rotary cutters. They are also employed in grinding machines for securing small-diameter tools, in routers and woodworking equipment for clamping bits, and in lathes for holding small workpieces or specialized tools. Their versatility makes them a standard component in many industries requiring precision.
The advantages of collet nuts include their ability to provide uniform clamping pressure, maintain excellent concentricity, and keep runout very low. They allow for secure gripping with minimal tool slippage, enable quick tool changes, and can accommodate a wide range of tool diameters through interchangeable collets. This combination of security and flexibility makes them indispensable in precision machining.
However, there are limitations. Collet nuts must be properly matched with the correct collet type to function correctly; using mismatched components can damage the collet, nut, or tool holder, and reduce accuracy. Over-tightening can deform the nut or collet, compromising performance. Both collets and nuts wear over time and need to be replaced periodically to maintain precision. Finally, collet systems are not ideal for very large tool diameters or heavy-duty clamping applications, where hydraulic chucks or shrink-fit tool holders may be more suitable.

Compression Nut
A compression nut is a type of specialized nut used in compression fittings, which are commonly found in plumbing, gas, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems. Its purpose is to secure a tube or pipe to a fitting and create a tight, leak-proof seal without the need for soldering, welding, or adhesives.
In a compression fitting, the nut works together with a ferrule (also called an olive) and the fitting body. The compression nut threads onto the body of the fitting and, as it is tightened, it forces the ferrule to compress around the outside diameter of the pipe or tube. This compression creates a secure mechanical grip and a pressure-tight seal between the tube and the fitting.

Compression nuts are typically made of brass, stainless steel, or other corrosion-resistant alloys depending on the application. Brass compression nuts are common in household plumbing for water lines, while stainless steel versions are used in harsher environments such as chemical, marine, or high-pressure industrial systems.
One of the main advantages of compression nuts is that they allow for reliable connections without special tools or heat, and they can often be disassembled and reassembled when maintenance or adjustments are needed. However, over-tightening can damage the ferrule or tubing, while under-tightening may cause leaks, so proper installation is essential.
In short, a compression nut is the threaded part of a compression fitting system that, when tightened, compresses a ferrule to lock a tube or pipe securely into place and provide a durable, leak-resistant seal.
Compression Washer
A compression washer is a type of washer designed to act as a spring element in a bolted joint, helping to maintain tension, absorb shock, and resist loosening caused by vibration or thermal expansion. Unlike plain flat washers, which simply distribute load, compression washers are engineered with a specific geometry—often conical, curved, or split—that allows them to deflect slightly under load. This deflection provides a spring-like action that compensates for any relaxation in the joint, helping keep the fastener tight.
The most common form of compression washer is the spring washer (such as a split lock washer), which has a helical cut so that when compressed, it exerts a continuous force against the nut and bolt head. Another type is the Belleville washer, a conical washer that flattens under load and provides high spring force in a compact space. Wave washers, with a wavy profile, are also used in lighter-duty applications where elastic cushioning is needed.
Compression washers are widely used in machinery, automotive systems, electrical assemblies, and industrial equipment where fasteners are subject to vibration, dynamic loads, or thermal cycling. By maintaining tension, they reduce the likelihood of loosening, fatigue, or joint failure, making them an important component in critical fastening applications.
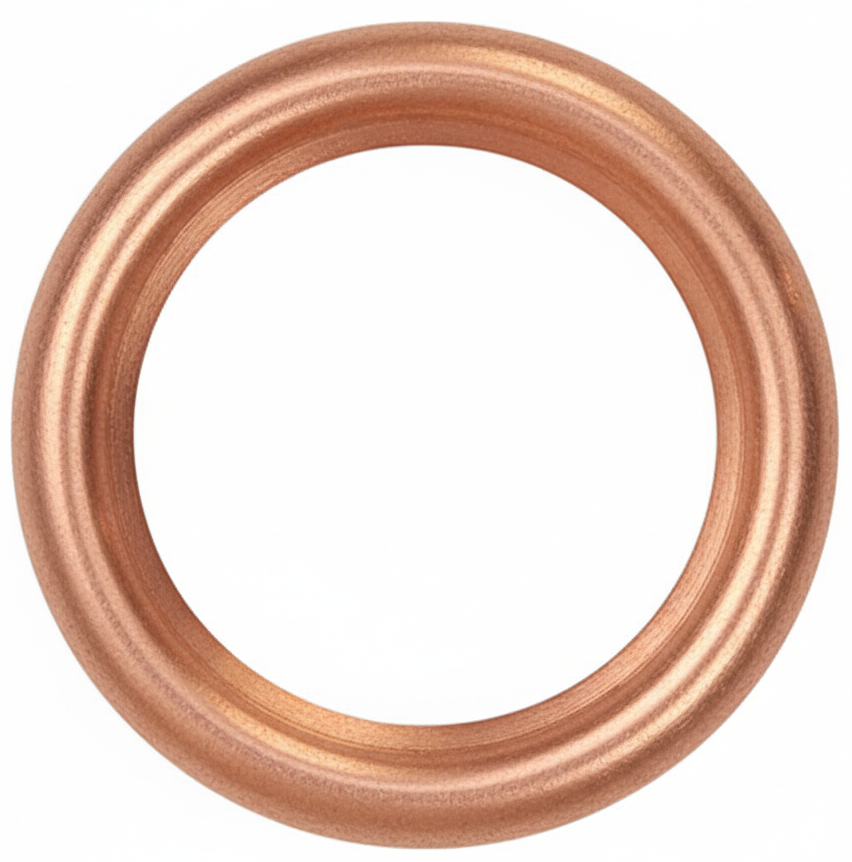

Concrete Cancer
Concrete cancer is a term used to describe the progressive deterioration of concrete caused by the corrosion of the steel reinforcement (rebar) embedded within it. When the reinforcing steel rusts, it expands—sometimes up to four times its original volume—creating internal pressure that causes the surrounding concrete to crack, spall (flake off), and weaken structurally. Over time, this process can compromise the integrity, safety, and appearance of a structure.

The root cause of concrete cancer is usually moisture and oxygen penetrating the concrete, which allows corrosion to begin. This often happens when the protective alkaline environment within concrete (which normally prevents rust) is disrupted. Common triggers include:
- Water ingress, especially through cracks or porous concrete.
- Chloride contamination, often from sea air, saltwater, or de-icing salts.
- Carbonation, a chemical reaction between carbon dioxide and the calcium hydroxide in concrete, which lowers the pH and allows steel to rust.
- Poor construction practices, such as insufficient concrete cover over rebar or use of low-quality materials.
Once corrosion begins, the rust expands and pushes against the surrounding concrete, causing visible symptoms like cracks, rust stains, bulging, flaking, or exposed rebar. If left untreated, the damage spreads and accelerates, leading to costly repairs or even structural failure.
Repairing concrete cancer typically involves removing the damaged concrete, cleaning or replacing corroded rebar, applying anti-corrosion treatments, and then recasting or patching the area with high-quality repair mortar. In some cases, protective coatings, sealants, or cathodic protection systems are used to prevent recurrence.
AKA: Reinforcement Corrosion
Concrete Nails
Concrete nails are hardened steel nails specifically designed to penetrate and hold in concrete, masonry, or brick. They are much stronger and more brittle than ordinary nails, allowing them to drive into tough materials without bending.
Conduit Fastener
A conduit fastener is a fastening device specifically designed to secure electrical conduit—tubing or piping that houses and protects electrical wires—to walls, ceilings, machinery, or structural elements. Because conduit provides both mechanical protection and routing for wiring, the fasteners must hold it firmly in place while allowing for proper alignment and safe installation.

Conduit fasteners come in many forms depending on the type of conduit being used (rigid metal conduit, EMT, flexible conduit, or PVC). Common examples include conduit straps, which are semi-circular clamps that screw into a surface to hold the conduit; conduit hangers, which suspend conduit runs from overhead supports; and beam clamps or channel fasteners, which attach conduit to structural framing. Some designs allow for quick installation with snap-in or spring mechanisms, while others require screws, bolts, or nuts for a more secure hold.
In use, conduit fasteners ensure that the conduit remains properly supported, aligned, and protected from vibration or movement that could damage wiring. They also help installations meet electrical code requirements, which specify spacing, support intervals, and secure mounting methods to ensure long-term safety and performance.
Conduit Locknut
A conduit locknut is a specialized nut used in electrical installations to secure a piece of electrical conduit (metal or plastic tubing) to an electrical box, enclosure, or panel. Its main purpose is to lock the conduit fitting firmly in place, ensuring a stable and grounded connection between the conduit and the box while preventing the conduit from loosening or rotating.
Structurally, a conduit locknut is a thin, hexagonal or round nut with sharp internal threads and often external gripping teeth or serrations on one face. These teeth bite into the metal of the electrical box or panel when tightened, creating a mechanically secure and electrically conductive bond. In metallic conduit systems—such as EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing), RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit), or IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit)—this bond ensures continuity of the grounding path, which is essential for electrical safety.
Locknuts are typically made from zinc-plated steel, galvanized steel, or stainless steel, though nylon or plastic versions exist for non-metallic conduits (PVC, ENT) where electrical grounding is not required.
During installation, the conduit is first inserted into the knockout hole of the box, and the locknut is threaded onto the conduit’s male threads from the inside. Once tightened (usually with a conduit locknut wrench or pliers), the nut compresses the connection, keeping the conduit from moving or vibrating loose.

Conical Keps Lock Nut
Conical Keps Lock Nuts feature a free-spinning nut and an integrated conical spring lock washer designed to prevent loosening caused by vibration. When tightened onto a bolt, screw, or stud, the spring action of the conical washer creates resistance against rotation. The added spring tension helps maintain a secure assembly and is suitable for light-duty automotive and machinery assemblies where vibration is a concern. This fastener is similar to the External Tooth Keps Lock Nut with the added advantage that the spring lock washer will not scratch or damage its installation surface.

Conversion Coating
Conversion coating is a chemical treatment applied to the surface of metals to enhance corrosion resistance, improve paint adhesion, and sometimes provide lubrication. Unlike simple coatings that add a separate layer on top of the metal, conversion coatings work by chemically altering the metal’s surface itself, creating a thin, protective compound layer that bonds directly to the substrate. This makes the finish more durable and resistant to chipping or peeling compared to applied coatings like paint.
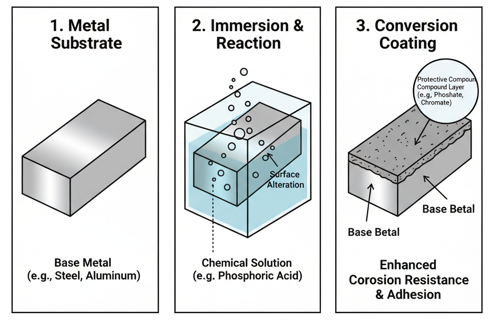
The process typically involves immersing or spraying the metal with a solution that reacts with its surface. The reaction converts the outermost metal layer into an insoluble compound—such as phosphate, chromate, or oxide—that tightly adheres to the base material. Each type of conversion coating has specific benefits: phosphate coatings are common in automotive and industrial uses for improving paint adhesion; chromate coatings are widely used on aluminum and zinc for corrosion protection; and anodizing, a form of oxide conversion, is used to harden aluminum surfaces while allowing for coloring.
Conversion coatings are commonly found in industries where both corrosion resistance and paint performance are critical. They are used in aerospace, automotive, appliances, and construction fasteners, where untreated metals might quickly corrode or fail. Beyond corrosion resistance, these coatings also reduce friction, prevent galling, and extend service life. In fastener applications, conversion coatings are particularly important because they not only protect against rust but also ensure that applied paints, sealants, or additional coatings adhere effectively, providing long-term reliability in harsh environments.
Copper (Cu)
Copper is a reddish-orange metallic element with the chemical symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is one of the oldest metals used by humans and remains one of the most important materials in modern industry due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability.
Copper is a ductile, soft, and highly conductive metal, second only to silver in electrical performance. Because of this, it is the primary material for electrical wiring, motors, generators, circuit boards, and power transmission systems. It’s also used extensively in plumbing, roofing, electronics, and industrial machinery. In addition, its ability to form alloys easily makes it the foundation for other important engineering metals such as brass (copper + zinc) and bronze (copper + tin).
When exposed to air, copper slowly oxidizes, forming a thin, protective surface layer known as a patina. Initially reddish-brown, this layer eventually turns greenish-blue (copper carbonate), as seen on the Statue of Liberty. This natural patina protects the metal underneath from further corrosion, which is why copper can last for centuries even in harsh environments.
Copper is also an essential trace element in the human body, necessary for enzymes that aid in energy production, connective tissue formation, and iron absorption. However, excessive exposure to copper dust or compounds can be toxic.
Industrially, copper is mined primarily from sulfide ores such as chalcopyrite (CuFeS₂) and bornite (Cu₅FeS₄). The metal is extracted and refined through smelting and electrorefining. Major producers include Chile, Peru, China, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
In terms of physical properties, copper has a melting point of 1,085°C (1,985°F), a density of 8.96 g/cm³, and an unmistakable metallic reddish luster. It is nonmagnetic, easily formed into sheets or wires, and highly recyclable—nearly all copper ever mined is still in use today because it can be reused without losing quality.

Corrosion (Metallic Corrosion)
Metallic corrosion is the gradual degradation of a metal through a chemical or electrochemical reaction with its environment, resulting in the conversion of the metal into more stable compounds such as oxides, hydroxides, or sulfides. In essence, it is the reversion of refined metal back to its natural, ore-like state—for example, iron rusting back into iron oxide.
Corrosion occurs because most metals exist in a high-energy, unstable state after refining from their ores. When exposed to oxygen, water, acids, salts, or other reactive substances, they naturally tend to return to a lower-energy, oxidized form. The most common and damaging type of metallic corrosion is electrochemical corrosion, which involves the flow of electrons between anodic (oxidizing) and cathodic (reducing) sites on the metal’s surface.
Here’s how it happens:
1. At the anode, metal atoms lose electrons and form positive metal ions — for example:
Fe → Fe²⁺ + 2e⁻
This is oxidation, and it’s the site of metal loss.
2. At the cathode, a reduction reaction occurs, often involving oxygen and water, such as:
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
3. The electrons released at the anode travel through the metal to the cathode, completing the circuit. The metal ions produced at the anode can react further with oxygen or water to form corrosion products like iron oxide (rust).
Environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, pH, and salt concentration greatly influence the rate of corrosion. For example, saltwater accelerates corrosion by increasing electrical conductivity, while acidic environments promote metal ion dissolution.
There are several types of metallic corrosion, including:
- Uniform corrosion, where the surface degrades evenly (common in steel rusting).
- Galvanic corrosion, which occurs when two dissimilar metals are electrically connected in an electrolyte, causing one to corrode preferentially.
- Pitting corrosion, a localized attack that produces small but deep holes.
- Crevice corrosion, which occurs in shielded or tight areas where oxygen levels are low.
- Intergranular and stress corrosion cracking, which occur along grain boundaries or under tensile stress in corrosive environments.
Prevention and control of corrosion rely on barrier coatings (paint, plating, galvanizing), cathodic protection, corrosion-resistant alloys (like stainless steel, titanium, or Inconel), and environmental control (e.g., desiccation or pH adjustment).
Corrosion Nucleation
Corrosion nucleation is the initial stage in the corrosion process where the very first microscopic sites of corrosion begin to form on a metal surface. At this stage, the metal is still mostly intact, but localized regions—often defects, impurities, scratches, grain boundaries, or inclusions—become energetically favorable spots where corrosion reactions can start.
When a metal is exposed to an aggressive environment (such as moisture, salts, acids, or other electrolytes), small electrochemical cells form on the surface. Certain areas act as anodic sites, where metal atoms begin to lose electrons and dissolve, while surrounding areas act as cathodic sites, where reduction reactions occur. This uneven distribution of activity causes specific points to become the “nuclei” or seeds of corrosion.

Nucleation is critical because it determines how corrosion will progress. If the nucleation sites remain few and isolated, corrosion may advance slowly and be easier to manage. But if many nuclei form across the surface, corrosion spreads more rapidly, leading to generalized damage. In other cases, nucleation may be highly localized, giving rise to pitting corrosion, crevice corrosion, or other aggressive localized attack that can cause sudden failures.
The factors influencing corrosion nucleation include the material’s microstructure, surface condition, applied stresses, environmental chemistry, and temperature. Understanding and controlling this stage is important in corrosion prevention because once nucleation sites establish themselves, corrosion tends to accelerate and propagate outward.
Cotter Pin Extended Tip
Cotter Pins are commonly used to lock slotted nuts into place in high-vibration applications. The pin slides through the bolt’s tap hole and in between the slots on the nut, preventing the nut from backing out. Earnest’s Cotter Pins are designed with an extended prong style and chisel point for easy insertion.
Countersunk Bolt
A countersunk bolt is a type of bolt designed so that its head sits flush with or below the surface of the surrounding material once installed. This is achieved by using a specially shaped head—typically flat or conical—that fits into a countersunk hole, which is a conical recess cut into the material. The result is a smooth surface without protrusions, making the joint both streamlined and snag-free.
The head of a countersunk bolt is usually angled at 82° or 90°, though other angles exist depending on standards and applications. The flat top and tapered underside of the head allow it to wedge into the countersunk hole, creating a tight, flush fit. The shank may be fully or partially threaded, depending on whether the design prioritizes clamping strength or shear resistance.

Countersunk bolts are widely used in applications where a flush surface is important for aerodynamics, aesthetics, safety, or clearance. In the aerospace and automotive industries, they reduce drag and prevent snag points. In machinery, furniture, and architectural assemblies, they allow for smooth finishes without bolt heads sticking out. They are often used with countersunk washers or special nuts in cases where extra load distribution or alignment is needed.
Because of their geometry, proper installation requires drilling and countersinking the hole before fastening. This ensures full contact between the bolt head and the conical recess, which helps distribute load evenly and prevents loosening.
Countersunk Washer
A countersunk washer is a specially shaped washer designed to be used with countersunk screws or bolts. Unlike flat washers, which have a level surface, countersunk washers have a beveled or angled top surface that matches the angle of a countersunk fastener head (commonly 82°, 90°, or 100°). This allows the screw head to sit flush within the washer, creating a smooth, even surface.
These washers serve two main purposes. First, they distribute the load of the fastener over a larger surface area, which helps prevent damage to the material being fastened—especially softer materials like wood, plastic, or aluminum. Second, they provide a clean, finished appearance by ensuring that the countersunk screw sits flush and properly aligned, even if the underlying material does not have a precisely machined countersink.
Countersunk washers are often used in applications where aesthetics and secure fastening are both important, such as furniture, aerospace components, and precision assemblies. In fastener and mechanical contexts, they are especially useful when the workpiece cannot be easily countersunk, or when additional strength and surface protection are required at the fastener interface.
Crane Mat Bolt
A crane mat bolt is a heavy-duty fastener designed to hold together crane mats—the large, thick wooden or composite platforms used to support cranes and heavy equipment on soft or unstable ground. These bolts secure the individual timbers or panels that make up the mat, ensuring it stays rigid, stable, and capable of distributing massive loads.

Crane mat bolts are typically long, high-strength bolts (often made from Grade 8 or equivalent alloy steel) with coarse threads and heavy hex heads or nuts. They’re engineered to resist shear, bending, and tensile stresses that occur when the mat flexes under extreme weight. Many versions include locking nuts or washers to prevent loosening due to vibration, and some use galvanized or zinc coatings for corrosion resistance in wet or muddy environments.
Crane Rail Clip
A crane rail clip is a mechanical clamping device that secures a crane rail to its supporting structure—usually a steel base plate or concrete foundation—while allowing slight movement to accommodate vibration and thermal expansion.
There are two main versions of crane rail clips:
The bolted version uses high-strength bolts and nuts to fasten the clip to the rail base plate. It is adjustable, making it easy to install and realign, and it typically allows limited lateral movement of the rail. Bolted clips are preferred for applications where rails may need to be repositioned or replaced, such as overhead cranes, gantry cranes, and rail-mounted material handling systems.
The welded version is permanently attached by welding the clip body directly to the supporting structure. It offers a stronger, vibration-resistant connection ideal for heavy-duty or high-impact environments like steel mills, ports, and shipyards. Although the clip itself is welded, it still includes a clamping bolt or block to secure the rail and allow minimal controlled movement for thermal expansion.

Creep Resistance
Creep resistance is the ability of a material to withstand time-dependent deformation under constant stress at elevated temperature. In high-temperature environments—such as in turbine blades, power plant piping, jet engines, or chemical reactors—materials experience a gradual, permanent strain called creep, even when the applied stress is well below their normal yield strength. The higher the temperature (usually above about 0.4 times the material’s melting temperature in Kelvin), the more pronounced the creep behavior becomes.
The rate at which creep occurs during long-term service is described by the Norton–Bailey power law, expressed as ε˙ = Aσⁿe^(−Q/RT). In this equation, ε˙ represents the steady-state creep strain rate, A is a material constant, σ is the applied stress, n is the stress exponent (indicating how strongly stress influences creep rate), Q is the activation energy for creep, R is the universal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature. The exponential term, e^(−Q/RT), shows how sensitively creep rate increases with temperature—small temperature rises can dramatically accelerate deformation.
Creep typically progresses through three stages: primary creep, where deformation slows as the material strain-hardens; secondary creep, the steady-state phase where the rate is nearly constant and most design calculations focus; and tertiary creep, where damage accelerates, leading to rupture. Materials that possess high creep resistance, such as nickel- and cobalt-based superalloys, stainless steels, titanium alloys, molybdenum, and tungsten, are engineered to limit dislocation motion and grain boundary sliding—the two main mechanisms that drive creep. Techniques like solid solution strengthening, precipitation hardening, and grain boundary stabilization enhance their ability to resist this slow, temperature-driven deformation.
Crescent Spring Washer
A Crescent Spring Washer—also known as a C-washer or curved spring washer—is a type of washer shaped like a slightly curved disc (resembling a crescent or shallow arc). It is used to provide light, continuous spring pressure between fastened surfaces, helping to maintain tension and absorb vibration.
Crevice Corrosion
Crevice corrosion is a localized form of corrosion that occurs in narrow, confined spaces where oxygen and other environmental conditions become trapped, creating a chemical imbalance. These spaces—called crevices—can exist between two metal surfaces or between a metal and a nonmetal, such as under washers, gaskets, fastener heads, lap joints, or even beneath dirt and deposits.
The problem begins when a small volume of electrolyte (like saltwater or moisture) enters the crevice. Inside the tight space, oxygen becomes depleted because it cannot easily circulate. Meanwhile, the surrounding surface outside the crevice remains exposed to oxygen. This difference in oxygen concentration creates an electrochemical cell: the area inside the crevice becomes anodic (where metal dissolves), and the area outside becomes cathodic (where reduction occurs). As a result, the trapped electrolyte inside the crevice becomes more acidic and chloride-rich, accelerating metal dissolution.

Over time, this process leads to pitting, discoloration, and material loss concentrated within the crevice. It is particularly problematic because it can occur beneath apparently intact surfaces, making it difficult to detect until severe damage has occurred. Stainless steels, aluminum alloys, and other passive metals are especially susceptible to crevice corrosion when their protective oxide film is compromised in these oxygen-starved environments.
Common prevention methods include designing joints to minimize tight gaps, using non-absorbent gaskets, selecting corrosion-resistant alloys, and applying protective coatings or sealants. Maintaining clean surfaces and avoiding stagnant conditions also help reduce risk.
In summary, crevice corrosion occurs when oxygen-starved microenvironments form within tight spaces on metal surfaces, leading to localized chemical attack that can severely weaken fasteners and assemblies over time.
Crimp Ring Retainer
A crimp ring retainer is a fastening component designed to secure, hold, or lock another part in place through the process of crimping, which permanently deforms the ring around a groove, shaft, tube, or fitting. Unlike removable retaining rings such as snap rings or circlips, a crimp ring retainer is intended to serve as a permanent or semi-permanent retention method once installed, making it highly reliable in demanding applications.
In terms of design and construction, a crimp ring retainer is typically made from a thin, ductile metal or alloy. It is manufactured to be slightly smaller than the groove or fitting it will secure. During installation, the ring is first positioned over the target feature and then mechanically crimped using a specialized tool. This crimping process plastically deforms the ring, forcing it to conform tightly to the shaft, groove, or housing, and creating a secure and lasting fit.
The primary purpose of a crimp ring retainer is to ensure retention by holding components in place on a shaft, tube, or within a housing to prevent axial movement. Unlike snap rings, which depend on spring tension, crimp ring retainers achieve permanent locking by deformation, making them much less likely to loosen in high-vibration environments. Their compact design provides secure retention without requiring large grooves, shoulders, or threaded fasteners, which helps save both space and material in an assembly.
These retainers see widespread use in several industries. In automotive applications, they are commonly found in steering systems, CV joints, and bearing assemblies. In aerospace and industrial equipment, they secure bushings, bearings, or seals where space is limited and reliability is essential. In plumbing and piping, a related variation known as the PEX crimp ring is used with fittings to create leak-proof connections, although this type is more often referred to as a crimp ring rather than a retainer.
Crimp ring retainers offer several advantages. They provide high resistance to loosening under shock and vibration, making them dependable in dynamic environments. They are simple, lightweight, and cost-effective, and they can be installed quickly using crimping tools. However, they also come with limitations. They are generally non-reusable because once crimped, the ring must be cut off for removal. They require tool access during assembly, which can restrict their use in confined spaces, and they are only suitable for applications where permanent fastening is acceptable.
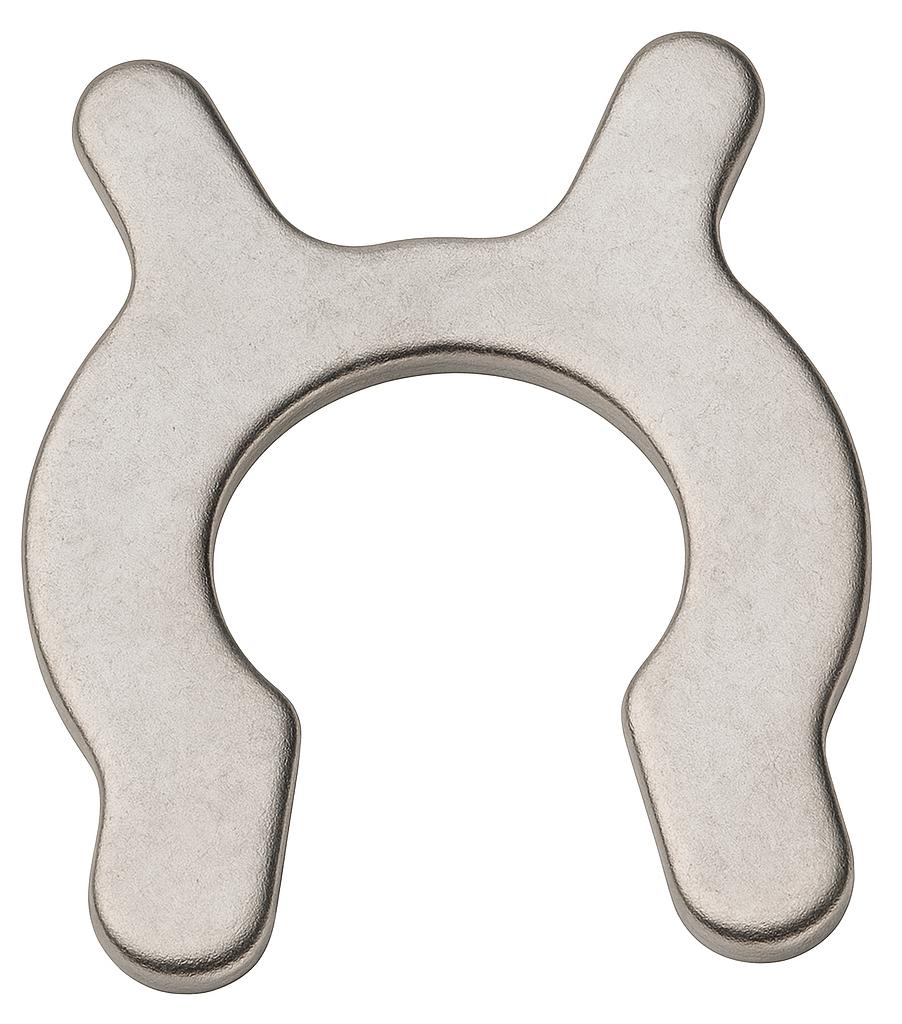

Crimp Sleeve
A crimp sleeve is a small cylindrical connector, typically made from metal such as copper, aluminum, or steel, that is used to join, terminate, or reinforce cables, wires, or rods by crimping it tightly around them. Instead of relying on threads or welding, a crimp sleeve is deformed mechanically with a crimping tool, compressing it onto the material inside to create a secure, permanent connection.
In electrical work, crimp sleeves are often used to splice wires or form grounding bonds. The sleeve is slipped over the stripped ends of the wires, and then crimped to ensure conductivity and mechanical strength. They are widely used in electrical installations, telecommunications, and control wiring because they provide reliable electrical contact while being quick to install.

In mechanical and structural applications, crimp sleeves are also used with wire rope and cables. For example, when forming loops at the end of a steel cable, a crimp sleeve (sometimes called a ferrule) is compressed around the rope to lock it in place, often together with a thimble for added wear resistance. This method is common in rigging, lifting equipment, fencing, and marine applications, where high tensile strength and security are needed.
Crimp sleeves come in various shapes and sizes—round, oval, seamless, or with inspection windows—depending on the application. When installed properly with the correct tool, they provide a long-lasting, vibration-resistant, and high-strength connection without the need for soldering or threading.
Critical Temperature (Tc)
Critical temperature refers to the specific temperature at which a material undergoes a fundamental change in phase, structure, or physical behavior.
In Metallurgy & Heat Treatment
In steels, critical temperatures correspond to phase transformation boundaries in the iron–carbon phase diagram. For example:
- Around 727°C → eutectoid temperature where austenite transforms to pearlite.
- At higher temperatures (A3 or Acm lines), ferrite fully converts to austenite during heating.
These temperatures define when microstructural changes occur during annealing, quenching, and normalizing.
In Superconductivity
For superconducting materials, the critical temperature (Tc) is the temperature below which the material loses electrical resistance and expels magnetic fields (Meissner effect). Above Tc, the material behaves like a normal conductor; below Tc, it enters the superconducting state.
Example:
- Niobium Tc ≈ 9.2 K
- YBCO (ceramic superconductor) Tc ≈ ~90 K
In this context:
Critical temperature is the cutoff where a material transitions to a superconducting state.
In Thermodynamics (Liquids/Gases)
For fluids, critical temperature is the point above which a gas cannot be liquefied by pressure alone, because the distinction between liquid and gas disappears. At this temperature, the substance reaches a supercritical state.
Example:
- Water critical temperature ≈ 374°C (647 K)
- This marks the top of the liquid–vapor phase boundary.
Cross Drilling
A machining process where a hole is drilled completely through a fastener, typically perpendicular to its axis. This hole can pass through the fastener's shank or head and is used to insert a locking device, such as a cotter pin or safety wire, to secure the fastener in place.
Cross Recess Screw
A cross recess screw is a screw that has a cross-shaped indentation in its head, designed to be driven with a matching driver bit (commonly called a Phillips or Pozidriv screwdriver). The cross recess allows torque to be applied more efficiently than a simple slotted screw, while also providing better alignment between the tool and the fastener.
The most common type of cross recess is the Phillips drive, which has angled slots that help center the screwdriver bit. However, there are variations such as Pozidriv, JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard), and Supadriv, each with slightly different cross geometries designed to improve torque transmission, reduce “cam-out” (slipping out of the recess under torque), or meet regional standards.
Cross recess screws are widely used because they are easy to align, can be installed quickly, and require less downward pressure than slotted screws. They are found in consumer products, automotive parts, construction fasteners, and industrial machinery, essentially anywhere a general-purpose fastening solution is needed.
One limitation is that some cross recess designs, like Phillips, are intentionally engineered to “cam-out” under high torque to prevent over-tightening, which can be a disadvantage in applications requiring precise torque control. Newer designs, such as Pozidriv, were created to minimize this issue.

Cross Threading
Cross threading is a fastening defect that occurs when the male and female threads of a fastener (such as a bolt and nut, or a screw and tapped hole) do not align properly during installation. Instead of the threads engaging smoothly, the fastener is driven in at an angle, forcing the threads to cut across each other. This damages the thread profiles and creates a misaligned, unstable joint.
When cross threading happens, the fastener may feel tight prematurely, even though it hasn’t been seated correctly. This false sense of tightness is dangerous because the joint may not have sufficient clamping force and can fail under load. Additionally, cross threading often causes permanent damage to both the fastener and the mating component, especially if they are made of softer materials like aluminum or plastic.
Cross threading is common when bolts or screws are started with too much force or at the wrong angle, or when power tools are used carelessly without first aligning the threads by hand. To prevent it, fasteners are typically started by hand until several threads are engaged smoothly before applying torque with a wrench, screwdriver, or power driver. Using lubricants, proper alignment, and thread guides can also reduce the risk.
Because cross threading compromises both the strength and integrity of the joint, damaged parts usually need to be repaired (e.g., with a thread chaser, tap and die, or helicoil insert) or replaced entirely.
Cross-Linking
A chemical process in which individual polymer chains are bonded together to form a three-dimensional network. In the context of fastener coatings, such as epoxy or PTFE, cross-linking typically occurs during the curing stage when heat or another catalyst causes the coating molecules to react and form these strong, interconnected bonds. This network of bonds improves the coating’s durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion to the fastener’s surface, making it more resistant to wear, corrosion, and environmental damage.
Cupped Washer
A cupped washer is a specialized type of washer with a concave or bowl-shaped profile instead of a flat surface. This unique design allows it to flex slightly when compressed, giving it a spring-like effect that makes it more versatile than a standard flat washer.
The primary purpose of a cupped washer is to provide spring action. Its curved shape helps absorb movement, vibration, and fluctuations in load, which in turn maintains tension in bolted joints and prevents fasteners from working loose. Like flat washers, cupped washers also help distribute the load over a wider area, but their shape adds the advantage of extra resistance to loosening. They also compensate for small variations in material thickness or joint settling over time, ensuring a more consistent hold.
Cupped washers are commonly used in situations where bolts or screws are prone to loosening from vibration, such as in machinery, automotive assemblies, and construction applications. They are also useful in joints that need a small amount of elasticity but do not require the strength of a full spring washer. Additionally, they are often employed with wood, sheet metal, or other assemblies where a slight amount of "give" helps keep the fastener secure.
There are several variations of cupped washers, and they are sometimes categorized alongside spring washers like Belleville or conical washers. However, cupped washers are generally simpler, shallower, and not intended for extremely high spring loads. They are manufactured in a range of materials—including steel, stainless steel, and brass—to suit different applications and levels of corrosion resistance.

Cut Nail
A cut nail is a metal fastener with a tapering, rectangular shank that wedges into wood, forcing fibers down rather than spreading them, and a blunt tip. Unlike modern wire nails, which have rounded shanks, the cutting process used to create cut nails results in a nail with a unique grip. They are known for their superior holding power, ability to reduce wood splitting, and use in restoration work or for attaching wood to masonry.

Cut Threads
Cut threads are created by removing material from the fastener’s surface using a cutting tool, typically performed on a lathe or CNC machine. This machining process physically cuts into the material to create the thread form, rather than deforming or compressing the material like in rolled threads.
Cut, Thread, and Chamfer
A secondary machining service that modifies fasteners by cutting them to a specific length, forming threads by either cutting (removing material) or rolling (pressing threads into shape), and adding a chamfer, which is an angled edge at the start of the fastener’s threaded section. This service customizes fasteners to meet precise application requirements.
Cyclic Loading
Cyclic loading refers to the process of repeatedly applying and removing stresses or strains to a material or structure over time — a pattern that causes the stress state to vary in a regular, cyclic manner. This can involve tension and compression, bending, torsion, or any combination of these forces.
When a material is subjected to cyclic loading, even if each individual load is below its ultimate tensile strength, the repeated stress fluctuations can lead to a progressive form of structural damage known as fatigue. Over thousands or millions of cycles, microscopic cracks can initiate at points of stress concentration — such as notches, holes, surface defects, or inclusions — and slowly propagate through the material. Eventually, this crack growth can cause sudden, brittle failure without significant plastic deformation, a phenomenon known as fatigue failure.

Cyclic loading is most often seen in mechanical components and structures that experience repeated motion or vibration, such as:
- Rotating shafts, gears, and crankshafts in engines and machinery.
- Aircraft wings and fuselage skins, which flex during flight.
- Bridges and rail tracks, which undergo loading from vehicles and trains.
- Bolts, fasteners, and springs, which experience repeated tightening, loosening, or oscillation.
Engineers characterize cyclic loading using terms like stress amplitude, mean stress, and stress ratio (R = σ_min / σ_max), and they study fatigue behavior through S–N curves (stress vs. number of cycles to failure). Materials tested under cyclic conditions exhibit a fatigue limit or endurance limit — a stress level below which the material can theoretically withstand an infinite number of cycles without failing (though not all materials, such as aluminum, possess one).
Cylinder Head Bolt
A cylinder head bolt is a high-strength fastener used to secure the cylinder head of an internal combustion engine to the engine block. Since the cylinder head seals the combustion chamber and contains critical components like valves, spark plugs, or injectors, the bolts must withstand extreme heat, pressure, and mechanical stress. Their design ensures that the head is clamped tightly against the block to maintain engine integrity and performance.
These bolts are usually made from hardened alloy steel and heat-treated to achieve exceptional tensile strength. They are long in length so they can pass through the cylinder head and provide strong clamping force. Some engines use conventional head bolts, while many modern engines rely on torque-to-yield (TTY) bolts, which are tightened beyond their elastic limit to produce maximum and uniform clamping force. While highly effective, TTY bolts cannot be reused once removed because they permanently stretch during installation.
The purpose of cylinder head bolts is to apply and maintain even pressure on the cylinder head, the head gasket, and the engine block. This even compression seals the combustion chamber, preventing gases from escaping and ensuring that coolant and oil passages remain leak-free. Without this proper sealing, problems such as gasket blowouts, coolant leaks, and loss of compression could occur, leading to serious engine damage.
Cylinder head bolts are used across a wide range of engines. In automobiles, both gasoline and diesel engines rely on them to maintain combustion chamber sealing. Motorcycles and small engines use them in more compact designs, while heavy machinery and marine engines require them to withstand even greater stress levels. Their role is universal wherever a cylinder head must be secured to an engine block.
These bolts have several advantages. They provide very high tensile strength to resist the immense forces of combustion, and their precise engineering ensures consistent clamping and reliable sealing. Torque-to-yield designs, in particular, offer superior performance by maximizing head gasket sealing. However, they also come with limitations. TTY head bolts must be replaced every time they are removed, which adds to maintenance costs. Improper installation, such as reusing old bolts or failing to follow the correct torque sequence, can lead to gasket failure or severe engine damage. Additionally, removal of head bolts requires careful loosening in sequence to avoid warping the cylinder head.

