Resources
Glossary
Radial Growth
Radial growth is an increase in diameter (radius) of a part—or an outward change from its centerline—caused by manufacturing, loading, thermal effects, or material behavior. In industrial and fastener contexts, it most often describes outward expansion of a cylindrical feature (a hole, sleeve, bushing, tube, or the shank/body of a fastener) as conditions change.
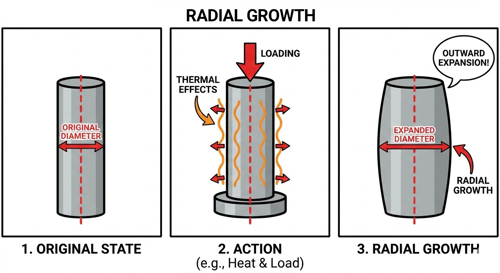
In threaded fasteners and joints, radial growth commonly shows up in a few practical ways. During installation of mechanical expansion anchors or rivets, components are intentionally driven to expand outward, and that resulting radial growth creates holding power by friction/bearing in the base material. In press-fit or interference-fit assemblies, radial growth can occur when a component is forced into place, when temperature rises (thermal expansion), or when internal contact stresses redistribute. In high-load or high-temperature bolting (and rotating equipment), radial growth can also refer to diametral increase of a flange, hub, or bolt circle as the assembly heats up or spins, which can change alignment, fit, and load distribution.
Because “radial growth” is a geometry change term rather than a single standardized test value, it’s usually specified by what feature is growing (OD, ID, bolt circle, etc.), the driver (temperature, RPM, pressure, installation), and how it’s measured (ΔD, Δr, or percent change).
Radial Lines
Lines or markings that extend outward from the center of a fastener’s head toward its outer edge. In bolts and screws, these radial lines serve as grade markings to indicate strength classification. For example, SAE J429 fasteners use three radial lines to signify Grade 5 and six radial lines for Grade 8.
Radiographic testing (RT)
Radiographic Testing (RT) is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method that uses X-rays or gamma rays to examine the internal structure of a material or component. Just like medical X-rays, this technique produces an image (radiograph) that shows variations in thickness, density, or composition. Defects such as cracks, porosity, voids, inclusions, and incomplete welds appear as differences in contrast or shading on the radiograph, allowing inspectors to identify internal flaws without cutting or damaging the part.
The process involves placing a radiation source (X-ray tube or gamma ray isotope) on one side of the object and a detector or film on the opposite side. As the radiation passes through the material, some of it is absorbed depending on the material’s density and thickness, while the remainder exposes the film or digital detector. Areas with flaws or reduced thickness allow more radiation to pass through, producing darker spots, while denser areas appear lighter. Modern RT often uses digital radiography, which provides faster results and easier image storage compared to traditional film.

Applications: RT is widely used in aerospace, automotive, oil & gas, power generation, and construction to inspect welds, castings, pipelines, and critical structural parts.
Advantages: It provides a permanent visual record of the inspection, can reveal internal and volumetric flaws, and works on a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
Limitations: It requires strict safety precautions due to radiation exposure, can be costly and time-consuming compared to other methods, and may struggle to detect very fine surface defects that ultrasonic or dye penetrant testing would catch.
Rail Drag Clamp
A rail drag clamp is a mechanical fastening device used to secure and hold railway rails firmly to their supporting structures, such as rail ties, base plates, or crane rails. Its primary purpose is to prevent lateral or longitudinal movement of the rail—particularly drag or slip—caused by the forces of passing trains, thermal expansion, or mechanical vibration.

The rail drag clamp typically consists of a forged or cast steel body shaped to fit over the rail’s base (flange) and a bolt or stud assembly that anchors it to the supporting surface. When tightened, the clamp exerts strong downward and side pressure against the rail foot, creating a frictional grip that resists both vertical uplift and horizontal drag forces. Some designs also include spring washers or lock plates to maintain tension and resist loosening under vibration or dynamic loads.
Rail drag clamps are commonly used in railway tracks, crane runways, mining rail systems, and industrial rail lines—anywhere the rails must remain securely fixed under high loads and repeated movement. They are often found in heavy-duty rail systems, such as ports, steel mills, and material handling facilities.
Rebar
Rebar—short for “reinforcing bar”—is steel reinforcement embedded in concrete to carry tensile forces the concrete itself can’t resist. Concrete is strong in compression but weak in tension; deformed steel bars bond to the surrounding concrete so the two materials act together, limiting cracking, increasing load capacity, and providing ductility so structures don’t fail suddenly.
Modern rebar is almost always “deformed,” meaning the bar surface has raised ribs or patterns that mechanically lock into the concrete. In North America bar sizes are #3 through #11 and larger, where the number is the nominal diameter in eighths of an inch (#4 ≈ 1/2 in, #8 ≈ 1 in). Metric systems use 10M, 15M, 20M, etc., with slightly different diameters. Common strength grades are 60 ksi yield (Grade 60) and higher grades like 75, 80, and 100 ksi for longer spans or congested areas. Typical specifications include ASTM A615 (carbon steel), A706 (low-alloy weldable), A955 (stainless), and A1035 (low-corrosion “microcomposite”/CR rebar); A706 is preferred when welding is required, while A615 generally is not welded unless procedures per AWS D1.4 are followed.

To resist corrosion, rebar may be coated or made from corrosion-resistant alloys. Epoxy-coated bars (often green) are common for bridge decks and marine exposure; hot-dip galvanized and stainless bars offer longer life at higher cost. Because coatings can reduce bond, development and splice lengths are increased compared with black bar. In very aggressive environments, nonmetallic FRP (glass- or carbon-fiber) “rebar” is also used; it doesn’t corrode but behaves differently in design.
Bars are detailed and placed to carry different actions: longitudinal reinforcement for bending, stirrups and ties for shear and confinement, and compression bars where needed. Proper concrete cover protects steel from corrosion and fire. Bars are anchored by hooks or sufficient development length, spliced by lap splices or mechanical couplers, and supported on chairs or spacers to maintain cover. Installers tie bars together with wire to hold the cage during placement, then concrete is placed and vibrated so it fully surrounds the steel.
In short, rebar is the hidden steel skeleton inside reinforced concrete. The right grade, size, spacing, cover, anchorage, and corrosion protection are what turn brittle concrete into the tough, crack-controlled, and ductile material used for buildings, bridges, pavements, tanks, and foundations.
Rebar Bolt
A rebar bolt is a specialized type of steel anchor used in construction, particularly for projects involving underground rock or concrete, such as mining and tunneling. Unlike a standard bolt, it has a surface with ribs or corrugations similar to rebar, which is designed to enhance its grip and friction with the surrounding material. One end of the bolt is threaded to allow for the attachment of a nut and a bearing plate, while the other end is often angled at 45 degrees to help with installation.

The installation of a rebar bolt involves inserting it into a pre-drilled hole, where it is secured using either a fast-setting resin cartridge or a more traditional cement mortar. Once in place, the threaded end of the bolt is tightened, which tensions the bolt and presses a bearing plate against the surface. This creates a stable anchor point. Rebar bolts are an important component in various applications, including rock support, stabilizing retaining walls and slopes, and reinforcing underground mines and tunnels.
Red Rust
The reddish-brown corrosion that occurs when the steel base of any fastener, plated or coated, is exposed to moisture and begins to oxidize. Red rust damages the structural integrity and ductility of the fastener. Once red rust appears, fasteners should be replaced to maintain assembly strength and prevent equipment damage.
Regular Square Nut
An industrial regular square nut is a type of fastener commonly used in mechanical and industrial applications. It has a square shape with four equal sides and a threaded hole in the center, designed to mate with a bolt or threaded rod. The square design provides several advantages over hexagonal nuts, such as greater surface area for contact with the material being fastened, which can improve resistance to loosening under vibration or torque. It also allows for easy tightening with a wrench, as the flat sides offer a good grip.
Relaxation Pass
A relaxation pass is a controlled re-torque step used on gasketed bolted joints (especially pipe flanges, heat exchangers, and other pressure-boundary joints) to recover bolt load lost shortly after initial assembly. It is performed by reapplying torque to all bolts in a circular pattern at the same final/initial target torque value, after a specified dwell time, typically at ambient temperature and steady-state.
The purpose of a relaxation pass is to compensate for early gasket seating, embedment, and short-term creep (relaxation/cold flow) that can reduce preload soon after tightening, which in turn can reduce gasket stress and increase leakage risk. By re-torquing after the gasket has had time to settle, the installer restores preload that was lost during that initial relaxation period.
Relaxation passes are often contrasted with a startup retorque (formerly “hot torque”), which is a similar circular re-torque performed during warm-up when the joint is heating up; guidance commonly emphasizes doing that retorque before ~450°F (232°C) because lubricant behavior and torque accuracy can change as temperatures rise.
Ribbed Neck Carriage Bolt
You may be familiar with them being called Serrated Shoulder Bolts or Ribbed Bolts. However you refer to them, they often secure the bed of a truck to its frame. The Ribbed Neck Carriage Bolts are perfect for assembling wood, plastic, or soft metals requiring high wear resistance applications. The low-profile head ensures that there is no interference with objects as they slide over the head. The ribbed neck prevents the bolts from loosening over time. Earnest carries Ribbed Neck Carriage Bolts in Grade 5.

Right-Handed Threads
Threads that tighten when turned clockwise (to the right). This is the most common thread direction used in fasteners, meaning the fastener is screwed in by turning it to the right and loosened by turning it to the left.
Ring Eye Bolt
A ring eye bolt is a type of lifting or anchoring fastener that features a round, closed loop (ring) at one end and a threaded shank at the other. It is used to attach ropes, cables, or chains and can serve as a lifting point, tie-down, or suspension anchor.
Ring Gear Bolt
A ring gear bolt is a high-strength fastener used to secure the ring gear to the differential carrier (or differential case) inside a vehicle’s differential assembly. The ring gear is the large, toothed gear that meshes with the pinion gear to transfer rotational motion from the driveshaft to the axle shafts, enabling power to reach the wheels.
Because the ring gear experiences intense torque, shock loads, and continuous rotational forces, ring gear bolts are engineered for exceptional strength, precision, and durability.
Design and Construction
Ring gear bolts are typically fine-threaded, grade 8 or higher, and made from alloy steels such as 4140 chromoly or 8740 steel. These materials are often heat-treated for maximum tensile and shear strength. The heads are usually flanged hex, 12-point, or socket-style, depending on the differential design.
The threads are rolled (not cut) to improve fatigue life, and many manufacturers apply pre-applied threadlocker or use safety wire holes to ensure the bolts cannot loosen under vibration or load cycling.
Function in the Differential
When installed, ring gear bolts clamp the ring gear tightly against the carrier flange, ensuring perfect alignment between the ring and pinion gears. This alignment is critical—any movement or loosening can cause:
- Gear misalignment
- Excessive noise (gear whine)
- Rapid wear or tooth breakage
- Catastrophic differential failure
Because of this, ring gear bolts are often replaced whenever the differential is rebuilt or upgraded, and torque values are always set according to manufacturer specifications.
Applications
- Automotive and truck differentials (rear-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and racing differentials)
- Off-road and heavy-duty equipment (where differential loads are extreme)
- Performance builds, where aftermarket ARP ring gear bolts or chromoly replacements are common for added reliability

Ring Nut
A ring nut is a type of threaded nut with a loop or ring on one side, also referred to as an eye nut. This design creates a secure and strong attachment point for various items such as ropes, cables, and hooks. It is the nut counterpart to the ring bolt, or eye bolt, which serves a similar function.
There are several variations of ring nuts that serve different functions. Lifting or rigging ring nuts are specifically engineered to handle heavy loads in contexts like construction and logistics. They are screwed onto a threaded rod, with the ring used to attach hoisting equipment such as winch lines or crane cables. Another type is the adjusting ring nut, or shaft ring nut, which is a specialized locknut with slots for a spanner wrench. These are used to securely hold components like bearings or gears on a shaft. Other types include blind rivet nuts, which create threaded inserts in thin materials, and pushbutton ring nuts, which secure electrical components to control panels.
A key distinction exists between a ring nut and a castellated nut, despite both being used in applications with movement and vibration. A ring nut's primary function is as a secure attachment point for rigging, and its strength comes from its anchor point. In contrast, a castellated nut is a locking nut with a notched top that uses a cotter pin to prevent it from loosening. This cotter pin is inserted through the nut and a hole in the bolt to lock it in place.
The installation method for a ring nut depends on its specific type. For lifting ring nuts, installation involves hand-tightening onto a threaded stud, followed by final tightening with a tool inserted through the ring. It is recommended to use a washer with this type of nut to protect the surface. Adjusting ring nuts require a specialized spanner wrench for tightening, which engages with the slots on the nut's face. Blind rivet nuts, on the other hand, need a special setting tool to compress and secure them into a material.

Rivet nut
A rivet nut, also known as a rivnut or blind nut, is a tubular, internally threaded fastener used to add strong, reusable threads to thin or soft materials like sheet metal and plastics. It is installed into a pre-drilled hole and then deformed on the blind side using a special setting tool, which locks it securely in place without needing access to both sides of the material.
Rivet nuts are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and furniture applications, where they provide a durable fastening point in materials that cannot be tapped for conventional threads. They are especially useful in blind applications and offer a vibration-resistant, permanent solution for mounting bolts or screws.

Robertson Screw
A Robertson screw is a type of screw distinguished by its square-shaped socket in the head, designed to be driven with a matching square screwdriver. It was invented in 1908 by Canadian inventor P.L. Robertson and became especially popular in Canada, where it remains a standard fastener. The square recess design allows for excellent torque transfer between the driver and the screw while minimizing the risk of the driver slipping out, a problem common with slotted screws.
The Robertson screw is known for several advantages. The square recess holds the driver bit securely in place, allowing for one-handed operation and making it easier to start the screw without it falling off the driver. This design reduces the chance of “cam-out,” where the driver slips and damages the screw head, and it permits higher torque to be applied without stripping. These qualities made it a favorite in woodworking, construction, and especially in industries where efficiency and durability were critical.
Although the Robertson screw offered clear benefits, it never became as widely used in the United States as the Phillips screw, mainly due to licensing and manufacturing issues in its early history. Today, it is still very common in Canada, where it is considered a national standard fastener, and is increasingly found worldwide in furniture assembly, cabinetry, and construction applications.

Rock Bolt
A rock bolt is a long, high-strength anchor used to stabilize rock formations, typically in tunnels, mines, slopes, and underground excavations. It works by securing loose or fractured rock layers to more stable sections, effectively creating a single, reinforced rock mass that resists collapse or movement.
Rock bolts are installed by drilling a hole into the rock, inserting the bolt, and then anchoring it using mechanical expansion, resin bonding, or grouting. Once tensioned, the bolt applies a compressive force that holds the rock layers together and prevents separation or shifting. The tensioned bolt transfers loads from weaker, fractured zones to stronger, intact rock deeper within the formation.
Several types of rock bolts exist, including mechanically anchored bolts, resin-grouted bolts, and friction bolts (also called split-set stabilizers). The choice depends on the ground conditions, load requirements, and construction environment.
Rock bolts are usually made from high-tensile steel and may include corrosion protection such as galvanizing, epoxy coating, or plastic sheathing for long-term durability.

Rockwell Hardness Scale
The Rockwell Hardness Scale is one of the most widely used systems for measuring the hardness of metals, alloys, and other materials. Unlike the Mohs scale, which relies on scratch resistance, the Rockwell method determines hardness by measuring how deeply a steel or tungsten carbide indenter penetrates the surface of a material under a specific load. This makes it more precise, standardized, and applicable to a broad range of engineering materials.
The testing process begins by pressing an indenter—either a cone-shaped diamond, known as a Brale indenter, or a hardened steel ball—into the surface of the sample. First, a minor load is applied to seat the indenter and establish a reference point. A larger major load is then applied and held for a set time before being released. The depth of penetration relative to the initial position is measured, and the result is expressed as a Rockwell Hardness Number (HR). In this system, a shallower indentation indicates a harder material.

There are multiple Rockwell scales, each tailored to different materials and hardness ranges, and identified by a letter suffix after the HR value. For example, the Rockwell C scale (HRC) uses a diamond cone indenter and is typically applied to hardened steels, cutting tools, and high-strength fasteners. The Rockwell B scale (HRB) uses a steel ball indenter and is more suitable for softer metals such as copper, aluminum, and softer steels. Other variations—such as HRA, HRD, HRE, and HRF—are used for specific materials and testing conditions. As an example, a hardened steel bolt might fall in the range of HRC 35–45, while a softer structural steel may measure HRB 70–90.
The purpose and function of the Rockwell test is to provide a quick, reliable, and reproducible measure of a material’s resistance to indentation and deformation. This measurement correlates directly to the strength, wear resistance, and durability of the material being tested, making it highly valuable for both quality control and engineering design.
The Rockwell method offers several advantages. It is fast and easy to perform, requires minimal sample preparation, and is considered non-destructive for large parts since it only leaves a small indentation. It applies to a wide variety of metals and alloys and gives direct numerical results without the need for conversions.
There are also limitations. The test works best on flat or smoothly curved surfaces and is not suitable for rough or irregular geometries. It requires precise test conditions and proper calibration to ensure accuracy. It is less effective for very thin materials, coatings, or small parts where indentation depth may compromise the sample.
In applications, the Rockwell Hardness Scale is frequently used in fasteners and other industrial components to verify that they meet strength and wear resistance requirements. Automotive bolts, aerospace fasteners, and cutting tools are commonly measured on the Rockwell C scale, ensuring consistent quality and reliability in critical assemblies.
RoHS Compliance
A European Union directive that limits the use of 10 hazardous materials, including lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and certain flame retardants and phthalates, in electrical and electronic products. The goal of RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) is to protect human health and the environment by reducing hazardous materials in manufacturing, consumer use, and product disposal.
For fasteners, RoHS compliance most often relates to platings and coatings. Substances such as hexavalent chromium, once common in corrosion-resistant finishes, are restricted, and many suppliers now use alternatives like trivalent chromium or zinc-nickel platings.
Blog Post: Understanding RoHS Compliance and Its Impact on Fasteners
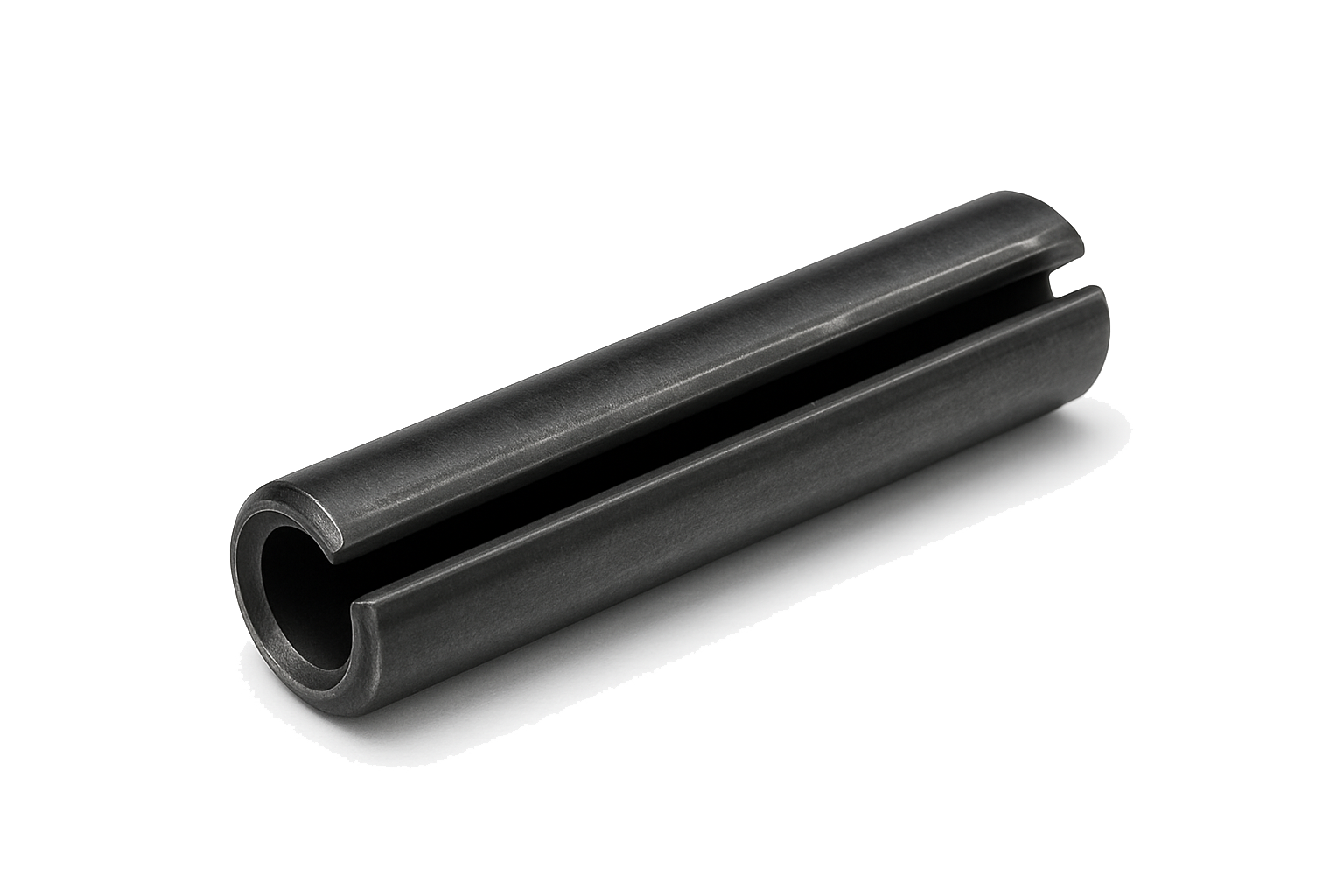
Roll Pin (Spring Pin)
A roll pin, also called a spring pin, is a hollow, cylindrical fastener made of spring steel with a small gap along its length. When pressed into a slightly undersized hole, it compresses and exerts outward tension, which securely locks it in place without the need for threads or additional hardware. This self-retaining design makes it simple yet highly effective for joining or aligning parts.
Roll pins are commonly used in machinery, tools, and automotive applications where vibration resistance and durability are important. They come in slotted or coiled varieties, with coiled versions offering greater strength and fatigue resistance. Because of their resilience and reusability, they’re widely relied upon for dynamic assemblies.

Rolled Threads
Rolled threads are created by deforming the fastener’s surface through a rolling process using hardened dies, which displace and compress the fastener to form the thread profile without removing any material. This process creates stronger threads with a smoother surface finish compared to cut threads.
Roofing Nails
Roofing nails are specialized nails used to attach roofing materials—like shingles, felt paper, sheet metal, or roofing tiles—to wooden or other structural substrates. They are specifically designed for durability, weather resistance, and holding power in demanding outdoor conditions.
Rosette Weld
A rosette weld (also known as a plug weld) is a circular spot weld used to join two overlapping metal components by filling a pre-drilled or punched hole in the top sheet with molten metal that fuses to the surface beneath it. Once cooled, the weld forms a strong, localized bond that resembles a small circular “rosette” pattern—hence the name.

This type of weld is commonly used in structural fabrication, automotive, and steel construction, particularly when access to only one side of the material is available. The process works by applying heat (via MIG, TIG, or spot welding) around the edge of the hole, melting both the perimeter of the hole and a small portion of the underlying metal. The molten metal pool then fills the cavity and solidifies, locking the two pieces together.
Rosette welds are often used to:
- Reinforce tubular joints, such as when inserting one tube into another and welding through drilled holes.
- Replace rivets or bolts in sheet metal assemblies.
- Attach plates, brackets, or gussets where a continuous seam weld isn’t practical.
Compared to fillet or groove welds, rosette welds are generally not used for sealing but rather for shear or tensile strength in overlapping joints. The size and spacing of the holes determine the overall load capacity of the joint.
Rubber Plumbing Cone Washer
A rubber plumbing cone washer is a soft, conical-shaped sealing washer commonly used in plumbing connections to create a watertight seal between two mating parts. Unlike flat washers, the cone shape allows it to fit snugly into tapered seats, compression fittings, or couplings, where it deforms slightly under pressure to fill any gaps and prevent leaks.
These washers are typically made from rubber, neoprene, or other elastomeric materials that are flexible, resilient, and resistant to water. The soft material allows them to compress and adapt to irregularities in the surfaces being joined, which makes them especially effective in plumbing systems where metal-to-metal or plastic-to-metal connections might otherwise leak.
Cone washers are often used in sink faucets, toilet tanks, water supply lines, and garden hoses—anywhere a secure, watertight seal is needed in a joint that may be tightened by hand or with light tool pressure. Their cone profile ensures proper alignment within fittings, reduces the risk of over-tightening, and makes them easier to replace than more rigid seals.

Rust
A destructive, reddish-brown corrosion that forms on iron or steel fasteners due to exposure to oxygen and moisture weakening their structure and impeding function. It is commonly mitigated by the use of protective finishes or corrosion-resistant materials, like stainless steel.
