Resources
Glossary
Grade
A fastener grade is a standardized classification that indicates the strength, material properties, hardness, and performance capabilities of a bolt, screw, or similar fastener. Grades tell you how strong the fastener is, how it was manufactured (such as material type and heat treatment), and what applications it is suitable for.
In the fastener world, grades are essential because not all bolts are created equal—some are meant for light-duty household use, while others must withstand the extreme loads of heavy machinery, automotive suspensions, or structural steel assemblies. A grade ensures that no matter who manufactures the fastener, its minimum strength and performance characteristics remain consistent.
In the SAE (inch-series) system, common grades include Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8, each with specific tensile strength, yield strength, hardness, and identification markings. Metric fasteners use a different system (e.g., Class 8.8, 10.9, 12.9) but serve the same purpose—defining strength levels so engineers, mechanics, and distributors know exactly what they’re working with.
Fastener grades are especially important in industrial settings because using the wrong grade can lead to joint failure, equipment damage, or safety hazards. Distributors like Earnest Machine rely on grades to cross-reference, recommend alternatives, and ensure customers are using the correct fastener for the load, environment, torque requirements, and safety standards of their application.
Grade 2 (SAE)
A Grade 2 fastener is a low-carbon steel bolt or screw that represents the basic, entry-level strength grade in the SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) grading system used primarily in the United States. These fasteners are typically made from low-carbon steels such as 1006, 1008, or 1010 and are not heat-treated, which keeps their strength lower but makes them inexpensive, ductile, and suitable for general-purpose applications.
In industrial and fastener-distribution environments, Grade 2 fasteners are considered non-critical, light-duty hardware. They are commonly used in non-structural, non-load-bearing assemblies, household applications, light machinery, basic construction, appliance manufacturing, and farm equipment where high tensile or shear strength is not required. Their typical mechanical properties include a minimum tensile strength around 60,000 psi for bolts under 1" diameter and roughly 55,000 psi for bolts 1" and above—significantly lower than Grade 5 or Grade 8.
Grade 2 bolts are usually identified by a plain head with no markings (hex bolts without radial lines). In distribution, they are often supplied zinc-plated, hot-dip galvanized, or plain and are widely stocked due to their versatility and low cost. For situations requiring structural integrity, vibration resistance, high torque, or elevated temperature performance, Grade 2 fasteners are not appropriate and are replaced by higher-grade fasteners like Grade 5, Grade 8, or alloy/metric equivalents (Class 8.8, 10.9, etc.).
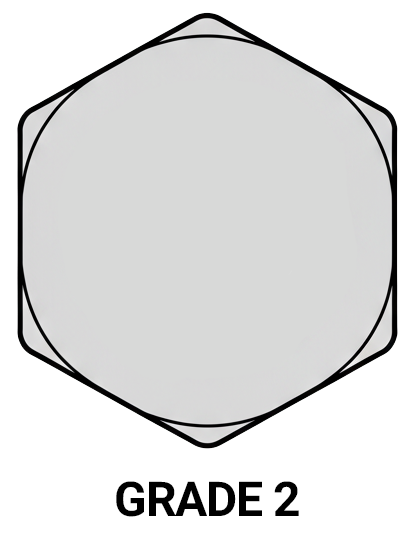
Grade 5 (SAE)
A Grade 5 fastener is a medium-strength, heat-treated carbon steel bolt or screw defined by the SAE J429 standard. It represents the “general-purpose high-strength” category in the SAE grading system—stronger than Grade 2, but not as strong as Grade 8. Grade 5 is one of the most widely used fastener grades in North American industrial, automotive, and machinery applications.
Grade 5 bolts are typically made from medium-carbon steel (such as 1038, 1541, or similar steels) and are quenched and tempered to increase their tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. Their mechanical properties are significantly higher than Grade 2, with a minimum tensile strength of about 120,000 psi (for diameters up to 1 inch). This added strength makes them suitable for load-bearing assemblies, machinery, automotive components, agricultural equipment, heavy-duty brackets, structural joints, and general industrial equipment where durability and performance are essential.
Grade 5 fasteners are easy to identify: the head of a standard hex bolt will have three radial lines, evenly spaced, indicating its grade. They are often supplied in zinc-plated, plain/oil finish, or phosphate and oil variants. Because they offer an excellent balance of strength, cost, and availability, Grade 5 bolts are one of the most commonly stocked fastener grades in distribution, especially for MRO and OEM customers.
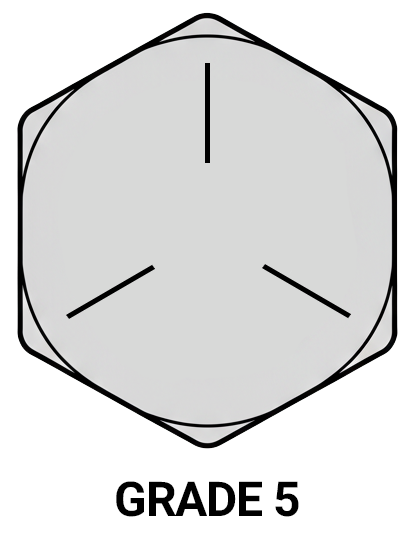
Grade 8 (SAE)
A Grade 8 fastener is a high-strength, high-performance bolt or screw made from medium-carbon alloy steel and heat-treated to achieve some of the highest mechanical properties in the SAE J429 grading system. Grade 8 bolts are significantly stronger than both Grade 2 and Grade 5 and are used whenever the joint must withstand high loads, shock, vibration, or critical structural forces.
Grade 8 fasteners are typically manufactured from steels such as medium-carbon alloy (like 4037 or 4140) and are quenched and tempered to achieve very high hardness and tensile strength. Their minimum tensile strength is approximately 150,000 psi, and their yield strength is around 130,000 psi, making them one of the strongest readily available standard inch-series bolt grades.
In practical industrial settings, these fasteners are used in heavy equipment, automotive suspensions, engine assemblies, agricultural machinery, off-highway vehicles, structural support systems, hydraulic components, and any application where failure would be dangerous or costly. They handle high clamping force, resist deformation under heavy loads, and hold up well in dynamic or vibration-prone environments.
Grade 8 hex bolts are easily identified by six radial lines on the head, which is a universal SAE marking. They are usually supplied in yellow zinc, clear zinc, phosphate and oil, or plain finishes depending on corrosion requirements. For customers choosing between grades, Grade 8 is ideal when maximum strength is required, while still being compatible with standard inch-series tooling and thread classes.
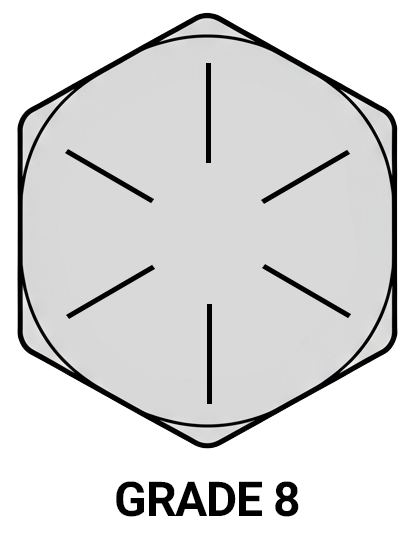
Grade Markings
Grade markings are the identification symbols stamped onto the head of a fastener (usually hex bolts) that indicate the fastener’s grade, strength level, and manufacturing standard. These markings allow engineers, mechanics, distributors, and end-users to instantly recognize how strong a bolt is and whether it is suitable for a specific application—without needing packaging, paperwork, or guessing.
In the SAE inch-series system, grade markings appear as radial lines on the bolt head:
- No lines = Grade 2 (low strength, non-critical applications)
- 3 radial lines = Grade 5 (medium strength, heat-treated)
- 6 radial lines = Grade 8 (high strength, heat-treated alloy steel)
The number of lines + 2 equals the grade number. These markings are standardized so that a Grade 5 bolt from one manufacturer matches the properties of a Grade 5 bolt from another.
Metric fasteners use raised numbers instead of lines (like 8.8, 10.9, 12.9), and many specialty fasteners use proprietary or additional symbols to denote manufacturer identity, material type, or compliance with standards such as ASTM, ISO, or SAE J429.
Grade markings serve several critical industrial functions: they help prevent mixing of low-strength and high-strength bolts, ensure safety in structural or load-bearing applications, simplify quality control, and allow distributors to quickly identify inventory. In fastener selection, installation, and inspection processes, grade markings are often the first and most important piece of information used to determine whether a fastener is appropriate for the job.
SAE J429 Grade 1
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners made from low-carbon steel. SAE J429 Grade 1 fasteners provide the lowest strength level within the SAE J429 standard and are typically used in light-duty, non-critical applications where only minimal strength is needed. Common uses include furniture assembly, light-duty brackets, automotive trim, electrical enclosures, and other non-load-bearing or temporary connections not subject to high stress or vibration.
SAE J429 Grade 2
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners that are made from low to medium carbon steel. SAE Grade 2 fasteners offer a basic level of strength and are typically used in non-critical, general-purpose applications where high strength is not required.
SAE J429 Grade 4
A common strength classification for carbon steel fasteners made from medium carbon steel that are typically quenched and tempered. SAE J429 Grade 4 fasteners provide a moderate strength level under the SAE J429 standard and are commonly used in applications requiring greater strength than Grade 2 but not as high as Grade 5. These fasteners are suitable for general-purpose mechanical and structural applications where improved load capacity is needed. Common uses include automotive components, machinery parts, and light structural assemblies.
SAE J429 Grade 5
A strength classification for medium carbon steel fasteners that have undergone heat treatment to enhance their strength and durability. SAE Grade 5 fasteners provide greater strength than Grade 2 and are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and structural applications where higher load-bearing capacity is required.
SAE J429 Grade 5.1
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are typically quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 5.1 fasteners provide a higher strength level than Grade 5 and are intended for applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance and durability. Common uses include automotive, heavy machinery, and structural applications where improved toughness and tensile strength are necessary.
SAE J429 Grade 5.2
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are typically quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 5.2 fasteners offer a higher strength level than Grade 5.1 and are used in demanding applications requiring superior mechanical performance and durability. Common uses include heavy-duty automotive, industrial machinery, and structural applications where maximum toughness and tensile strength are critical.
SAE J429 Grade 8
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that have been heat treated to provide high tensile strength and excellent durability. SAE Grade 8 fasteners are stronger than Grade 5 and are commonly used in heavy-duty automotive, industrial, and structural applications requiring maximum load capacity and toughness.
SAE J429 Grade 8.1
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners that are quenched and tempered, conforming to the SAE J429 standard. Grade 8.1 fasteners provide higher tensile strength and improved toughness compared to Grade 8, making them suitable for high-stress, heavy-duty applications. Typical uses include automotive suspension components, heavy machinery, and structural assemblies requiring superior strength.
SAE J429 Grade 8.2
A strength classification for alloy steel fasteners, quenched and tempered to exceed the mechanical properties of Grade 8.1 under the SAE J429 standard. Grade 8.2 fasteners are designed for extremely demanding applications where maximum strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue are required. Common applications include critical heavy machinery parts, high-performance automotive, and structural components subjected to intense stress.
SAE J995 Grade 2 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from low-carbon steel. Grade 2 nuts are intended for use in light-duty, non-critical applications and are typically paired with SAE J429 Grade 1 or Grade 2 bolts. They offer low mechanical strength and usually lack grade markings.
SAE J995 Grade 5 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from medium carbon steel, quenched and tempered. Grade 5 nuts are intended for medium-strength applications and are typically used with SAE J429 Grade 5 bolts. They offer greater mechanical strength than Grade 2 nuts and are identified by two circumferential grade markings located 120 degrees apart, typically with one mark on the top face and the other wrapping partially around the side of the nut.
SAE J995 Grade 8 (Nuts)
A classification under the SAE J995 standard for inch-series hex nuts made from medium carbon alloy steel, quenched and tempered. Grade 8 nuts are used in high-strength applications and are typically paired with SAE J429 Grade 8 bolts. They provide the highest strength among SAE J995 grades and are identified by two circumferential grade markings located 60 degrees apart, both positioned clearly on the top face of the nut.
